
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
This question asks you to look at the details of energy transformation in the Electron Transport Chain of cellular respiration , through ATP synthesis.
Your starting point will be Figure 6.10 in your textbook (page 99). The figure is titled"How electron transport drives ATP synthase machines".
Here is your task:
Describe every energy transformation you can identify in the image! State what type of energy is being converted. This might seem like a very esoteric question, but here are four VER
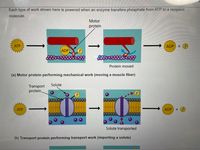
Transcribed Image Text:Each type of work shown here is powered when an enzyme transfers phosphate from ATP to a recipient
molecule.
Motor
protein
ATP
ADP + P
ADP
Protein moved
(a) Motor protein performing mechanical work (moving a muscle fiber)
Solute
Transport
protein.
АТР
ADP +P
Solute transported
(b) Transport protein performing transport work (importing a solute)
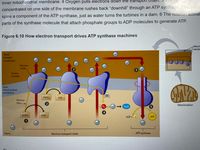
Transcribed Image Text:inner mitochondrial membrane. 4 Oxygen pulls electrons down the transport
concentrated on one side of the membrane rushes back "downhill" through an ATP synthase. This action
spins a component of the ATP synthase, just as water turns the turbines in a dam. 6 The rotation activat
parts of the synthase molecule that attach phosphate groups to ADP molecules to generate ATP.
Figure 6.10 How electron transport drives ATP synthase machines
Mitoch
memb
Ht
Space
between
membranes
H*
H
H*
Ht
H*
Electron
H*
carrier
H*
H*
Protein
complex
Inner
mitochondrial
membrane
FADH,
FAD
Electron
flow
2
Mitochondrion
O,
H*
H20
NADH
NAD*
ADP + P
АТР
1
H*
H*
H*
Ht
Matrix
Electron transport chain
ATP synthase
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For each step of the citric acid cycle, name the enzyme responsible for the chemical transformation that occurs and classify the enzyme type: Step 1. Step 2. Step 3. Step 4. Step 5. Step 6. Step 7. Step 8. i. oxidoreductase (oxidases, reductases, dehydrogenases) ii. transferase (transaminases, kinses) iii. hydrolase (lipases, proteases, nucleases, carbohydrases, phosphateses) iv. lyase (dehydratase, decarboxylase, deaminase, hydratase) v. isomerase (racemases, mutases) vi. ligase (synthetases, carboxylaces) Enzyme Name Enzyme Typearrow_forwardCyanide is a rapidly acting, potentially deadly chemical that can exist in various forms. If accidentally ingested or inhaled, cyanide can cause rapid death by binding to complex IV (cytochrome oxidase) of the electron transport chain in the mitochondria. A.What is the mechanism by which cyanide stops cellular respiration? Be specific. B.Does cyanide cause an effect at the beginning or the end of the cellular respiration pathway? C.Does this make a difference on the effect that this chemical can have on our cells? Why? D.How does cyanide’s course of action affect the remainder of the cellular respiration pathway? E.If a person accidentally swallows cyanide, mention a potential treatment that is currently available. What is the mechanism of action of this treatment? Be specific. Please answer completely will give rating surely All questions answers neededarrow_forwardIodoacetate reacts irreversibly with the free -SH groups of cysteine residues in proteins. List which Calvin cycle enzyme(s) you would predict to be inhibited by iodoacetate, and briefly explain whyarrow_forward
- During cellular respiration, approximately 34 ATP are produced from one molecule of glucose. a. How Many ATP are made during glycolysis? b. How many ATP/GTP are made during the Citric Acid Cycle? c. How many are made during oxidative phosphorylation? d. If you recall electrons from FADH2 pump less proton than electrons from NADH, This is because Complex II does not pump electrons. Because of this FADH2 leads to the production of less ATP, 1 FADH2 produces about 1.5 ATPs Given this value how many ATP are NADH electrons worth? Please answer all parts with good explanationarrow_forwardThe reaction pictured is an oxidation-reduction reaction in the citric acid cycle in which the energy-carrier molecule NADH is generated. Identify which molecule in the reaction will be oxidized and which molecule will be reduced. Place a single answer choice in each box. COO- HO-C-H H-C-H COO- Malate NAD+ NADH + H+ Oxidized malate oxaloacetate COO- H-C-H ī COO- Oxaloacetate Reduced NADH NAD+arrow_forwardA new ATP-producing protein is discovered that couples ATP production to the oxidation of NADPH by oxidative phosphorylation. Assume that the value of ΔGo for ATP synthesis is 30 kJ•mol−1. If this protein only produces 1 molecule of ATP per reaction that consumes one NADPH: a. How much free energy is wasted, under standard conditions?b. How many more ATP molecules could be created by a perfectly efficient electron transport chain from one NADPH?arrow_forward
- Below is an image showing how cellular respiration is regulated. Imagine someone ingested a toxin that prevents pyruvate from entering the mitochondria. Which of the following statements is true? Inhibits ATP Glucose GLYCOLYSIS Copyright 2018 Pearson Canada Inc. Fructose 6-phosphate Phosphofructokinase Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate Pyruvate Acetyl COA CITRIC ACID CYCLE Oxidative phosphorylation AMP I Stimulates Inhibits Citrate The amount of citrate in the cell would decrease, leading to a decrease in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would increase, leading to a decrease in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would decrease, leading to an increase in the activity of phosphofructokinse. The amount of citrate in the cell would increase, leading to an increase in the activity of phosphofructokinse.arrow_forwardKinases catalyze the transfer of a phosphate group from a phosphate donor such as adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to a substrate. A well‑known kinase is hexokinase. Hexokinase catalyzes the first step of the glycolysis cycle, and converts glucose to glucose‑6‑phosphate. The reaction of glucose with ATP is shown. The enzyme‑bound base is abbreviated as :B−, and ATP is abbreviated as a diphosphate bonded to adenosine monophosphate (AMP).arrow_forwardQuestion 1: The 4 kinase steps in glycolysis are catalyzed by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, phosphoglycerate kinase, and pyruvate kinase. Write each of these four reactions, including all participants. i. ii. iii. iv.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education