
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
HOW DO I FIGURE OUT THE FIFO, LIFO AND AVERAGE-COST . FOR THE ENDING INVENTORY AND THE COST OF GOODS SOLD?
Vaughn Distribution markets CDs of the performing artist Unique. At the beginning of October, Vaughn had in beginning inventory 2,000 of Unique’s CDs with a unit cost of $5. During October, Vaughn made the following purchases of Unique’s CDs.
| Oct. 3 | 2,500 | @ | $6 | Oct. 19 | 3,000 | @ | $8 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oct. 9 | 3,500 | @ | $7 | Oct. 25 | 4,000 | @ | $9 |
During October, 10,850 units were sold. Vaughn uses a periodic inventory system.
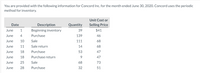
Transcribed Image Text:You are provided with the following information for Concord Inc. for the month ended June 30, 2020. Concord uses the periodic
method for inventory.
Unit Cost or
Date
Description
Quantity
Selling Price
June
1
Beginning inventory
39
$41
June
Purchase
139
46
June
10
Sale
111
68
June
11
Sale return
14
68
June
18
Purchase
53
47
June
18
Purchase return
47
June
25
Sale
68
73
June
28
Purchase
32
51
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Glee Distribution markets CDs of the performing artist Unique. At the beginning of October, Glee had in beginning inventory 2,000 of Unique's CDs with a unit cost of $7. During October, Glee made the following purchases of Unique's CDs. Oct. 3 2,500 @ $8 Oct. 19 3,000 @ $10 Oct. 9 3,500 @ $9 Oct. 25 4,000 @ $11 During October, 10,900 units were sold. Glee uses a periodic inventory system. v (a) Determine the cost of goods available for sale. Cost of goods available for sale Open Show Work Click if you would like to Show Work for this question: LINK TO TEXTarrow_forwardNov. 5 Purchased 600 units of product at a cost of $10 per unit. Terms of the sale are 2/10, n/60; the invoice is dated November 5. Nov. 7 Returned 25 defective units from the November 5 purchase and received full credit. Nov. 15 Paid the amount due from the November 5 purchase, less the return on November 7. Prepare journal entries to record each of the merchandising transactions assuming that the periodic inventory system is used Please don't provide answer in image format thank youarrow_forwardThe following three identical units of Item JC07 are purchased during April: Item Beta Units Cost April 2 Purchase $264 April 15 Purchase 268 April 20 Purchase 272 Total $804 Average cost per unit $268 ($804 ÷ 3 units) Assume that one unit is sold on April 27 for $367. Determine the gross profit for April and ending inventory on April 30 using the (a) first-in, first-out (FIFO); (b) last-in, first-out (LIFO); and (c) weighted average cost method. Gross Profit Ending Inventory a. First-in, first-out (FIFO) b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) c. Weighted average cost 3.arrow_forward
- Please help determine the image attachedarrow_forwardAssume that J R Toys store purchased and sold a line of dolls during December as follows: (Click the icon to view the transactions.) JR Toys uses the perpetual inventory system. More info Dec. 1 Beginning merchandise inventory 8 Sale 14 Purchase 21 Sale 13 7 14 13 units @ $ 8 each units @ $18 each units @ $ 16 each units @ $ 18 each. - X Requirements 1. Compute the cost of goods sold, cost of ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit using the FIFO inventory costing method. 2. Compute the cost of goods sold, cost of ending merchandise inventory, and gross profit using the LIFO inventory costing method. 3. Which method results in a higher cost of goods sold? 4. Which method results in a higher cost of ending merchandise inventory? 5. Which method results in a higher gross profit?arrow_forwardRequired information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Trey Monson starts a merchandising business on December 1 and enters into the following three inventory purchases. Monson uses a perpetual inventory system. Also, on December 15, Monson sells 15 units for $34 each. Purchases on December 7 Purchases on December 14 10 units @ $20.00 cost 20 units @ $26.00 cost Purchases on December 21 15 units @ $28.00 cost Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on the LIFO method.arrow_forward
- Required information Use the following information for the Quick Study below. Trey Monson starts a merchandising business on December 1 and enters into three inventory purchases: Purchases on December 7 15 units @ $18.00 cost Purchases on December 14 29 units @ $27.00 cost Purchases on December 21 25 units @ $32.00 cost QS 5-13 Periodic: Inventory costing with specific identification LO P1 Required:Monson sells 25 units for $45 each on December 15. Of the units sold, 12 are from the December 7 purchase and 13 are from the December 14 purchase and assume the periodic inventory system is used. Determine the costs assigned to ending inventory when costs are assigned based on specific identification.arrow_forwardMary's Boards sells a snowboard, Xpert, that is popular with snowboard enthusiasts. Information relating to Mary's purchases of Xpert snowboards during September is shown below. During the same month, 119Xpertsnowboards were sold. Mary's uses a periodic inventory system. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost Sept 1 Inventory 25 $95 $2,375 Sept. 12 Purchases 45 100 4.500 Sept 19 Purchases 20 102 2,040 Sept. 26 Purchases 50 103 5.150 Totals 140 $14.065 (a) Compute the ending inventory at September 30 and cost of goods sold using the FIFO and LIFO methods. FIFO LIFO The ending inventory at September 30 Cost of goods soldarrow_forwardi need the answer quicklyarrow_forward
- The Shirt Shop had the following transactions for T-shirts for Year 1, its first year of operations: Jan. 20 Apr. 21 July 25 Sept. 19 Purchased Purchased Purchased Purchased Required A During the year, The Shirt Shop sold 810 T-shirts for $20 each. Required a. Compute the amount of ending inventory The Shirt Shop would report on the balance sheet, assuming the following cost flow assumptions: (1) FIFO, (2) LIFO, and (3) weighted average. b. Compute the difference in gross margin between the FIFO and LIFO cost flow assumptions. 400 units 200 units 280 units 90 units Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required B Ending inventory @ @ FIFO $8 = $3,200 $10 = 2,000 $13 = 3,640 $15 = 1,350 Compute the amount of ending inventory The Shirt Shop would report on the balance sheet, assuming the following cost flow assumptions: (1) FIFO, (2) LIFO, and (3) weighted average. (Round intermediate calculations to 2 decimal places and final answers to nearest whole dollar…arrow_forwardREI sells snowboards. Assume the following information relates to REI's purchases of snowboards during September. During the same month, 109 snowboards were sold. REI uses a periodic inventory system. Date Explanation Units Unit Cost Total Cost Sept. 1 Inventory 14 $102 $1,428 Sept. 12 Purchases 48 105 5,040 Sept. 19 Purchases 50 106 5,300 Sept. 26 Purchases 23 107 2,461 Totals 135 $14,229 (a) Your answer is correct. Compute the ending inventory at September 30 using FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, e.g. 125.153 and final answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) (b) Ending inventory at September 30 $ eTextbook and Media FIFO 2779 $ LIFO 2688 $ AVERAGE-COST 2740 Attempts: 2 of 3 used Compute the cost of goods sold for the month using the FIFO, LIFO, and average-cost methods. (Round average cost per unit to 3 decimal places, e.g. 125.153 and final answers to O decimal places, e.g. 125.) Cost of goods sold $ FIFO $ LIFO AVERAGE-COST $arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education