
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
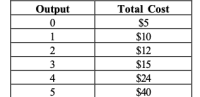
if the market
A) produce 4 units of output in the short run and exit in the long run.
B) produce 5 units of output in the short run and exit in the long run.
C) produce 5 units of output in the short run and face competition from new market entrants in the long run.
D) shut down in the short run and exit in the long run.
E) Shut down in the short run and enter in the long run.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION 6 Use the model of the perfectly competitive firm shown below to fill in the following blanks: $ 8 7 6 сл 5 4 3 2 1 MC If the firm produces Q* units their profit will be $ If the firm shown above shuts down their profit will be $ The profit maximizing firm should In the long run firms will ATC 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 AVC MR Q this market, this will cause market price toarrow_forwardMy answer was wrong can I be shown explained what the right answer is?arrow_forwardAssume the following regarding a firm in Perfect Competition: Market Demand = Qd 460-3P Market Supply = Qs = 9 P Each identical firm has: MC=4q ATC = 14 1. What price will the firm charge? Number 2. What is the firm's equilibrium quantity? Number 3. What is the firm's total cost? Number 4. What is the firm's total revenue? Number 5. What is the firm's profit or loss? (use a negative sign to indicate a loss) Number 6. Is the firm in a short-run or long-run situation? Click for Listarrow_forward
- Refer to the figure above. When the demand curve is given by P2 = $15, this firm should ______ A. continue to operate in the short run and think about shutting down in the long run B. discontinue operation in the short run since there is a loss when operating. C. keep operating as long as loss is not greater than total cost D. discontinue operation in the short run since average total cost is greater than price. When the demand is P3 = $10, this firm should ______ A. continue to operate in the short run and think about shutting down in the long run B. discontinue operation in the short run since the firm is unable to cover variable costs. C. keep operating as long as loss is not greater than total cost D. discontinue operation in the short run since average total cost is greater than price.arrow_forward39) If a perfectly competitive firm operates in the short run but exits the industry in the long run, then the firm's short run condition isA) TR > TVC and TR < TC. B) TR > TC.C) TR < TVC. D) TR < TFC.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements applies to a purely competitive producer? a. it will not advertise its product b. in long-run equilibrium, it will earn an economic profit c. its product will have a brand name that elicits customer loyalty d. its product is slightly different from those of its competitors [ don't give chatgpt answer]arrow_forward
- 1) If a firm in a purely competitive industry is confronted with an equilibrium price of $5, its marginal revenue: 2) A firm that is motivated by self interest should 3) If price is above the equilibrium level, competition among sellers to reduce the resulting 4) Camille's Creations and Julia's Jewels both sell beads in a competitive market. If at the market price of $5, both are running out of beads to sell (they can't keep up with the quantity demanded at that price), then we would expect both Camille's and Julia's to 5) Since their introduction, prices of DVD players have fallen and the quantity purchased has increased. This statement 6) In a market economy the distribution of output will be determined primarily by 7) In a competitive market economy firms will select the least-cost production technique because 8) Suppose that the price of peanuts falls from $3 to $2 per bushel and that, as a result, the total revenue received by peanut…arrow_forwardSuppose, under Perfect Competition, firms are earning an economic profit in the Short-Run. What will happen in the Long-Run? Group of answer choices Firms will enter the industry in the Long-Run There will be no change in the number of firms in the industry in the Long-Run Some firms will exit the industry in the Long-Run There isn’t enough information to determine what will happen in the Long-Runarrow_forwardThe canola farming industry is perfectly competitive. Assume that it is in long-run equilibrium at quantity Q0 and price P0. Assume also that it is a constant-cost industry. a) Draw a supply and demand diagram for the canola market showing this equilibrium b.) draw diagram for a typical canola growing farm in its initial long run equilibrium, showing its Marginal Cost, Average Total Cost, and Long Run Average Cost curves. Are there any profits being made by this firm?arrow_forward
- Perfect Competition MC - Marginal Cost MR - Marginal Revenue ATC - Average Total Cost Refer to the figure above. If this firm is producing the profit-maximizing quantity and selling it at the profit-maximizing price, the firm's total revenue will be: $240 $90 $60 $180arrow_forwardCamara's lawn-mowing service is a profit-maximizing competitive firm. Camara mows lawn for $27 each. His Total Cost each day is $280, of which $30 is a fixed cost. He mows 10 lawns a day. Camara should exit this market in the long-run but continue to operate in the short-run. O True Falsearrow_forwardume the pizza market is a perfectly competitive constant cost industry, and all firms have identical homogenous firms). The market demand and market supply functions for this perfectly competit stry are given below. L 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 q=TP 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 TC 100 205 2.45 280 340 430 545 720 930 1190 P = 30.5-.005Q P = 1.7+.003Q TFC TVC 100 0 100 105 20.50 10.50 100 145 12.25 7.25 100 180 9.33 6.00 100 240 8.50 6.00 100 330 8.60 6.60 100 445 9.08 7.42 100 620 10.29 8.86 100 830 11.63 10.38 100 1090 13.22 12.11 ATC AVC MC 10.50 4.60 3.50 6.00 9.00 11.5 17.50 21.00 26.00arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education