
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
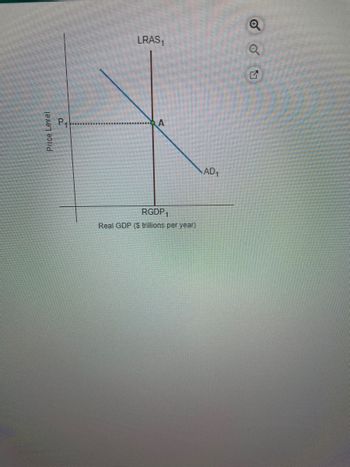
Transcribed Image Text:Price Level
a
LRAS₁
A
RGDP1
Real GDP ($ trillions per year)
AD₁
Q
Transcribed Image Text:The
figure to the right shows an economy in an initial long-run equilibrium at point A
a. Using the line drawing tool, show how, if at all, the equilibrium real GDP and the long-run equilibrium price level are affected by an income tax rebate (the return
of previously paid taxes) from the government to households, which they can apply only to purchases of goods and services. Properly label this line.
Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects
b. According to your graph, the equilibrium price level
here to search
O
while the equilibrium real GDP
▼
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. Why the aggregate supply curve slopes upward in the short run In the short run, the quantity of output that firms supply can deviate from the natural level output if the actual price level in the economy deviates from the expected price level. Several theories explain how this might happen. For example, the sticky-price theory asserts that the output prices of some goods and services adjust slowly to changes in the price level. Suppose firms announce the prices for their products in advance, based on an expected price level of 100 for the coming year. Many of the firms sell their goods through catalogs and face high costs of reprinting if they change prices. The actual price level turns out to be 90. Faced with high menu costs, and firms that rely on catalogs the firms that rely on catalog sales choose not to adjust their prices. Sales from catalogs will will respond by the quantity of output they supply. If enough firms face high costs of adjusting prices, the unexpected decrease…arrow_forward(2) With the help of aggregate supply (AS) and aggregate demand (AD) curves, describe the effects of the following events on the price level and on equilibrium GDP in the short run and the long run, assuming that input prices fully adjust to output prices after some lag.< ■ (i) An increase in the money supply with GDP being below its potential. (ii) Advancement in information technology in the 1990s.arrow_forwardThe Canadian government passes a series of tax cuts into law in order to counteract a recession they have been experiencing. All else equal, illustrate the effects of this change in government policy on the aggregate demand curve by shifting it in the appropriate direction. Provide your answer below: Price Level Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand Real GDParrow_forward
- The following graph represents the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) based on an expected price level of 180. The economy's full- employment output level is $9 trillion. Major unions across the country have recently negotiated three-year wage contracts with employers. The wage contracts are based on an expected price level of 180, but the actual price level turns out to be 240. Show the short-run effect of the unexpectedly high price level by dragging the curve or moving the point to the appropriate position. PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 380 300 240 180 80 0 3 SRAS[180] 9 12 REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 15 18 0 SRAS[180] 0arrow_forwardAn economy is described by the following equations: C= 60 +0.75 (Y - T) IP= 100 G= 150 NX= 30 T= 180 Y*= 760 The multiplier in this economy is 4. a. Find a numerical equation relating planned aggregate expenditure to output. Instructions: Enter your response for mpc rounded to two decimal places. PAE= b. Construct a table to find the value of short-run equilibrium output. Instructions: If you are entering any negative numbers be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of those numbers. Planned aggregate Output Y expenditure (PAE) Y - PAE 620 720 820 920 1,020 Short-run equilibrium output is c. By how much would government purchases have to change in order to eliminate any output gap? By how much would taxes have to change? In order to eliminate any output gap, government purchases would have to be reduced by In order to eliminate any output gap, taxes would have to be increased by d. If Y*=856, then by how much would government purchases have to change in order to eliminate any…arrow_forwardPlease answer in bold print or clear writingarrow_forward
- Instructions: Enter your answers as whole numbers. A) What are the equilibrium price level and the equilibrium level of real output in this hypothetical economy? Is the equilibrium real output also necessarily the full-employment real output? B)If the price level in this economy is 150, will quantity demanded equal, exceed, or fall short of quantity supplied? By what amount? If the price level is 250, will quantity demanded equal, exceed, or fall short of quantity supplied? By what amount? C) Suppose that buyers desire to purchase $ 200 billion of extra real output at each price level. What are the new equilibrium price level and level of real output?arrow_forwardMake 1 demand graph and 1 supply graph to plot the data in the table Suppose that the aggregate demand and aggregate supply schedules for a hypothetical economy are as shown below: Amount of Real GDP Demanded, Billions Price Level (Price Index) Amount of Real GDP Supplied, Billions $100 300 $450 200 250 400 300 200 300 400 150 200 500 100 100arrow_forwardLook at Figure 2. Assume this aggregate demand diagram represents an economy with government, where: a = exogenous consumption b = the marginal propensity to consume t = the tax rate |= investment G = government spending Y = income Figure 2 Aggregate demand AD, AD. 45° Income What is the equation for the aggregate demand schedule ADo? Select one: O ADO = b+ a(1 - t)G +1+ Y O ADO = a + b(1 – 1)Y + 1+ G O ADO = a + b(1 - t) I+ Y+ G O ADO = b+ a(1 – 1)Y + /+ G Next page > ( Previous page PHILIPSarrow_forward
- The following graph shows the aggregate demand (AD) curve in a hypothetical economy. At point A, the price level is 140, and the quantity of output demanded is $300 billion. Moving down along the aggregate demand curve from point A to point B, the price level falls to 120, and the quantity of output demanded rises to $500 billion. 170 100 180 140 130 120 110 AD 100 00 100 200 300 400 B00 700 OUTPUT (Billians of dollars) As the price level falls, the cost of borrowing money will , causing the quantity of output demanded to Additionally, as the price level falls, the impact on the domestic interest rate will cause the real value of the dollar to in foreign exchange markets. The number of domestic products purchased by foreigners (exports) will therefore and the number of foreign products purchased by domestic consumers and firms (imports) will Net exports will therefore causing the quantity of domestic output demanded toarrow_forwardConsider the graph at right showing an economy in recession. Aggregate demand is currently at AD. Equilibrium currently occurs at Eo. If aggregate demand was ADF, there would be full employment. Suppose the government engages in fiscal policy that results in full crowding out. Using the line drawing tool, draw the new demand curve that shows full crowding out. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required object. Price level Eo EF ADO F Real GDP per Year ($ trillions) SRASO ADF O Uarrow_forwardDear expert bro hand written not allowed.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education