
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
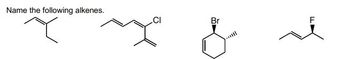
Transcribed Image Text:### Naming Alkenes - Practice Problems
Below are the structural formulas of several alkenes. The task is to name each compound correctly based on its chemical structure.
1. **First Structure:**
- Description: The structure is a branched alkene with three carbon atoms forming a backbone. An additional methyl group is attached to the middle carbon, creating a branch. This compound is a simple alkene without any additional substituent atoms.
- Visual: A carbon skeleton with a double bond between the first and second carbon atoms.
2. **Second Structure:**
- Description: The structure has a linear carbon backbone with five carbon atoms. The double bond is located between the second and third carbons. Additionally, there is a chlorine atom (Cl) attached to the fourth carbon.
- Visual: A pentane chain with a double bond and chlorine substituent.
3. **Third Structure:**
- Description: This is a cyclohexene ring with a bromine atom (Br) attached to one of the carbons. The double bond is located within the ring, between two carbon atoms. A wedge is used to indicate the 3D spatial position of the bromine atom.
- Visual: A six-carbon ring with a double bond and a 3D representation of the bromine substituent.
4. **Fourth Structure:**
- Description: This molecule consists of a four-carbon chain with a double bond between the second and third carbon atoms. A fluorine atom (F) is attached to the second carbon, demonstrated with a wedge to show spatial orientation.
- Visual: A butene chain with a double bond and fluorine substituent in a 3D orientation.
These structural diagrams are commonly used in organic chemistry to practice and reinforce the understanding of alkene nomenclature. Understanding the placement of double bonds and naming substituents is crucial for accurate chemical communication.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- III. Essay. Answer the following questions concisely. 1. Ether and alcohol are functional isomers. Give the functional isomer of 3- Methoxyhexane. Name and draw the condensed structural formula of this alcohol. 2. Both dimethyl ether and ethanol has the same molecular mass because they are functional isomers. Why is dimethyl ether a gas at room temperature while ethanol is a liquid? 3. Why has use of MTBE as a gasoline additive been discontinued in the United States?arrow_forward4 HW: Brooke Jeffers 2576 pts 500 achieve.macmillanlearning.com Chapter 4 HW - General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry for Health Sciences - Ac Resources Solution Penalized Feedback Try Again Question 23 of 35 > © Macmillan Learning Draw the expanded, or complete, structural formula for the hydrocarbon represented by the line-angle, or skeletal, structure shown. Draw the complete structural formula. Include all hydrogen atoms. Attenarrow_forwardPls can you explain how to get the observation below Physical properties of Hydrocarbons: Test for water solubility of hydrocarbons: 1. Label three test tubes as alkanes, alkenes and aromatics. 2. Add 4 drops of each in their respective test tube; add equal amounts of distilled water. Gently swirl. Water is polar solvent. Are there any separations of layers between the water layer and organic liquid layer? If separated, which layer is on top, the organic layer or thewater layer? 3. Record your observations in the data table below. If separation of layers occurs, increase the amounts of water and gently swirl again to confirm the insolubility property. 4. Disposal: All contents to be disposed into the waste container marked as organic waste. Wash the test tubes and clean them using brush, soap and water. Keep these inverted in the test tube rack. Data Table: Test tube Observations 1) Alkane 2) Alkene 3) Aromaticsarrow_forward
- 7. How many isomers does hexane have? Draw and name them below. Discussion 1. Consider the following data table of the boiling points of alkanes. Alkanė Boiling Point (°C) Нeptane Propane Pentane 98.5 -42 36 Butane 0.5 Methane -161 Ethane -88.5 Hexane On a separate piece of graph paper, make a line graph of this data. Be sure to label the axes and give the graph a title. Based on information contained in the table, predict the approximate boiling point of hexane, and explain why.arrow_forwardWhat is a hydrocarbon? What is the difference between a saturated hydrocarbon and an unsaturated hydrocarbon? Distinguish between normal and branched hydrocarbons. What is an alkane? What is a cyclic alkane? What are the two general formulas for alkanes? What is the hybridization of carbon atoms in alkanes? What are the bond angles in alkanes? Why are cyclopropane and cyclobutane so reactive? The normal (unbranched) hydrocarbons are often referred to as straight-chain hydrocarbons. What does this name refer to? Does it mean that the carbon atoms in a straight-chain hydrocarbon really have a linear arrangement? Explain. In the shorthand notation for cyclic alkanes, the hydrogens are usually omitted. How do you determine the number of hydrogens bonded to each carbon in a ring structure?arrow_forwardFor this problem, please draw skeletal structures for the following two molecules (you will have two drawings in your answer.) Take a picture of your structures and upload it for grading. • 1-chloro-3,3-dimethylpentane 1,1-dibromo-2-methylcyclohexanearrow_forward
- Bb2.arrow_forwardDetermine the functional group(s) for the following molecule (choose all that apply).CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY(It is NOT alcohol, I already tried and it was wrong) a. acetal b. aldehyde c. hemiacetal d. alcohol e. aromatic f. ketone g. carboxylic acid h. esterarrow_forwardNext, let's explore what happens when you remove two hydrogens from the structure above and form ethene, CH,CH,. How many bonds should be between the two carbons to give each carbon a total of four bonds? Draw the structural formula for ethene, CH,CH,.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning
