
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
main binding pocket inside the GLP-1 receptor and the critical residues found in GLP-1 particularly in its N-terminus. what are the amino acids found particularly in its N terminus
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: GLP-1 receptor
GLP-1 receptor is glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. It is a G-protein-coupled receptor that is involved in the process of glucose homeostasis. The N terminus plays an important role in binding to the GLP-1 receptor.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
please identify amino acids in the N terminus in the picture below.
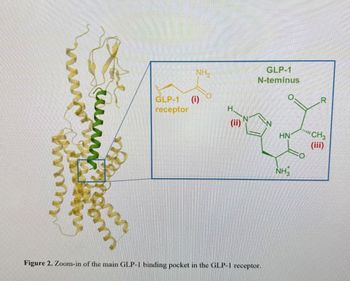
Transcribed Image Text:шалай
am
NH₂
GLP-1 (i)
receptor
H
(ii)
GLP-1
N-teminus
Figure 2. Zoom-in of the main GLP-1 binding pocket in the GLP-1 receptor.
HN
NH₂
R
CH3
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
please identify amino acids in the N terminus in the picture below.

Transcribed Image Text:шалай
am
NH₂
GLP-1 (i)
receptor
H
(ii)
GLP-1
N-teminus
Figure 2. Zoom-in of the main GLP-1 binding pocket in the GLP-1 receptor.
HN
NH₂
R
CH3
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biochemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Would an extracellular signal receptor protein mostly likely consist of type 1 or type 2 alpha helices? Explain your reasoningarrow_forwardSpecificity in fusion between vesicles involves two discrete and sequential processes. Describe the first of the two processes and its regulation by GTPase switch proteins. What effect on the size of early endosomes might result from overexpression of a mutant form of Rab5 that is stuck in the GTP-bound state?arrow_forwardWhen you think about the primary structure of the mannose-6-P receptor, assuming that it is an integral membrane protein with one membrane-spanning domain and assuming that it has a ERSS, what are all of the different protein domains that must be present in this protein's primary structure to get it to where it needs to go and to carry out all of the functions/activities? (Draw a schematic of the protein structure/sequence and explain each region). What do you think would happen to a soluble protein that normally contains a KDEL tag (ER retrieval) if the tag was cleaved off (where would the protein end up)?arrow_forward
- The figure from Moore (2020) shows a G protein-coupled receptor in a membrane. Note that "out" means outside the cell and "in" means facing the cytoplasm. The three amino acids "DRY" in loop I2 are required for protein targeting. What is the name of this kind of sequence, and what is its function? What protein targeting sequence is no longer included in this diagram? Why? The sequence "QXXNK" (where X is any amino acid) found in loop I3 has been identified based on its enzymatic activity. What is this activity? What particular domain would you expect to find in either Loop E1, E2, or E3? The gene that codes for this protein is a member of a family of genes that has arisen over evolutionary time. If you compared several of the genes in this family, would you expect their sequences to be most homologous (similar) in the region you describe in #3 above or #4 above? Why?arrow_forwardDuring elongation eEF1α complexed to GTP escorts the aminoacyl tRNA to the ribosome. True Falsearrow_forwardIf you were to remove the ER retrieval signal fromprotein disulfide isomerase (PDI), which is normally a sol-uble resident of the ER lumen, where would you expect themodified PDI to be located?arrow_forward
- Effects of BPA on phosphorylation of MAPKfamily in RAW264.7 cells conclusionarrow_forwardSame question but two different sectionsarrow_forwardExpression of the muscle specific protein dystrophin is important in the functional formation of muscle tissue by integrating the internal cytoskeleton through a transmembrane complex with the extracellular matrix. aiding transcription factors in entry into the muscle cells nucleus degrading non-muscle cell proteins. none of thesearrow_forward
- From experiments in which cells expressing normal myosin II heavy chain were altered to either lack (mhckA-) or overexpress (MHCKA ++) a myosin heavy chain kinase (MHCKA). For answering this question recall the earlier the variants on the myosin II heavy chain, in which three key threonines, normally subject to reversible phosphorylation, were altered in various ways: 3X Ser = Serines in place of Threonines 3X Ala = Alanines in place of Threonines 3X Asp = Aspartate in place of Threonines MHCKA is present at normal levels. Which of the two mutants (mhcp- or MHCP++) would be most likely to have a defect in cytokinesis?arrow_forwardThe mutation in hemoglobin at B82 Lys → Asp results in lowered O,-binding affinity compared to normal hemoglobin. B82 is one of the residues that lines the 2,3-BPG binding site (see Figure 7.29; B82 is adjacent to His143). Based on the location of this residue and the differences between Lys and Asp, sug- gest a rationale for the observed reduction in Oz-binding affinity.arrow_forwardSars-CoV-2 spike protein: VGIYLQKTSDHRPEFALAMN What is its isoelectric point of this peptide?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON