Formal Charges
Formal charges have an important role in organic chemistry since this concept helps us to know whether an atom in a molecule is neutral/bears a positive or negative charge. Even if some molecules are neutral, the atoms within that molecule need not be neutral atoms.
Polarity Of Water
In simple chemical terms, polarity refers to the separation of charges in a chemical species leading into formation of two polar ends which are positively charged end and negatively charged end. Polarity in any molecule occurs due to the differences in the electronegativities of the bonded atoms. Water, as we all know has two hydrogen atoms bonded to an oxygen atom. As oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen thus, there exists polarity in the bonds which is why water is known as a polar solvent.
Valence Bond Theory Vbt
Valence bond theory (VBT) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. It gives a quantum mechanical approach to the formation of covalent bonds with the help of wavefunctions using attractive and repulsive energies when two atoms are brought from infinity to their internuclear distance.
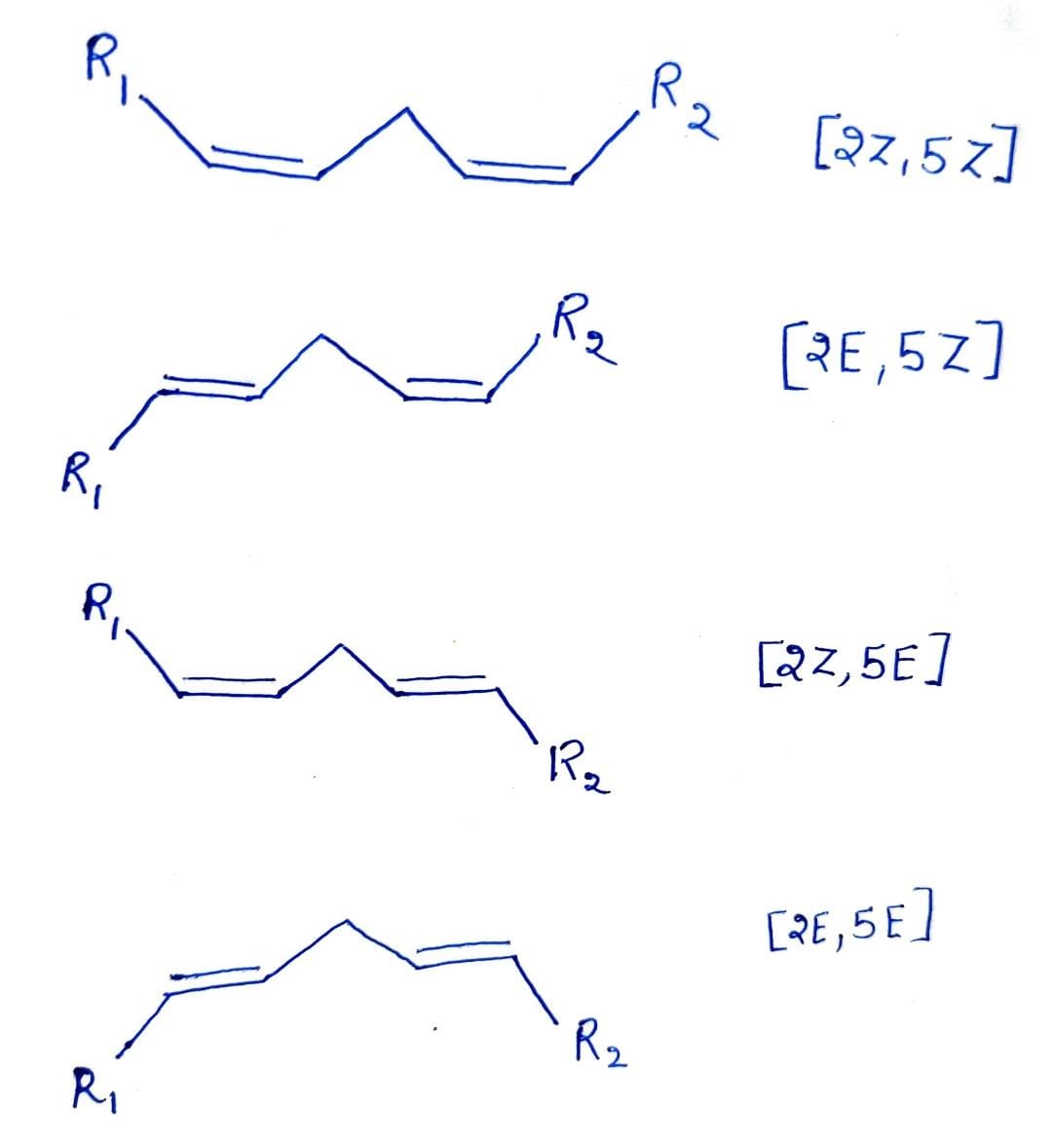
Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid found in many veg-etable oils, such as soy, peanut, and cottonseed. A key structural feature of the molecule is the c is orientation around its two dou-ble bonds, where R1and R2 represent two different groups thatform the rest of the molecule. (a) How many different compounds are possible, changing onlythe cis-trans arrangements around these two double bonds?(b) How many are possible for a similar compound with three double bonds?


- Each carbon in the pi bond is attached to two substituents. For each carbon, these two substituents are ranked (1 or 2) according to the atomic numbers of the atom directly attached to the carbon. (e.g. Cl > F )
- If both substituents ranked 1 are on the same side of the pi bond, the bond is given the descriptor Z (short for German Zusammen, which means “together”).
- If both substituents ranked 1 are on the opposite side of the pi bond, the bond is given the descriptor E (short for German Entgegen, which means “opposite”).
So Z resembles “cis” and E resembles “trans” . (Note: they are not necessarily the same and do not always correlate) .The E/Z system is comprehensive for all alkenes capable of geometric isomerism, including the cis/trans alkene . We often use cis/trans for convenience, but E/Z is the “official”, IUPAC approved way to name alkene stereoisomers
Trending now
This is a popular solution!
Step by step
Solved in 3 steps with 1 images









