
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
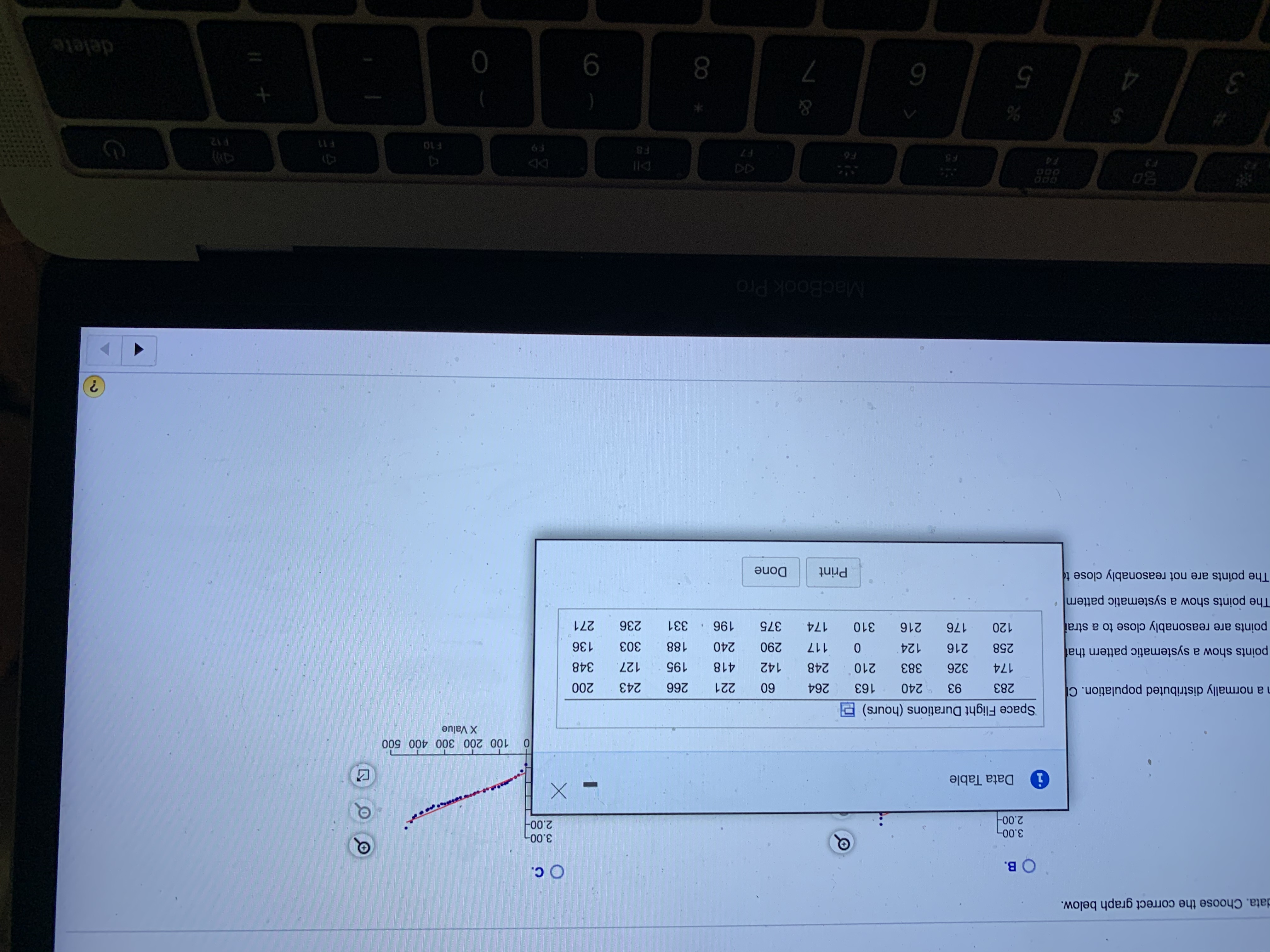
Transcribed Image Text:### Data Table Overview
**Title:** Space Flight Durations (hours)
This table displays a series of durations representing space flight hours. The data set consists of multiple rows and columns with various numeric values.
**Data Values:**
- Row 1: 283, 93, 240, 163, 264, 60, 221, 266, 243, 200
- Row 2: 174, 326, 383, 210, 248, 142, 418, 195, 227, 348
- Row 3: 258, 216, 124, 0, 117, 290, 240, 188, 303, 136
- Row 4: 120, 176, 216, 310, 174, 375, 196, 331, 236, 271
### Graph Analysis
The graph visible in the image seems to display plotted points against an axis labeled "X Value." Various graph options (A, B, C) suggest a choice between potential visual representations of the data.
- **X-Axis:** Labeled as “X Value” and possibly depicting a sequence of numbers ranging approximately from 0 to 500.
- **Y-Axis:** No specific details visible, but potential values range around 2.00 to 3.00 as suggested by the labels in C.
- **Data Trend:** The graph in option C appears to show an upward trend, likely depicting how the space flight durations increase as the X value increases.
### Conclusion
Such a data set and graph may be used to analyze the distribution, variability, and trends in space flight durations over time or various conditions. The choice of graph type is essential to appropriately convey the right information or answering specific analytical questions regarding the data set.

Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Normal Quantile Plots
Normal quantile plots are used to determine if data points come from a normally distributed population. Below are three graphs (A, B, C), each plotting data points on an X-Y axis. The y-axis represents the quantiles of the data, while the x-axis represents the ordered data values.
#### Graph Descriptions:
- **Graph A**
- X-axis: Ranges from 0 to 500 (X Value)
- Y-axis: Ranges from -3 to 3
- The data points appear to follow a curve, deviating from a straight-line pattern.
- **Graph B**
- X-axis: Ranges from 0 to 500 (X Value)
- Y-axis: Ranges from -3 to 3
- Data points form a straight line, indicating the data may be normally distributed.
- **Graph C**
- X-axis: Ranges from 0 to 500 (X Value)
- Y-axis: Ranges from -3 to 3
- The points show a slight systematic pattern that deviates from a straight line.
#### Question and Answer Choices:
Determine whether the data come from a normally distributed population. Choose the correct answer below.
- **A.** The distribution is normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern.
- **B.** The distribution is normal. The points are reasonably close to a straight line and do not show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern.
- **C.** The distribution is not normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern.
- **D.** The distribution is not normal. The points are not reasonably close to a straight line.
**Correct Answer:** (Not given; requires interpretation of the plots.)
---
This educational content is intended to guide students in understanding how normal quantile plots can be used to assess the normality of data distributions. Students are encouraged to examine the alignment of data points with a straight line to draw conclusions about normality.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- NEED HELP WITH: E, F, Garrow_forwardFind the margin of error for the given values of c, s, and n. cequals=0.99 sequals=3.9 nequals=15 view the t-distribution table. The margin of error is(Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwarda. Find X23,10. Draw the distribution and identify the x²-value in the distribution. b. Find F24,30,.05. Draw the distribution and identify the F-value in the distribution. c. Find t18,005. Draw the distribution and identify the t-value in the distribution.arrow_forward
- need help with B, C, Darrow_forwardUse a calculator or computer software to generate a normal quantile plot for the data in the accompanying table. Then determine whether the data come from a normally distributed population. Click the icon to view the data set. Generate a normal quantile plot for the data. Choose the correct graph below. OA. 3.00 2.00- 1.00- 0.00- -1.00- Q Q -2.00 -3.00 100 200 300 400 500 0 X Value OB. 3.00 2.00- 1.00- 0.00- -1.00- -2.00- -3.00- ... 0 100 200 300 400 500 X Value Q Q G O C. 3.00 2.00 P 1.00 0.00- -1.00- -2.00- 0 100 200 300 400 500 X Value -3.00+ Determine whether the data come from a normally distributed population. Choose the correct answer below. OA. The distribution is not normal. The points are not reasonably close to a straight line. OB. The distribution is normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern. OC. The distribution is not normal. The points show a systematic pattern that is not a straight-line pattern. OD. The distribution is normal. The…arrow_forwardSelect the correct answer and write the appropriate letter in the space provided _____ 1. A grouping of data into classes giving the number of observations in each class is called a(an) a bar chart. b. frequency distribution. c. pie chart. d. cumulative frequency distribution. ______ 2. The distance between consecutive lower class limits is called the a. class interval. b. frequency distribution. c. class midpoint. d. class frequency. ______ 3. The class midpoint is a. equal to the number of observations. b. found by adding the lower class limits of two consecutive classes and dividing by 2. c. equal to the class interval. d. all of the above. ______ 4. The number of observations in a particular class is called the a. class interval. b. class frequency. c. frequency distribution. d. none of the above. ______ 5. A bar chart is used most often when a. you want to show frequencies as compared to total observations. b. you want to show…arrow_forward
- Assume that a randomly selected subject is given a bone density test. Those test scores are normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Draw a graph and find the probability of a bone density test score between 1.83 and 1.83. Sketch the region. Choose the correct graph below. O A. -1.83 1.83 B. -1.83 *** 1.83 O C. -1.83 1.83 O D. -1.83 1.83arrow_forward10. Find the mean of the following data: l2, 10,15, 10, 16, 12,10,15, 15, a. 13 b. 12.5 с. 15 d. 12.8 11. Find the mode of the following data: 20, 14, 12, 14, 26, 16, 18, 19, 1 a. 14 b. 17 c. 26 d. 16 12. Find the mean of the following data: 0, 5, 2, 4, o, 5, 0, 3, 0, 5, 0, 3 a. 0 b. 2.25 c. 2.5 d. 3.86 13. Find the mean of the following data: 20, 24, 24, 24, 22, 22, 24, 22, 23, 25 a. 23.5 b. 23 c. 24 d. 16 14. A standard normal distribution has which of the following properties? a. The mean is equal to the standard deviation. b. The mean is equal to 0 and the variance is equal to 1. c. The mean is equal to the variance. d. The mean and the variance both equal 1. 15. Let z be a normal random variable with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Determine P(z 1.4). a. 0.9192 b. 0.4192 c. O because P(z = 1.4) = 0. d. 0,0808 16. In which of the following continuous distributions are extreme values most likely (within its range) ? a. Norma1 b. Extreme values are rare for all continuous…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman