
Introductory Chemistry For Today
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285644561
Author: Seager
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
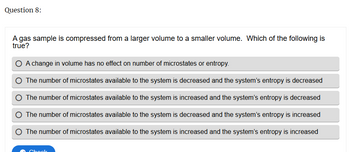
Transcribed Image Text:Question 8:
A gas sample is compressed from a larger volume to a smaller volume. Which of the following is
true?
A change in volume has no effect on number of microstates or entropy.
The number of microstates available to the system is decreased and the system's entropy is decreased
The number of microstates available to the system is increased and the system's entropy is decreased
The number of microstates available to the system is decreased and the system's entropy is increased
The number of microstates available to the system is increased and the system's entropy is increased
Chock
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For each situation described in Question 13, predict whether the entropy of the system increases or decreases.arrow_forwardOne statement of the second law of thermodynamics is that heat cannot be turned completely into work. Another is that the entropy of the universe always increases. How are these two statements related?arrow_forwardWhich of the following processes will lead to a decrease in the internal energy of a system? (1) Energy is transferred as heat to the system; (2) energy is transferred as heat from the system; (3) energy is transferred as work done on the system; or (4) energy is transferred as work done by the system. (a) 1 and 3 (b) 2 and 4 (c) 1 and 4 (d) 2and3arrow_forward
- Classify the following processes as exergonic or endergonic. Explain your answers. a.An automobile being pushed up a slight hill from point of view of the pushing b.Ice melting from point of view of the ice c.Ice melting from point of view of surrounding of the ice d.Steam condensing to liquid water from point of view of the steam e.Steam condensing to liquid water from point of view of surrounding of the steamarrow_forwardThe internal energy of a system is said to be the sum of the kinetic and potential energies of all the particles in the system. Section 10. 1 discusses potential energy and kinetic energy in terms of a ball on a hill. Explain potential energy and kinetic energy for a chemical reaction.arrow_forwardxplain why aluminum cans make good storage containers for soft drinks. Styrofoam cups can be used to keep coffee hot and cola cold. How can this be?arrow_forward
- Would the amount of heat absorbed by the dissolution in Example 5.6 appear greater, lesser, or remain the same if the experimenter used a calorimeter that was a poorer insulator than a coffee cup calorimeter? Explain your answer.arrow_forward9.68 What are some features of petroleum that make it such an attractive fuel?arrow_forwardFor each process, tell whether the entropy change of the system is positive or negative. Water vapor (the system) deposits as ice crystals on a cold windowpane. A can of carbonated beverage loses its fizz. (Consider the beverage but not the can as the system. What happens to the entropy of the dissolved gas?) A glassblower heats glass (the system) to its softening temperature.arrow_forward
- Consider the system shown in Figure 16.9. What is the change in entropy for the process where the energy is initially associated with particles A and B, and the energy is distributed between two particles in different boxes (one in A-B, the other in C-D)?arrow_forwardDescribe the energy and entropy changes that occur in the following processes, and indicate whether the processes are spontaneous under the conditions stated: a.Lumber becomes a house b.A seed grows into a tree. c.On a hot day, water evaporates from a lake.arrow_forwardExplain in your own words what is meant by the term entropy. Explain how both matter spread and energy spread are related to the concept of entropy.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning


Chemistry for Engineering Students
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337398909
Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom Holme
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399074
Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David Treichel
Publisher:Cengage Learning