
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A torque T is applied to a thin-walled tube
having a cross section in the shape of a regular hexagon
with constant wall thickness t and side length b
(see figure). Obtain formulas for the shear stress τ and
the rate of twist θ.
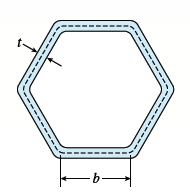
Transcribed Image Text:-b-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- = 1.3-18 A stepped shaft ABC consisting of two solid,circular segments is subjected to uniformly distrib uted torque i,acting over segment 1 and concentrated torqueT₂applied at C,as shown in the figure。Seg ment 1 of the shaft has a diameter ofd₁= 57 mm and length ofL₁= 0.75 m; segment 2 has a diameterd₂= 44 mm and lengthL₂= 0.5 m。Torque intensity1₁3100 N m / m andT₂= 1100 N·m。(a)Find reaction torque T at support A.(b)Find the internal torque T(x)at two locations:arrow_forwardA 3 m long steel angle shown in the figure has a section thickness of 12.7 mm and a cross sectional area of 4350 mm². Since tem = 50 MPa and G = 77.2 GPa, find the maximum applicable torque T.arrow_forwardF3.A shaft is composed of two 6-in. diameter sections coupled together (see figure below). Part AB is bronze and part BC is steel. A torque is applied at the free end which causes a maximum shear stress in the bronze shaft of 10,000 psi. Find the angle of twist of the free end. Assume the modulus of rigidity of bronze is 6 (106) psi and that of steel is 12(106) psi. Bronze Dia. = 6 in. A 3' Steel B Match each item to a choice: Angle of twist Tarrow_forward
- T.L Tr4 %3D J = " (r* – rf) (Tubular shaft) Tr (Solid shaft) G.J 3. The shaft in the figure below consists of 75 mm diameter bronze segment that is rigidly joint to 50 diameter steel segment. The ends of the shaft are attached to rigid supports (fixed supports). Calculate the absolute maximum shear stress developed in each segment when the torque T= 5.1 kN-m is applied (a = 2 m and b = 1.5 m). Use G = 35 GPa for bronze, and G = 75 GPa for steel. (21 pts) 75 mm 50 mm Bronze Steelarrow_forward3.8-5 A stepped shaft ACB having solid circular cross sec- tions with two different diameters is held against rotation at the ends (see figure). (a) If the allowable shear stress in the shaft is 42 MPa, what is the maximum torque (Tmax that may be applied at section C? [Hint: Use Eqs. (3-49a and b) of Example 3-9 to obtain the reactive torques.] (b) Find (7)max if the maximum angle of twist is limited to 0.55°. Let G = 73 GPa. 38 mm 19 mm B 150 mm- PROB 3.8-5 To 380 mm Iarrow_forwardI need the answer as soon as possiblearrow_forward
- A thin tube of uniform thickness 5 mm and square cross section, shown below, is subject to a torque of 1500 N·m. The shear modulus of the material is 80 GPa. What will be the angle of twist per length (in unit: rad/m)? 50 mm 50 mmarrow_forwardA shaft ABCD is supported by a clamp at point A and is subjected to point torques at B, C and D, as shown in the figure. The shaft has variable cross-section and is solid in segments AB and CD and hollow in segment BC. The lengths and diameters of each segment are shown in the figure. Assume that the deformation is linear elastic and take the shear modulus of elasticity G = 12.1 × 10° psi. a) Using method of sections, plot the torsion moment diagram. b) Find the angle of twist for the free end (point D) with respect to the fixed support at A, QAD and the angle of twist for point C with respect to the fixed support at A, QCA. Find both angles in degrees. d₁ = 4 in d20 3.5 in, d2=2.5 in d3 = 3.0 in 25 kip-in 20 kip-in 10 kip-in A 20 in B с D ++ 25 in 30 inarrow_forwardA circular steel tube of length L = 1.1 m is loaded in torsion by torques T (see figure). T T r2 (a) If the inner radius of the tube is r, = 51 mm and the measured angle of twist between the ends is 0.5°, what is the shear strain y, (in radians) at the inner surface? (Enter the magnitude.) rad (b) If the maximum allowable shear strain is 0.00043 rad and the angle of twist is to be kept at 0.45° by adjusting the torque T, what is the maximum permissible outer radius (r,)may (in mm)? mmarrow_forward
- A circular hollow shaft is subjected to a torsional moment T = 30 kNm and a compressiveload P = 80 kN, as shown. The shaft has an outer diameter D = 120 mmand inner diameter d = 100 mm. Points A and B are on the surface of the shaft. (a)Calculate the direct and shear stress at point A. (b)Calculate the maximum,minimum and oriention of the max and min principal stresses at point A. (c)Calculate the maximum in-plane shear stress at point A and the orientation.arrow_forward. Compute the shearing stress if a torque T = 200 N-m is applied to a thin-walled tube having a cross section in the shape of a regular hexagon with constant wall thickness 2 mm and side length b = 100 mm (see figure). (arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY