
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:LESSEU
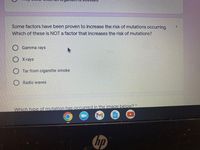
Some factors have been proven to increase the risk of mutations occurring.
Which of these is NOT a factor that increases the risk of mutations?
Gamma rays
Tar from cigarette smoke
Radio waves
Which type of mutation has occurred in the image below? *
hp
OX-rays
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Why should people care about mutations and about generating mutations?arrow_forwardMatch the structures of the male and female reproductive systems numbered above with their names given below. Number: Answer Answer Answer Answer Name: Fallopian tube Uterus Vas deferens Prostate glandarrow_forwardHow do silent mutations generally affect the function of the protein encoded by the mutated gene? They generally do not affect protein function They always result in a nonfunctional protein They always lead to a gain of function They always lead to a loss of functionarrow_forward
- Compare and contrast nonsense mutations, silent mutations, and missense mutations including the impact of the mutation on the protein produced. Your answer should be 3-7 sentences sentences long and fully explain how they are similar and what is different between the mutations.arrow_forwardAs discussed, the overall rate of mutations in humans is estimated to be about 1 × 10−8 mutations per base pair per generation. How many new mutations would you expect each person to carry, on average, based on this mutation rate? Other studies have estimated that each person carries about 100 new loss-of-function mutations. How does this number compare with your estimate of the number of mutations based on the mutation rate? What might account for any differences?arrow_forwardIs a random mutation more likely to be beneficial or harmful?Explain your answer.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is NOT true about mutations? A. Mutations can be harmful but not beneficial to the cell B. Nucleotide substitution in DNA can cause nonsense mutations C. Nucleotide substitution in DNA can cause missense mutations D. Mutagens increase the rate of mutation, but mutations are still random E. Nucleotide insertion or deletion in DNA can cause frameshift mutationsarrow_forwardWhat type of mutation causes the "mutant" variety of the PTC gene? a A point mutation which lead to a nonsense mutation b A addition mutation which lead to a frameshift c A substitution mutation which lead to a missense mutation d A deletion mutation which lead to a SNP mutationarrow_forwardWhat are point mutations? Of the different mutations, which is the most deleterious? Justify your answer with suitable genetic disease.arrow_forward
- List two specific causes of DNA mutations. - environmental agents like ultraviolet light or ionizing radiation - chemicalsarrow_forwardWhich of the following types of mutations will have the most devastating effect on a cell?A.frameshift mutationB. missense mutationC. nonsense mutationD. silent mutationarrow_forwardIf you have a mutation in your skin cells from falling asleep in a tanning bed, how will this affect your offspring? Group of answer choices It won't affect them because mutations cannot be passed down to offspring It will affect their entire body because their entire body grew out of the fertilized egg It will affect your offspring's skin cells only It may affect them, depending on whether those particular skin cells are passed on to them It won't affect them because the mutation is not in a gametearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education