
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
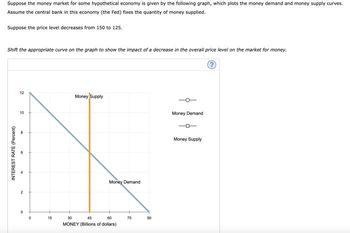
Transcribed Image Text:Suppose the money market for some hypothetical economy is given by the following graph, which plots the money demand and money supply curves.
Assume the central bank in this economy (the Fed) fixes the quantity of money supplied.
Suppose the price level decreases from 150 to 125.
Shift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of a decrease in the overall price level on the market for money.
?
INTEREST RATE (Percent)
12
10
2
0
0
15
Money Supply
Money Demand
30
45
60
MONEY (Billions of dollars)
75
90
Money Demand
Money Supply
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- TOPIC: A possible break in the Note: everything you need will be in the picturearrow_forwardHomework (Ch 21) Consider a hypothetical economy in which households spend $0.50 of each additional dollar they earn and save the remaining $0.50. The following graph shows the economy's initial aggregate demand curve (AD₁). Suppose the government increases its purchases by $3 billion. Use the green line (triangle symbol) on the following graph to show the aggregate demand curve (AD2) after the multiplier effect takes place. Hint: Be sure the new aggregate demand curve (AD2) is parallel to AD₁. You can see the slope of AD₁ by selecting it on the following graph. PRICE LEVEL 116 114 112 110 108 106 104 102 100 100 AD1 102 112 104 106 108 110 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) 114 116 AD₂ AD 3arrow_forwardSuppose in the economy of Apple Republic, the demand for money is given by Md = $Y (0.3 - i), where $Y = 100 and the supply of money (Ms) is $20. a. What is the equilibrium interest rate (i)? Answer: i = [ Select ] v %. b. If the central bank increases money supply (Ms) to $25, what is the impact on the interest rate? Answer: Interest rate (i) will [ Select ] to [ Select ] %.arrow_forward
- Suppose the Federal Reserve (the US central bank) increases the money stock. Create a graph that explains the effect of the Fed's expansionary monetary policy in the Long Run.arrow_forwardhow to calculate the equilibrium price.....arrow_forwardSuppose that money demand is given by the function MD=55+P, and the Bank of Canada maintains the supply of money at MS=$58b. If the Bank of Canada suddenly increases the money supply to MS'-$60b, what has happened to equilibrium value of money? a)It has decreased from 5 to 2 b)MD will shift, and the value of money will remain unchanged c)It has increased from 3 to 5 d) It has decreased from 1/3 to 1/5arrow_forward
- how might this change in interest rates and the supply of money affect the value of money? What happens in the circular-flow-diagram if borrowing money becomes expensive for businesses and consumers? What happens to employment?arrow_forwardFor the quantity theory of money (Mv=PY), if v and Y were fixed, what would an increase in M do to P?arrow_forwardAccording to Keynes, increasing the money supply should lower interest rates in the economy. Milton Friedman notes that while it is true that expansionary monetary policy can lower interest rates, it is only part of the story. a. Briefly explain under what conditions an expansionary monetary policy will indeed lower interest rates, both in the short and long run. A graph may help answering this question.b. Briefly explain under what conditions an expansionary monetary policy will increase interest rates. A graph may help answering this question.arrow_forward
- The following diagram shows the Money Market for a hypothetical economy. Suppose that the economy begins with a Money Supply (Ms) of $300 million, and an equilibrium interest rate of 5.0%. Finally suppose that the required reserve ratio (rr) is 15%. Use the scenario to answer Questions 10 to 13. Interest rates (i) 5.5% 5% 4.5% Ms O increase the money supply $10 million O increase the money supply $100 million O decrease the money supply $300 million O decrease the money supply $200 million O decrease the money supply $100 million $200 $300 $350 Mp Quantity of Money (millions) Suppose that the Central Bank wished to raise the equilibrium interest rate up to 5.5%. In order to achieve this, it would need I toarrow_forwardWhich of the following will most likely cause a decrease in the quantity of money demanded? Group of answer choices an increase in the interest rate an increase in the price level an increase in nominal aggregate output a decrease in the interest ratearrow_forwardSuppose the Federal Reserve (the US central bank) increases the money stock. Create a graph that explains the effect of the Fed's expansionary monetary policy in the Short Run.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education