
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
You have the following pathway:
If an isolated liver cell runs out of glucose, the cell will break down glycogen into Glucose-1-Phosphate (Glucose-1-P). The isolated liver cell will then use the enzyme phosphoglucomutase to convert Glucose-1-P to Glucose-6-P, which can enter glycolysis. If you remove all glucose and add a drug that inhibits phosphoglucomutase, which molecule will most likely accumulate in this system?
A. Glucose
B. Glucose 1 phosphate
C. Glucose 6 phosphate
D. Lactate
E. CO2
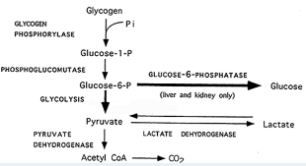
Transcribed Image Text:GLYCOGEN
PHOSPHORYLASE
Glycogen
Glucose-1-P
PHOSPHOGLUCOMUTASE
Glucose-6-P
GLYCOLYSIS
Pyruvate
PYRUVATE
DEHYDROGENASE
Acetyl COA
GLUCOSE-6-PHOSPHATASE
(liver and kidney only)
LACTATE DEHYDROGENASE
00₂
Glucose
Lactate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following conditions will produce active glycogen phosphorylase? AMP АТР Phosphorylation of Serine 14 Glucose Glucose-6-Phosphate Phosphorylation of Serine 14 and AMP Phosphorylation of Serine 14 and ATParrow_forwardExplain the purpose of the glycerol 3 phosphate shuttle (Don’t worry about the mechanism, just the purpose of the shuttle. Just one sentence here!). Suppose a cell could only rely on the glycerol 3 phosphate shuttle and not the malate-aspartate shuttle, how would that affect the amount of ATP that could be generated from the complete oxidation of 1 molecule of glucose in that cell? How would this change the amount of ATP that could be generated from the complete oxidation of 1 molecule of palmitate in this cell?arrow_forwardThe glycolytic enzyme glucokinase (in human liver cells) catalyzes the conversion of: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate into 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate (producing NADH) phosphoenolpyruvate into pyruvate (producing ATP) fructose-6-phosphate into fructose-1,6-bisphosphate (consuming ATP) glucose into glucose-6-phosphate (consuming ATP) 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate into 3-phosphoglycerate (producing ATP)arrow_forward
- In the cell, ATP can be enzymatically produced from glycerol-3-phosphate (glycerol-3-P) and PO,. This enczymatic synthesis utilizes selected enzymes from glycolysis. Glycerol-3-P+ dihydroxyacetone phosphate-→ x→Y+3-phosphoglycerate What is compound X? Note that the cofactors, co-substrates, and details for the use of PO, for this set of reactions have been omitted, You should know them! O Phosphoenolpyruvate O Pyruvate o 2-Phosphoglycerate O Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate O Oxaloacetatearrow_forwardA mutation has occurred that results in phosphofructokinase not being able to bind ATP in its allosteric site. What impact will this mutation have on the production of ATP in the cell? Select one: a. If no ATP can bind to the allosteric site, then phosphofructokinase will not be able to add the phosphate to fructose-6-phosphate to make fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and glycolysis will not work. So no pyruvate, not cellular respiration. b. If ATP cannot bind to the allosteric site, phosphofructokinase will not be activated to make more ATP by substrate-level phosphorylation. c. No impact on the production but will not be able to effectively shut off over production of ATP with feedback inhibition.arrow_forwardOne condition is ketoacidosis (low blood pH) which is a potentially life-threatening state, most commonly experienced by diabetics. Ketoacidosis, however, is not typically an issue for healthy people who are following a ketogenic diet. What is the difference between ketoacidosis and ketosis? Why do diabetics sometimes develop ketoacidosis, while healthy people rarely do? Healthy people are well equipped to survive on a ketogenic diet. Why is it important that humans evolved to have the ability to survive without carbohydrate nutrients?arrow_forward
- Corticosteroids (a type of hormone), and Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs) are non-narcotic pain relievers. Both medications are prescribed to reduce inflammation in the body. NSAIDs such as aspirin, acetaminophen, and ibuprofen are able to reduce pain, fever, and inflammation by blocking the action of the cyclooxygenase enzyme (COX) that catalyzes the conversion of arachidonic acid into prostaglandins. Common corticosteroids include prednisone, cortisone, and methylprednisolone. Choose one of these three corticosteroids. Do some internet research on the corticosteroid that you choose and then explain how the drug works to reduce inflammation.arrow_forwardThe following reaction would most likely be catalyzed by an enzyme of which class? sucrose + H2O → glucose + fructosearrow_forwardIn the regulation of glycogen phosphorylase, which of the following statements is true? The inactive T form becomes activated when it gets dephosphorylated. The active R form is inhibited by glucose. Phosphoprotein phosphatase catalyzes the attachment of a phosphate group to a Ser residue in glycogen phosphorylase. The allosteric modulator glucose-6-phosphate promotes the conformation change from inactive T state to active R state.arrow_forward
- The reaction in which glucose 6-phosphate (G6P) is converted to fructose 6-phosphate (F6P) is an example of an isomerization reaction. Notice that both molecules have the molecular formula C6H13O9P. The isomerization is catalyzed by glucose 6-phosphate isomerase. This is a reversible reaction in cells, with a moderately negative ΔG, but a very high activation energy. If you have a flask that contains a solution containing cellular concentrations of G6P and F6P, but no enzyme, how will the concentration of each molecule change over time?arrow_forwardIf sucrase breaks down sucrose and a mystery sugar inhibits sucrase from breaking down sucrose allowing sucrose to mobilize in the body, what kind of inhibition is the mystery sugar? i.e. uncompetitive, competitive, non-competitivearrow_forwardYou are studying energy production and metabolic activities of prostate cancer cells in the lab. You compare energy metabolism in these cancer cells with normal cells. Which of the following would you observe? Select all that apply Oxidative phosphorylation is reduced in cancer cells compared to normal cells Glycolysis is reduced in cancer cells compared to normal cells Oxidative phosphorylation is enhanced in cancer cells compared to normal cells Glycolysis is enhanced in cancer cells compared to normal cellsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education