
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
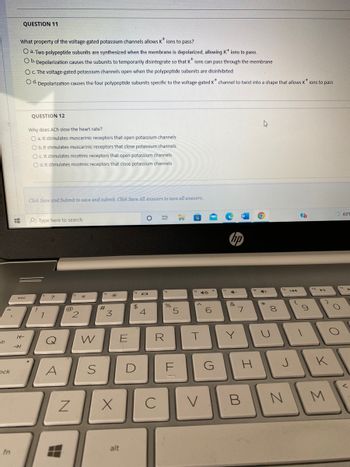
Transcribed Image Text:### Scientific Quiz - Exciting Neurobiology Questions
Welcome to our educational quiz section focusing on neurobiology. Below, we present intriguing questions on voltage-gated potassium channels and the effect of acetylcholine (ACh) on heart rate. Test your understanding and deepen your knowledge!
---
**Question 11**
**What property of the voltage-gated potassium channels allows K⁺ ions to pass?**
- A. Two polypeptide subunits are synthesized when the membrane is depolarized, allowing K⁺ ions to pass.
- B. Depolarization causes the subunits to temporarily disintegrate so that K⁺ ions can pass through the membrane.
- C. The voltage-gated potassium channels open when the polypeptide subunits are disinhibited.
- D. Depolarization causes the four polypeptide subunits specific to the voltage gated K⁺ channel to twist into a shape that allows K⁺ ions to pass.
---
**Question 12**
**Why does ACh slow the heart rate?**
- A. It stimulates muscarinic receptors that open potassium channels.
- B. It stimulates muscarinic receptors that close potassium channels.
- C. It stimulates nicotinic receptors that open potassium channels.
- D. It stimulates nicotinic receptors that close potassium channels.
---
Ensure to save and submit your answers by clicking "Save All Answers" to see all your answers.
We hope you enjoy this learning experience and expand your knowledge about the fascinating topics of ionic channels and neurotransmitters!
---
Feel free to participate in the quiz and explore more on this subject in our detailed articles and study materials. Happy learning!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 6 You treat a biological membrane with an enzyme that degrades proteins. Do you expect this treatment to alter the diffusion rate for CO2? What about for sodium ions (Na*)? For the toolbar, press ALT+F10 (PC) or ALT+FN+F10 (Mac).arrow_forwardQuestion 4. Which of the following statements are true of kinases? A. They always bind to a dimeric ligand. B. They phosphorylate themselves or another protein. C. They must be associated with a G-protein to function. D. They always contain seven membrane-spanning domains. E. They always dephos phorylate proteins.arrow_forwardQuestion 3. You have identified a mouse that develops dry skin due to increased evaporation. Which of the four junction that we discussed do you think may be dysfunctional in this mouse?arrow_forward
- QUESTION 14 What switches off an activated G protein? A molecule of GDP replaces the GTP. There is an enzyme that reassembles the trimeric G protein. Ca2+ ions activate CAMKII, which inactivates the protein. The protein contains intrinsic GTPase activity which converts GTP to GDP. A phosphorylase enzyme removes the phosphate from the GTP.arrow_forwardQuestion 26arrow_forwardQuestion 7. What is the rate-limiting step in the formation of an actin microfilament?arrow_forward
- QUESTION 14 Which of the following statements is FALSE? A Microtubules will rapidly disassemble in response to a drop in the ATP concentration. B G-actin monomers and alpha-tubulin/beta-tubulin dimers assemble into filaments in their ATP-bound and GTP-bound forms, respectively. C Microtubules are stabilized by microtubule-binding proteins, such as Tau. D Actin-binding proteins allow F-actin to assemble in cells in many different ways. E Hydrolysis of ATP and GTP changes the conformation of the monomers once they are incorporated into actin filaments and microtubules, respectively.arrow_forwardQUESTION 4 Which of the following G protein subunits activate K+ channels in response to the GPCR for acetylcholine on heart muscle? a. Galpha inhibitory. b. G alpha stimulatory c. G beta gamma dimer. d. G alpha transducin.arrow_forwardQuestion 34 Which is the target cell response to ADH? O gluconeogenesis, saving glucose for the brain smooth muscle contraction in mammary ducts and milk let down O the insertion of aquaporin cells facilitates water reabsorption An increase in sodium channels and sodium ion reabsorption, water followsarrow_forward
- QUESTION 42 Which of the following statements is INCORRECT? O a. In a protein kinase cascade, the signal is amplified at each step of the cascade. O b. The major difference between a cell that responds to a signal and one that does not is the presence of a receptor O c. Adenylyl cyclase is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of ATP to CAMP. Od. In a protein kinase cascade, variation in the response is not possible. O e. Signals can reach target cells in multicellular organisms by diffusion or by circulation in the blood.arrow_forwardQuestion 4. In an axon, where all of the microtubules are oriented with their minus end facing the cell body, a researcher observes vesicles transporting cargo toward the synaptic terminals. Which type of molecular motor protein do you predict is transporting these vesicles?arrow_forwardQUESTION 10 Which of the following is NOT true of intermediate filaments? A They provide mechanical strength to cells. B They are composed of 8 oppositely oriented tetramers that are assembled into a rope-like filament. C They have a non-polar orientation. D They are rigid and do not deform before breaking E Keratins, neurofilaments, vimentin, and desmin are examples of intermediate filaments.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education