
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
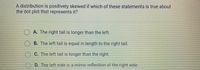
Transcribed Image Text:### Understanding Positively Skewed Distributions
A positively skewed distribution occurs when the data values tend to gather around the lower end of the scale, with the longer tail extending towards the higher end. When interpreting dot plots for such distributions, understanding the characteristics of their tails is crucial.
Consider the following question regarding positively skewed distributions:
**Question:**
A distribution is positively skewed if which of these statements is true about the dot plot that represents it?
- **A.** The right tail is longer than the left.
- **B.** The left tail is equal in length to the right tail.
- **C.** The left tail is longer than the right.
- **D.** The left side is a mirror reflection of the right side.
**Correct Answer:**
- **A.** The right tail is longer than the left.
### Explanation:
In a positively skewed distribution, where more lower values are clustered, the data's "tail" on the right side (higher values) is longer. This indicates that while most data points fall within the lower ranges, a few exceptionally high values stretch out the tail on the right side. Hence, for a positively skewed dot plot, look for a longer right tail.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Match each word to its definition. 1. Pi A. A line passing from side-to-side through the center of a circle. 2. Semi-Circle B. Pi times diameter or 2 times pi times radius is.. C. The interior region of an enclosed figure measured in square feet. 3. Radius 4. Quarter-Circle D. Circumference divided by diameter equals 5. Area E. Half a Circle. F. A straight-line from the center of a circle to the edge. 6. Diameter 7. Circumference G. One-fourth of a circle.arrow_forwardL0. Use the listing method to express the set S = ((1, 3] × {2, 4}) nZ². %3Darrow_forwardDetermine if the two triangles are similar or not. d. 44 D B R 18 58.5 211.2 202.4 W Y 90arrow_forward
- W4. For a trapezoid, the midsegment is one-half of the opposing leg. the sum of the bases. the same as the smallest leg. O the square of the largest leg. P Type here to search enov 近arrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls show all work. Pls do both of the asked questions pls i BEG.arrow_forwardI need help on number 3arrow_forward
- a. State whether or not the following pair of figures is similar? a. Explain your reasoning. 24 20 16 12 30 20arrow_forwardIn the parallelogram below, if m21 = m22 = 3x what is the missing value for x? to 80 45 120 60 earch F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 F8 F9 F10 $ % 4. 6 8. # 3arrow_forwardFind a5 when a = 13 and d = 5arrow_forward
- 17 Mrs. Joplin is the teacher sponsor for her school's book club. She recorded the number of books each book club member read over the summer in the dot plot below. (Note: Each dot represents one student.) Book Club Members 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Number of Books Read What is the ratio of the number of students who read four books to the number of students who read eight books? OA. 2 to 5 В. 5 to 2 С. 1 to 2 D. 2 to 1arrow_forwardsolvearrow_forwardAnswer Plzarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
