
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The graph shows the measured force for a spring as it is compressed through various displacements.
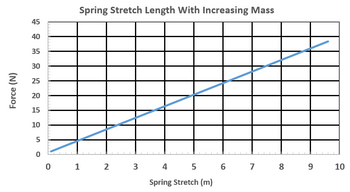
Transcribed Image Text:Force (N)
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
Spring Stretch Length With Increasing Mass
0
0 1 2
3
4
5
6 7
8 9
10
Spring Stretch (m)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- SSN 11. When a 0.34-kg block is suspended on a vertical spring, it causes it to stretch 3.20 cm. If the block is now pulled 7.80 cm below its equilibrium position and released, what is the speed of the block when it is 1.40 cm above the equilibrium position? m/s 160 ssf60 ssf60 ss of the f60 ssf60* 0 ssf60 ss 09J$$arrow_forwardA 0.81-kg block is hung from and stretches a spring that is attached to the ceiling. A second block is attached to the first one, and the amount that the spring stretches from its unstretched length triples. What is the mass of the second block? Unstretched length m1 X2 = 3x1 m1 m2 Number Unitsarrow_forwardThe springs of a pickup truck act like a single spring with a force constant of k = 1.15 × 105 N/m. Part (a) How many centimeters will the truck be lowered by its maximum load of 960 kg? Part (b) If the pickup truck has four identical springs, what is the force constant of each, in newtons per meter? Assume the allowed compression is the same as in part (a).arrow_forward
- An automobile having a mass of 1000 kg is driven into a brick wall in a safety test. The bumper behaves like a spring with constant 4.75 106 N/m and is compressed 2.70 cm as the car is brought to rest. What was the speed of the car before impact, assuming no energy is lost in the collision with the wall? m/sarrow_forwardAn object has a mass of 0.5 kg is placed in front of a compressed spring. When the spring was released, the 0.5kg object collides with another object with mass 1.5kg and they move together as one unit. Find the velocity of boxes if the spring constant is 40N/m, and spring. was initially compressed by 20cm. Answer with text and/or attachments:arrow_forward(b) Neglecting all resistive forces, determine the spring constant. N/m (c) Neglecting all resistive forces, find the speed of the projectile as it moves through the equilibrium position of the spring (where x = 0), as shown in Figure (b). m/sarrow_forward
- The tension in a ligament in the human knee is approximately proportional to the extension of the ligament, if the extension is not too large. If a particular ligament has an effective spring constant of 152 N/mm as it is stretched, what is the tension in this ligament when it is stretched by 0.800 cm?arrow_forwardProblem 6: A child's toy consists of a m = 42 g monkey suspended from a spring of negligible mass and spring constant k. When the toy monkey is first hung on the spring and the system reaches equilibrium, the spring has stretched a distance of x = 16.1 cm, as shown in the diagram. This toy is so adorable you pull the monkey down an additional d = 4.1 cm from equilibrium and release it from rest, and smile with delight as it bounces playfully up and down. Unstretched Position Equilibrium Stretched Position Part (a) Using the given information, determine the spring constant, k, in Newtons per meter, of the spring. Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. k = 2.557 Part (b) Select the free-body diagram that best represents the forces acting on the monkey as you are pulling it down, immediately before you let go. SchematicChoice : F. AF, spring spring spring F. F. F gravity .F applied applied F, A F spring spring F. Fopplied spring F E. gravity F. gravit gravity applied…arrow_forwardA mass of 1.2kg is attached to a spring with a constant 12N/m. it is then displaced to a maximum point of 2m. How much time does it take for the block to travel to the point x=1.5m? answer in secondsarrow_forward
- A mass resting on a horizontal, frictionless surface is attached to one end of a spring; the other end is fixed to a wall. It takes 3.1 J of work to compress the spring by 0.15 m . If the spring is compressed, and the mass is released from rest, it experiences a maximum acceleration of 12 m/s2. Find the value of the spring constant. Find the value of the mass.arrow_forwardA mass of 0.3 kg hangs motionless from a vertical spring whose length is 0.75 m and whose unstretched length is 0.55 m. Next the mass is pulled down to where the spring has a length of 1.05 m and given an initial speed upwards of 1.7 m/s. What is the maximum length of the spring during the motion that follows? maximum length= Hint: the conceptually-simplest approach is to track the changes in kinetic, spring-potential, and gravitational-potential energies; the mathematically-simplest approach is to observe that the sole effect of gravitation is to lower the spring's equilibrium position, then track just the kinetic and spring-potential (relative to the lower equilibrium) energies.arrow_forwardA 2.8 kg box is sliding along a frictionless horizontal surface with a speed of 1.8 m/s when it encounters a spring, (a) Determine the force constant (in N/m) of the spring, if the box compresses the spring 7.5 cm before coming to rest. N/m (b) Determine the initial speed (in m/s) the box would need in order to compress the spring by 1.4 cm. m/s Additional Materialsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON