
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
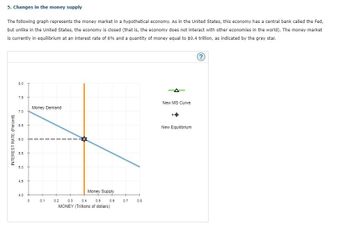
Transcribed Image Text:5. Changes in the money supply
The following graph represents the money market in a hypothetical economy. As in the United States, this economy has a central bank called the Fed,
but unlike in the United States, the economy is closed (that is, the economy does not interact with other economies in the world). The money market
is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 6% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, as indicated by the grey star.
INTEREST RATE (Percent)
8.0
7.5
7.0
6.5
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.5
4.0
0
Money Demand
+
0.1
Money Supply
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
MONEY (Trillions of dollars)
0.6
0.7
0.8
New MS Curve
New Equilibrium
?
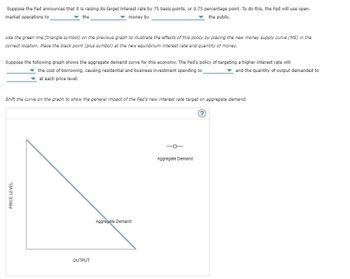
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the Fed announces that it is raising its target interest rate by 75 basis points, or 0.75 percentage point. To do this, the Fed will use open-
▼ the
money by
the public.
market operations to
Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing the new money supply curve (MS) in the
correct location. Place the black point (plus symbol) at the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money.
Suppose the following graph shows the aggregate demand curve for this economy. The Fed's policy of targeting a higher interest rate will
the cost of borrowing, causing residential and business investment spending to
at each price level.
and the quantity of output demanded to
Shift the curve on the graph to show the general impact of the Fed's new interest rate target on aggregate demand.
PRICE LEVEL
OUTPUT
Aggregate Demand
Aggregate Demar
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose that the central bank wants to stimulate the economy by increasing the money supply. The bankers estimate that the velocity of money is 3.3 and that the price level will increase from 120 to 128 due to the stimulus. Using the quantity equation of money, what will be the increment of a $320 billion dollar increase in the money supply on the quantity of goods (In Billions)and services in the economy given an initial money supply of $4.1 trillion? (Please round your answer to include 2 decimal places. Enter the ammoun in Billions, that is, If the total quantity decreases by 1 billion, enter your answer as -1.)arrow_forwardSuppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves. Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied. Suppose the price level decreases from 150 to 125. Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money. ? INTEREST RATE (Percent) 12 10 2 0 0 15 Money Supply Money Demand 30 45 60 MONEY (Billions of dollars) 75 90 Money Demand Money Supplyarrow_forwardIf Money Supply increases, the equilibrium interest rate will: a) be ambiguous b) increase c) decrease d) not changearrow_forward
- The following table shows the quantity of money supplied and the quantity of money demanded for various interest rates. Interest Rate (Percent) Demand for Money (Billions of dollars) Supply of Money (Billions of dollars) 11 50 250 9 150 250 7 250 250 5 350 250 3 450 250 The following graph depicts the money supply curve in orange. On the graph, use the blue points (circle symbol) to graph the money demand, and the black point (plus symbol) to signify the initial equilibrium point in the market. Next, shift the money supply curve to show the affects of a $200 billion increase in the money supply. Then, plot the point corresponding to the new equilibrium point using the purple point (diamond symbol). 13 MS 12 11 10 INTEREST RATE (Percent) + 5 M 9 3 2 MS Money Demand Equilibrium Equilibrium,arrow_forwardSuppose that the central bank wants to stimulate the economy by increasing the money supply. The bankers estimate that the velocity of money is 2.8, and that the price level will increase from 130 to 150 due to the stimulus. Using the quantity equation of money, what will be the impact of an $800 billion dollar increase in the money supply on the quantity of goods(In billions) and services in the economy given an initial money supply of $4 trillion?(Please round your answer to include 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardSuppose the Fed announces that it is raising its target interest rate by 25 basis points, or 0.25 percentage point. To do this, the Fed will use open-market operations to the money by the public. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing the new money supply curve (MS) in the correct location. Place the black point (plus symbol) at the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity of money. Suppose the following graph shows the aggregate demand curve for this economy. The Fed's policy of targeting a higher interest rate will the cost of borrowing, causing residential and business investment spending to and the quantity of output demanded to at each price level. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- Q1. Suppose that money demand is given by the following function MD=$Y (0.5 - i) and that nominal GDP is given by $200. Moreover, assume that the monetary base is given by H³ = $8. It is also known that people in this economy hold all their wealth either in form of checkable deposits or in form of bonds (i.e. people hold no currency) and that banks must hold 10% of the checkable deposits as reserves. (a) Calculate the money market equilibrium using that the supply and the demand for central bank money is equal. (b) Calculate the overall supply of money. (c) What happens to the money market equilibrium if the central bank decides to increase the monetary base to Hs = $9? (d) What are the effects on the overall money supply in the economy? (Calculate the new overall supply of money and explain your result.)arrow_forward6. Changes in the money supply The following graph represents the money market for some hypothetical economy. This economy is similar to the United States in the sense that it has a central bank called the Fed, but a major difference is that this economy is closed (and therefore does not have any interaction with other world economies). The money market is currently in equilibrium at an interest rate of 3.5% and a quantity of money equal to $0.4 trillion, designated on the graph by the grey star symbol. INTEREST RATE (Percent) 5.5 5.0 New MS Curve Money Demand 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 0 0.1 0.2 Money Supply 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 MONEY (Trillions of dollars) New Equilibrium (?) Suppose the Fed announces that it is raising its target interest rate by 50 basis points, or 0.5 percentage points. To do this, the Fed will use open- market operations to the money by the public. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the previous graph to illustrate the effects of this policy by placing…arrow_forwardAssume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency, so the only form of money is demand deposits. To simplify the analysis, suppose the banking system has total reserves of $100. Determine the money multiplier and the money supply for each reserve requirement listed in the following table. Reserve Requirement Simple Money Multiplier Money Supply (Percent) (Dollars) 25 10 A lower reserve requirement is associated with a money supply. Suppose the Federal Reserve wants to increase the money supply by $100. Again, you can assume that banks do not hold excess reserves and that households do not hold currency. If the reserve requirement is 10%, the Fed will use open-market operations to worth of U.S. government bonds. Now, suppose that, rather than immediately lending out all excess reserves, banks begin holding some excess reserves due to uncertain economic conditions.…arrow_forward
- The following table gives the quantity of money demanded at various price levels (P), the money demand schedule. In the following table, fill in the column labeled Value of Money. Price Level (P) Value of Money (1/P) 0.80 1.00 1.33 2.00 Quantity of Money Demanded (Billions of dollars) 2.0 2.5 4.0 8.0 Now consider the relationship between the quantity of money that people demand and the price level. The lower the price level, the required to complete transactions, and the money people will want to hold in the form of currency or demand deposits. Assume that the Federal Reserve initially fixes the quantity of money supplied at $2.5 billion. money Use the orange line (square symbol) to plot the initial money supply (MS₁) set by the Fed. Then, referring to the previous table, use the blue connected points (circle symbol) to graph the money demand curve.arrow_forwardSuppose in the economy of Apple Republic, the demand for money is given by Md = $Y (0.3 - i), where $Y = 100 and the supply of money (Ms) is $20. a. What is the equilibrium interest rate (i)? Answer: i = [ Select ] v %. b. If the central bank increases money supply (Ms) to $25, what is the impact on the interest rate? Answer: Interest rate (i) will [ Select ] to [ Select ] %.arrow_forwardScenario 2 Suppose the money demand is given by MdYx (0.4 - i) = where i is the interest rate. Suppose income Y totals 250. 9. Refer to Scenario 2. If the money supply is M³ = 25, what is the equilibrium interest rate? 10. Refer to Scenario 2. Suppose the Federal Reserve just met and decided they would like to decrease the interest rate by 4 percentage points (compared to the equilibrium rate you found in the previous question). What kind of monetary policy should it use, and what would the money supply have to equal to achieve that goal? (Your answer should be two items: first is expansion or contraction, the second is the actual amount the money supply should be.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education