
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
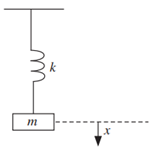
- Figure below shows a body of mass m attached to a spring of stiffness k. Find the differential equation for the displacement, x
Show that x=Acos(wt)+Bsin(wt) where A, B are constants and w= √k/m
Transcribed Image Text:w
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A point with mass m is a distance d from the end of a bar, which we'll call x = 0. The mass-per-length > of the bar is low at one end and steadily increases toward the other end at x = L like λ = bx. m = 0.9 kg d = 12 cm L = 56 cm b = 2.6 × 1012 kg/m² Find F [N] = L d x=0arrow_forwardA spring with a spring constant of k = 192 N/m is initially compressed by a block a distance d = 0.23 m. The block is on a horizontal surface with coefficient of kinetic friction μk, static friction μs, and has a mass of m = 7 kg. How large would the coefficient of static friction μs need to be to keep the block from moving? Recall that to keep the block from moving, the acceleration is zero. Assuming the block has just begun to move and the coefficient of kinetic friction is μk = 0.2, what is the block's acceleration in meters per square second?arrow_forwardAn ideal spring hangs vertically. When a 359- g object is hung from the bottom end, and lowered gently, the spring stretches 6.23cm. How much would the spring have stretched, in cm, if the mass of the object had been 601 g instead ?arrow_forward
- Problem 2: A student pushes a baseball of m = 0.18 kg down onto the top of a vertical spring that has its lower end fixed to a table, compressing the spring a distance of d = 0.14 meters from its equilibrium length. The spring constant of the spring is k = 740 N/m. Let the gravitational potential energy be zero at the position of the baseball in the compressed spring. Randomized Variables m = 0.18 kg k = 740 N/m d = 0.14 marrow_forwardJum The mass of the block depicted in the image is 1.60 kg. The spring has a spring constant of 76.9 N/m. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the floor is 0.726. Assume that the spring makes no contact with the floor and therefore friction only acts on the block. How far must the block and spring assembly be compressed to just barely overcome the force of static friction acting on the block? Report your result in meters.arrow_forwardThe graph shows the measured force for a spring as it is compressed through various displacements.arrow_forward
- A 25.0 cm long spring is hung vertically from a ceiling and stretches to 30.5 cm when a 6.50 kg mass is hung from its free end. HINT (a) Find the spring constant (in N/m). N/m (b) Find the length of the spring (in cm) if the 6.50 kg weight is replaced with a 165 N weight. cmarrow_forwardI need help solving the equations symbolically and I don't know how to get the m value for the first part.arrow_forwardThree forces act on a statue. Force F⃗ 1F→1 (magnitude 45.0 NN) points in the +x-direction, Force F⃗ 2F→2 (magnitude 105 NN) points in the +y-direction, and force F⃗ 3F→3 (magnitude 235 NN) is at an angle of 36.9∘∘ from the -x-direction and 53.1∘∘ from the +y-direction. counterclockwise from the +x-direction. Find the x- and y-components of the net external force F⃗ F→ on the statue. Find the magnitude and direction of the net external force exerted on the statue.arrow_forward
- Two blocks of masses m, = 4.0 kg and mg = 8.0 kg are connected with a string that passes over a very light pulley (Figure 1). Friction in the pulley can be ignored. Block 1 is resting on a rough table and block 2 is hanging over the edge. The coefficient of friction between the block 1 and the table is 0.70 (assume static and kinetic friction have the same value). Block 1 is also connected to a spring with a constant 300 N/m. In the initial state, the spring is relaxed as a person is holding block 2, but the string is still taut. When block 2 is released, it moves down for a distanced until it stops (the final state). Figure 1 of 1arrow_forwardAn engineer is designing a spring to be placed at the bottom of an elevator shaft. If the elevator cable should break when the elevator is at a height of 103m above the top of the spring, calculate the value that the spring stiffness constant should have so that passengers undergo an acceleration of no more than 3.9g when brought to rest. Let 924kg be the total mass of the elevator and passengers.arrow_forwardThe tension in a ligament in the human knee is approximately proportional to the extension of the ligament, if the extension is not too large. If a particular ligament has an effective spring constant of 152 N/mm as it is stretched, what is the tension in this ligament when it is stretched by 0.800 cm?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON