
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
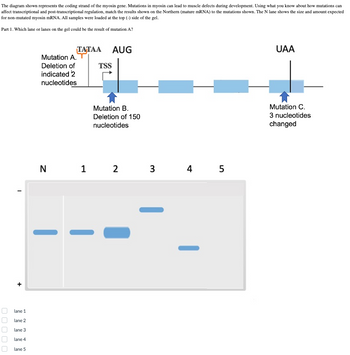
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram shown represents the coding strand of the myosin gene. Mutations in myosin can lead to muscle defects during development. Using what you know about how mutations can
affect transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation, match the results shown on the Northern (mature mRNA) to the mutations shown. The N lane shows the size and amount expected
for non-mutated myosin mRNA. All samples were loaded at the top (-) side of the gel.
Part 1. Which lane or lanes on the gel could be the result of mutation A?
00000
I
lane 1
lane 2
lane 3
lane 4
lane 5
TATAA
Mutation A.
Deletion of
indicated 2
nucleotides
AUG
TSS
Mutation B.
Deletion of 150
nucleotides
N 1 2
3 4 5
UAA
Mutation C.
3 nucleotides
changed
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
mRNA
The short chain of RNA molecule that is made by the process of transcription. And translated later to produce proteins.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What would the sequence of the immature mRNA be? Place the sequence of ALL the transcript that would be synthesized from the gene. In each of the available line you should transcribe all nucleotides that form the immature mRNA. If the sequence indicated is not transcribed then write NA. WRITE THE NUCLEOTIDES IN CAPITAL LETTERS. Promoter: EXON 1: Intron 1: Exon 2: Intron 2: Exon 3 without terminator : Exon 3 terminator:arrow_forwardGive only typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forwardRNA are extracted from liver cells and separated in agarose gel by electrophoresis side-by-side with a molecular weight marker. The separated RNA fragments are then transferred to an RNA-binding membrane. Next, this membrane is incubated with labelled probe specific for the gene X. This experiment determines: MOLECULAR BIOLOGY_basic how many copies of gene X there are in liver cells. if the gene X is translated in liver cells. if gene X has a point mutation in liver cells. the chromosomal location of gene X. the length of the transcript of gene X.arrow_forward
- Below is an mRNA molecule in its wild type form. 5’ CCGUACAUGGUGAAAAGUCAAUGACCAAA 3’ An individual experiences a DNA mutation that impacts the transcription of the mRNA molecule. The resulting mutated mRNA molecule is: 5’ CCGUACAUGGUGAAAGGUCAAUGACCAAA 3’ What type of mutation has occurred? (max 1 sentence) Does this result in an amino acid change? If yes, identify the change that has occurred. (max 1 sentence) Based on your answer to Part 2, will this mutation impact the structure of the protein? Justify your answer. (1-2 sentences) Responding in point form is allowed!arrow_forwardThis is a list of molecular changes that could happen during DNA replication, transcription, mRNA processing, or translation. For each, determine whether or not the change will be passed down through generations of cells after it occurs. Explain your answer. C->G point mutation in the DNA of a coding region of a gene A->T point mutation in the noncoding region of a gene An error in transcription changes the mRNA sequence such that what was an amino acid-coding codon in the DNA sequence is now a stop codon in the mRNA sequence. An error in translation causes the amino acid alanine (nonpolar) to be replaced by the amino acid glutamic acid (polar and negatively charged).arrow_forwardA woman has an egg with a mutation for the gene that expresses whether the child can produce lactase enzymes. Here is the new nucleotide sequence with the change in bold. 3’ – ACCTCTTACTTCTATATATAGGGAAGACTAATTGTC – 5’ what type of mutation is this? Will this affect the child's abilty to produce lactase enzymes needed to digest lactose?arrow_forward
- The diagram shown represents the coding strand of the myosin gene. Mutations in myosin can lead to muscle defects during development. Using what you know about how mutations can affect transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation, match the results shown on the Northern (mature mRNA) to the mutations shown. The N lane shows the size and amount expected for non-mutated myosin mRNA. All samples were loaded at the top (-) side of the gel. Part 1. Which lane or lanes on the gel could be the result of mutation A? --4 ТАТАА AUG UAA Only known regulatory region TSS Mutation B: Mutation C. A: 5-base 20 nucleotides 3 nucleotides deletion deleted changed N 1 2 3 4 5arrow_forwardProtein levels and mRNA levels for a particualr gene don’t always match. For example, the GCN4 gene in yeast is always producing mRNA, but the Gcn4 protein is only made when the cells are starved. A. what is one mechanism by which changes in mRNA levels are not always matched by changes in the protein product of that mRNA?arrow_forwardThe diagram shown represents the coding strand of the myosin gene. Mutations in myosin can lead to muscle defects during development. Using what you know about how mutations can affect transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation, match the results shown on the Northern (mature mRNA) to the mutations shown. The N lane shows the size and amount expected for non-mutated myosin mRNA. All samples were loaded at the top (-) side of the gel. Part 1. Which lane or lanes on the gel could be the result of mutation A? ТАТА AUG UAA Only known regulatory region TSS Mutation B: Mutation C. 3 nucleotides 20 nucleotides deleted A: 5-base deletion changed 1 2 4 5 lane 1 lane 2 lane 3 lane 4 lane 5 OOO0Oarrow_forward
- Which of the following mutations in the protein-coding region of a gene is more likely to lead to complete loss of function of the encoded protein: an insertion of six nucleotides or a deletion of two nucleotides? Briefly explain your answer.arrow_forwardA diagram of a gene is shown below. Normally, exons 1, 2, and 3 are present in the mature mRNA. (shown in attatched image) A mutation occurred at the 5’ splice site of exon 1 as shown by the star such that the spliceosome cannot bind to this location during mRNA processing of the pre-mRNA into the mature mRNA. Which of the following is/are a possible result of this mutation? (select all that apply) a)The pre-mRNA transcribed from this gene sequence will be longer than normal. b)The protein translated from this mRNA will be a different length than the normal protein. c)The mature mRNA will be longer. d)The mature mRNA will be shorter.arrow_forwardHaemochromatosis is a recessive disorder caused by mutations in the HFE gene. The disorder can be the result of nonfunctional HFE protein, or from very low levels (expression) of the HFE protein. Below is a northern blot gel showing the amount and size of HFE mRNA for a person who does not have haemochromatosis (WT). The mRNA was loaded at the top of the gel. WT A B C D Position the bands on the gel shown in each question as directed. Part 1 Tom has a mutation which changes the sequence of an enhancer region adjacent to the TATAA box for this gene. Position Tom's band in Lane A. WT A B 00arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education