
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
question 4
Chen et al. (2000) examined the foraging behaviour of northern elephant seals (Mirounga angustirostris) that breed along the west coast of Mexico and the USA. They attached platform satellite transmitter terminals (PTTs) to 22 male seals and recorded, for each seal, the distance (km) to its main feeding area offshore and the amount of time (days) it spent at the feeding area. The results are presented below:
- What two null hypotheses are being tested with the output shown above?
- What statistical conclusions would you draw about these hypotheses?
- Complete the regression equation by filling in the blanks (to the nearest 3 decimal places).
duration = + * distance
- What is one biological interpretation of this relationship between duration and distance ?
- What % of the variation in duration at main feeding area was explained by distance to feeding area?
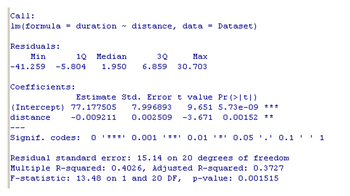
Transcribed Image Text:Call:
1m (formula = duration ~ distance, data = Dataset)
Residuals:
Min
1Q Median
3Q
-41.259 -5.804 1.950 6.859
Coefficients:
Max
30.703
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr (>|t|)
77.177505
7.996893
-0.009211 0.002509 -3.671 0.00152 **
Signif. codes: 0¹*** 0.001 ** 0.01 * 0.05 .0.1¹¹1
Residual standard error: 15.14 on 20 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.4026, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3727
F-statistic: 13.48 on 1 and 20 DF, p-value: 0.001515
(Intercept)
distance
9.651 5.73e-09 ***
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 7 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Mason is conducting a study on the effect of computer-based training on the math ability of seventh-graders. He randomly assigns one group of students to use a computer-based training method and another group of students to use workbooks. What type of analysis should be performed to determine if there is a difference between the two conditions? Group of answer choices A) paired samples t test B) Pearson's correlation C) independent samples t test D) z testarrow_forwardWhen an audit must be conducted that involves a tedious examination of a large inventory, the audit may be very costly and time consuming if each item in the inventory must be examined. In such situations, the auditor frequently obtains a random sample of items from the complete inventory and uses the results of an audit of the sampled items to check the validity of the company's financial statement. A large company’s financial statement claims an inventory that averages $600 per item. The following data are the auditor’s assessment of a random sample of 75 items from the company’s inventory. The values resulting from the audit are rounded to the nearest dollar. Estimate the mean value of an item in the inventory using a 95% confidence interval. Is there substantial evidence (a 5 .01) that the mean value of an item in the inventory is less than $600? What is the target population for the above inferences? Would normal distribution–based procedures be appropriate for answering the…arrow_forwardA small pilot study is run to compare a new drug for chronic pain to one that is currently available. Participants are randomly assigned to receive either the new drug or the currently available drug and report improvement in pain on a 5-point ordinal scale: 1=Pain is much worse, 2=Pain is slightly worse, 3= No change, 4=Pain improved slightly, 5=Pain much improved. Is there a significant difference in self-reported improvement in pain? Use the Mann-Whitney U test with a 5% level of significance. Please show work. New Drug: 4 5 3 3 4 2 Standard Drug: 2 3 4 1 2 3arrow_forward
- 8) The following results are from data that were collected from the various high schools around the county. The dependent variable is % OF STUDENTS GOING TO COLLEGE, and the independent variables are: AVERAGE CLASS SIZE, COMBINED SAT SCORES, SPENDING PER STUDENT, AVERAGE TEACHER SALARY, AND % TAKING THE SAT Since the 3 variables AVERAGE CLASS SIZE, SPENDING PER STUDENT, AND AVERAGE TEACHER SALARY are each not significant at the 10% level of significance individually, in order to test to see if as a group they are significant the 3 variables are excluded and another regression is run. The results are as follows: a) At the 10% level of significance, test whether as a group AVERAGE CLASS SIZE, SPENDING PER STUDENT, AND AVERAGE TEACHER SALARY are significant. Be sure to state the null and alternative hypotheses for this hypothesis test.arrow_forwardone- Oishi and Schimmack (2010) report that people who move from home to home frequently as children tend to have lower than average levels of well-being as adults. To further examine this relationship, a psychol- ogist obtains a sample of n = 12 young adults who each experienced 5 or more different homes before they were 16 years old. These participants were givenarrow_forwardBased on these tables, would you accept or reject the hypothesis that individuals in bad neighborhoods commit more crime?arrow_forward
- A father is concerned that his teenage son is watching too much television each day, since his son watches an average of 2 hours per day His son says that his TV habits are no different than those of his friends. Since this father has taken a stats class, he knows that can actually test to see whether or not his son is watching more TV than his peers The father collects a random sample of watching times from boys at his son's high school and gets the following data: 1.9, 2.3, 2.2, 1.9, 1.6, 2.6, 1.4, 2.0, 2.0, 2.2 Find a 95% confidence interval for the true mean number of hours teenagers at that school watch TV. a. Confidence Interval b. Conclusionarrow_forwardThe longest study time by Sarah was_______ hours.arrow_forwardMood variation is related to photoperiod in some people, and the likelihood of depression increases in the winter months. As a result, people often assume that suicide rates increase in winter. A study in Finland (Valtonen et al. 2006) divided the year 1997 into equal halves and compared the number of suicides in “winter” (24 September to 19 March) and “summer” (remainder of year). Out of a total of 1636 suicides, 766 were in winter and 870 were in the summer. Based on these data, estimate the proportion of suicides that occurred in winter, assuming that the suicides were independent. Are the data compatible with a greater suicide rate in winter than summer, based on a 95% confidence interval?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman