
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Refer to the graphs, in which the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point Y on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the Fed pursue to achieve a noninflationary, full-employment level of real
A) increase aggregate demand from AD3 to AD2.
B) decrease the money supply from $225 to $150 billion.
C) increase interest rates from 4 to 8 percent.
D) make no change in
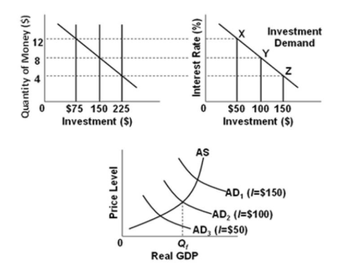
Transcribed Image Text:Quantity of Money ($)
$75 150 225
Investment ($)
Price Level
Interest Rate (%)
AS
Q₁
Real GDP
Investment
Demand
$50 100 150
Investment ($)
AD, (/=$150)
-AD, (/=$50)
-AD₂ (/=$100)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The policies of the federal government influence the outcomes of the various activities in that economy. When government policies change or unplanned events occur, the resulting economic events or activity will usually change. Listed below is a policy or event that affect the performance of the economy: Interest rates are kept artificially low by the Federal Reserve for several years. For the question above, describe what would be the likely outcome in the economy. Use the appropriate tools of analysis, such as aggregate demand and aggregate supply where appropriate, to justify and explain your answer.arrow_forwardWhen the housing bubble burst in 2007, home prices fell and this eliminated a large fraction of many households’ home equity. The most likely outcome of this large decrease in the value of households’ assets is: a rightward shift in the aggregate demand curve a rightward shift in the aggregate supply curve a leftward shift in the aggregate demand curve a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curvearrow_forward6. Why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run In the short run, the quantity of output that firms supply can deviate from the natural level output if the actual price level in the economy deviates from the expected price level. Several theories explain how this might happen. For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 90. Faced with high menu costs, and firms that rely on catalogs the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will will respond by the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected decrease…arrow_forward
- The figure to the right shows the result of an increase in aggregate demand from AD to AD₁.In its new short run equilibrium the economy is resting its potential output. Because the economy is producing beyond its potential output level, input prices and hence production costs are being pushed upward. Using either the line drawing tool or the 3-point curved line drawing tool, illustrate the impact of rising production costs. Properly label your new line or curve. Note: Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. According to your figure, the eventual long-run impact of the increase in aggregate demand is O A. higher prices, lower output. OB. higher prices, higher output. OC. higher prices, unchanged output. O D. higher output, unchanged prices. Price level, P AS (Long run) ASO (Short run) Yo Y₁ Aggregate output (income), Y AD₁ ADOarrow_forwardIn the IS-MP framework, starting from macroeconomic equilibrium at a 0% output gap: (a) a rise in the real interest rate will lead to (a recession, inflation). (b) a rise in the real interest rate will lead to (a negative output gap, a positive output gap). (c) a rise in the real interest rate will lead to (lower sales forecasts, higher sales forecasts).arrow_forwardIn the short run, the quantity of output supplied by firms can deviate from the natural level of output if the actual price level deviates from the expected price level in the economy. A number of theories explain reasons why this might happen. For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 110. Faced with high menu costs, the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will and firms that rely on catalogs will respond by the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected increase in the price level causes the quantity of output…arrow_forward
- can you elaborate?arrow_forwardShift the appropriate curve on the graph to show the impact of an increase in the overall price level on the market for money. Money Supply 10 8 4 2 5 10 15 20 MONEY (Billions of dollars) INTEREST RATE (Percent) 12 0 0 Money Demand 25 30 . Money Demand The following graph plots the aggregate demand curve for this economy. Money Supply Following the price level increase, the quantity of money demanded at the initial interest rate of 6% will be supplied by the Fed at this interest rate. As a result, individuals will attempt to bonds and other interest-bearing assets, and bond issuers will realize that they restored in the money market at an interest rate of % ? than the quantity of money their money holdings. In order to do so, they will interest rates until equilibrium isarrow_forwardAssume an economy operates in the Keynesian (horizontal) range of its aggregate supply curve. For each of the following changes in conditions, state the direction of the effect on Aggregate demand, aggregate supply, price level and real GDP 1. A decrease in government expenditure in infrastructure 2. A severe recession occurs in a country, which has been a major importer 3. The federal government reduces business taxes 4.The central bank increases the cash interest rate.arrow_forward
- If the aggregate supply (AS) curve is very steep, will expansionary fiscal or monetary policy have a bigger effect on real GDP or the price level? Draw a graph to support your answer to this question.arrow_forwardPart B: Aggregate Demand (AD) Curve shows the relationship between the economy’s price level and real GDP demanded. In other words, real GDP demanded by different groups of buyers, i.e., Consumers (C), Businesses (I), Government (G), and Net Amount by Foreigners (Export - Import), at different price levels give us points on a graph, which are connected to form a curve called AD curve. Review the textbook chapter, and conduct internet research to discuss determinants of AD or factors that shift AD curve.arrow_forwardUse the following diagram to answer the next question. Price Levell LRAS Y* AD1 AD2 Multiple Choice AD3 A51 Real GDP browser=0&launchUrl=https%253A 252F%252Fnewconnect.mheducation.com Assume the economy is initially at the full employment level of real GDP. If there is a decrease in imports, the Fed should increase money demand. decrease money demand Savedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education