
Electric Motor Control
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781133702818
Author: Herman
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
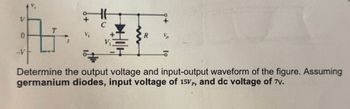
Transcribed Image Text:R
Determine the output voltage and input-output waveform of the figure. Assuming
germanium diodes, input voltage of 15Vp, and dc voltage of 7v.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- What is the difference between a diode and rectifier?arrow_forwardFor each circuit shown below, the input v, is a 60HZ, 12 volt peak sine wave. Sketch the waveform resulting at vo. Assume ideal diodes. What are its positive and negative peak values?arrow_forwardAnswr all the questions one by one and solve all the unknown values giving all the correct details Let the last digit of the ID = 9arrow_forward
- Two identical Schottky diodes are connected in series, one in the forward and the other in reverse direction, see figure. Assume the reverse saturation current, IS, of each diode to be known. Derive he current-voltage curve I(V) of this circuit. Plot it with the ratio I / IS on the y-axis and V / Vth on the x-axis. Make sure to cover a broad range of voltages, say, from –10 Vth to 10 Vth.arrow_forwardDesign a clipping circuit that will limit the output voltage to 5V when applying an input sinusoidal waveform with a peak value of 10V. Assume available diodes with voltage drop of 0.5V. Sketch the output waveform of the circuit.arrow_forward4. Sketch the output Vout for the given input Vin (shown on the right hand side) for each of the circuits (shown on the left hand side). )) Assume ideal diodes. Vin for (a) & (b) (a) R O Vin Vout Vin 1 -2V (b) R Vout Vin Voutarrow_forward
- Consider the following circuit diagram. Using practical diode model solve the following items. i. What is the type of rectification in this circuit? ii. Calculate the total peak secondary voltage (Note that “RMS" value is given in the circuit) iii. Sketch the plot of time vs voltage over Load (RL) iv. Find the average voltage over Load. v. Find the maximum current passing over diodes. vi. Find the peak inverse voltage (PIV) over the diodes. vii. Find the minimum fuse current rating for the primary coil. 5:1 D DA 120 V rms D3 D2 RL=10kQ RL out ell lelllarrow_forwardH.W4 The diode in the single-phase half wave rectifier has a reverse recovery time of tr frequency = 5 kHz. 150usec and the source voltage V₁ = 200V at Calculate the average output voltage. EParrow_forwardDescribe in detail how diodes work and their common applications. Design a clipper circuit that eliminates the positive portion of an AC waveform as shown below, leaving only the negative half-cycles to appear on the output. State approximations that you used.arrow_forward
- .Draw a full-wave rectifier circuit (using a diode bridge) and predict the output voltage signal when the input is a sinusoidal signal with amplitude 10 V (p p). Use the previous full wave rectifier to create a peak detector with a 2 V ripple.arrow_forwardWhat is a Zener diode? For what is it typically used? Draw the volt–ampere characteristic of an ideal 5.8-V Zener diode.arrow_forwardCompared to an ideal PN diode, what are the different characteristics of a practical PN diode? Please list two different characteristics when the diode is reversed biased.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning


Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337399128
Author:Russell E. Smith
Publisher:Cengage Learning