
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Name the
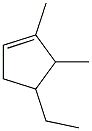
Transcribed Image Text:This image represents the chemical structure of limonene, a common terpene found in the rinds of citrus fruits. Let's break down the details for better understanding:
### Chemical Structure of Limonene
Limonene is a hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic terpene. It is predominantly known for its strong orange or lemon scent, which is why it is often associated with citrus fruits.
#### Structural Elements:
- **Carbon Atoms:** The basic skeleton of limonene consists of carbon atoms. In the diagram, these are represented as vertices where lines (bonds) intersect. Limonene has 10 carbon atoms.
- **Hydrogen Atoms:** These are not usually shown in simplified organic chemistry diagrams like the one here, but each carbon is bonded with enough hydrogen atoms to have four bonds total.
- **Double Bonds:** The diagram shows alternating single and double bonds in the carbon ring structure. These bonds are denoted by either single lines (single bonds) or double lines (double bonds). Limonene contains one double bond in the ring, making it a member of the class of compounds known as alkenes.
#### Cyclic Structure:
- Limonene's structure features a six-membered ring, which is common in cyclic alkenes.
- Attached to this ring at the upper right is a tetrahedral-shaped structure, which represents a methyl group (CH₃).
### Functionality and Uses:
Limonene is widely used in various applications:
- **Aromatics:** Due to its pleasant citrus scent, limonene is used in perfumes, household cleaners, and air fresheners.
- **Industrial Cleaning Agent:** Its solvent properties make it effective in removing oils, adhesives, and tar.
- **Medical and Therapeutic Uses:** Limonene has also been investigated for its potential anti-inflammatory and gastro-protective effects.
For an enhanced understanding, it would be useful to review materials on organic chemistry, particularly sections that cover hydrocarbon structures and functional groups. This will help in recognizing how the presence of double bonds and ring structures influences the properties and reactivity of limonene.
By studying the structure depicted in the image, students can gain insights into the intricate world of organic molecules and their functional uses in everyday life.
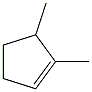
Transcribed Image Text:### Cyclopentane Structural Representation
The image depicts the structural formula of cyclopentane. This is an organic compound with the molecular formula \( C_5H_{10} \). Cyclopentane is a cyclic alkane consisting of five carbon atoms arranged in a ring, with each carbon bonded to two hydrogen atoms, completing the tetravalent structure of carbon.
**Structural Features:**
1. **Ring Structure**: The carbons are connected, forming a five-membered ring.
2. **Hydrogen Atoms**: Each carbon in the ring is bonded to two hydrogen atoms. However, in the typical skeletal structure shown, the hydrogen atoms are not explicitly depicted but are implied.
3. **Single Bonds**: The lines connecting the carbon atoms represent single covalent bonds.
### Key Points for Students:
- **Cyclic Compounds**: Cyclopentane is an example of a cycloalkane, which is characterized by having carbon atoms arranged in a ring or cyclic structure.
- **Hydrogen Atoms**: It’s important to remember that even if hydrogen atoms are not shown in skeletal formulas, they are present to satisfy the valency (4 bonds) of carbon atoms.
- **Drawing Conventions**: In skeletal formulas, corners represent carbon atoms, and lines represent the bonds between them. Hydrogen atoms attached to carbons are typically not shown unless needed for clarity.
Understanding the structure of cyclopentane is fundamental in organic chemistry, providing a basis for more complex studies of hydrocarbons and their reactions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 12 of 30 Submit Provide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. CH3 || H-C-CH2-CH-CH2-CH3 6- 1- 5-||4- 2- 3- tri iso cyclo di sec- tert- meth prop hex] pent but eth one oate an yl ol alarrow_forwardIs this alkene Z or Earrow_forwardPlease be clear in your writing The following names may have some errors. Correct the name and render the structures corresponding to the following names. g) 1,3-pentadiino h) cyclohexylacetylenearrow_forward
- Name the following alkenes. CI Br ill F LLarrow_forwardWhich of the following is incorrect about the molecule shown below? CH3CH=CH-CH=CH₂ it belongs to the alkene family Its name is pent-1,3-diene It is a hydrocarbon It is considered to be saturatedarrow_forwardDraw the following molecule: cis-1-tert-butyl-4-methylcyclohexane (in chair form)arrow_forward
- Name each of the following alkanes.arrow_forwardCH3 CH;-C=C-CH,-CH-CH; What is the correct IUPAC name for the compound above? O 1-isopropyl-2-butyne O 2-methylhexene O 2-methylhexyne 5-methyl-2-hexynearrow_forwardCH, The name of the molecule above is: 4-methyl-2-pentene 2-methyhexyne 2-methylhexene 2-methyl-4-pentenearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY