
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
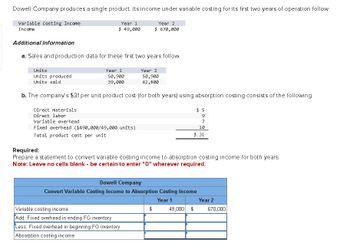
Transcribed Image Text:Dowell Company produces a single product. Its income under variable costing for its first two years of operation follow.
Variable Costing Income
Income
Year 1
$ 49,000
Year 2
$ 670,000
Additional Information
a. Sales and production data for these first two years follow.
Units
Units produced
Units sold
Year 1
50,900
39,000
Year 2
50,900
62,800
b. The company's $31 per unit product cost (for both years) using absorption costing consists of the following.
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable overhead
Fixed overhead ($490,000/49,000 units)
$ 5
9
7
10
$ 31
Total product cost per unit
Required:
Prepare a statement to convert variable costing income to absorption costing income for both years.
Note: Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.
Dowell Company
Convert Variable Costing Income to Absorption Costing Income
Variable costing income
Add: Fixed overhead in ending FG inventory
Less: Fixed overhead in beginning FG inventory
Absorption costing income
Year 1
Year 2
$
49,000 $
670,000
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A company has a net income of $918,000 based on variable costing method. Beginning and ending inventories were 56,800 units and 55,600 units. Assume the fixed overhead per unit was $2.15 for both the beginning and ending inventory. What will be the net income under absorption costing?arrow_forwardMunabhaiarrow_forwardPlease do not give image formatarrow_forward
- Assume the following information for a company that produced 10,000 units and sold 9,000 units during its first year of operations: Selling price Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Sales commission Fixed manufacturing overhead Per Unit $ 200 $ 72 $ 50 $ 10 $8 Multiple Choice $ 287,000 Which of the following choices explains the relationship between the absorption costing net operating income and the variable costing net operating income? The absorption costing net operating income will be lower than the variable costing net operating income by $28,700. The absorption costing net operating income will be lower than the variable costing net operating income by $100,700. Per Year The absorption costing net operating income will be higher than the variable costing net operating income by $28,700.arrow_forwardDomesticarrow_forwardDuring Heaton Company's first two years of operations, it reported absorption costing net operating income as follows: Sales (@ $62 per unit) Year 1 $ 1,178,000 Gross margin 513,000 Selling and administrative 303,000 expenses* Net operating $ income Cost of goods sold (@$35 665,000 1,015,000 per unit) Year 2 210,000 $ 1,798,000 783,000 333,000 $ 450,000 *$3 per unit variable; $246,000 fixed each year. The company's $35 unit product cost is computed as follows: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Fixed manufacturing overhead ($360,000 ÷ 24,000 units) Absorption costing unit product cost $9 9 2 15 $ 35arrow_forward
- Dowell Company produces a single product. Its Income under variable costing for its first two years of operation follow. Variable Costing Income Income Units Units produced Units sold Additional Information a. Sales and production data for these first two years follow. Year 1 $ 43,000 Year 1 44,300 33,000 Direct materials Direct labor Variable overhead Fixed overhead ($430,000/43,000 units) Total product cost per unit Variable costing income Year 2 b. The company's $32 per unit product cost (for both years) using absorption costing consists of the following. Absorption costing income 44,300 55,600 Year 2 $ 610,000 Required: Prepare a statement to convert variable costing income to absorption costing income for both years. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.) $6 Dowell Company Convert Variable Costing Income to Absorption Costing Income Year 1 $ 9 7 10 $32 43,000 $ Year 2 610,000arrow_forward1. Assume that the company uses absorption costing A) compute the unit product cost B) prepare an income statement for a year(do not leave empty spaces;input a 0 whatever it is required) 2. Assume the company uses variable costing A) compute the unit product cost B) prepare an income statmement(input 0 on empty spaces)arrow_forwardDowell Company produces a single product. Its income under variable costing for its first two years of operation follow. Variable Costing Income Year 1 Year 2 Income $ 50,000 $ 680,000 Additional Information Sales and production data for these first two years follow. Units Year 1 Year 2 Units produced 52,000 52,000 Units sold 40,000 64,000 The company’s $33 per unit product cost (for both years) using absorption costing consists of the following. Direct materials $ 6 Direct labor 9 Variable overhead 8 Fixed overhead ($500,000/50,000 units) 10 Total product cost per unit $ 33 Required:Prepare a statement to convert variable costing income to absorption costing income for both years. (Leave no cells blank - be certain to enter "0" wherever required.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education