
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
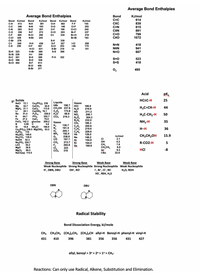
Transcribed Image Text:Average Bond Enthalpies
Average Bond Enthalpies
Bond
C=C
CEC
C=N
KJ/mol
614
839
Bond KJ/mol Bond
KJ/mol Bond KJ/mol Bond
KJ/mol
С-Н
413
N-H
391
O-H
463
F-F
155
146
190
C-C
348
N-N
163
201
0-0
O-F
CI-F
253
242
615
891
799
1072
C-N
293
N-O
CI-CI
CEN
C-O
C-F
C-CI
C-Br
358
N-F
N-CI
272
O-CI
203
Br-F
Br-CI
Br-Br
237
485
200
234
218
C=0
328
N-Br
243
193
CEO
276
240
259
S-H
S-F
S-CI
S-Br
339
327
253
218
C-I
C-S
H-H
H-F
H-CI
H-Br
436
567
431
I-CI
I-Br
208
175
151
N=N
418
NEN
941
Si-H 323
Si-Si 226
366
S-S
266
N=O
607
299
Si-C 301
B-H
389
P-H
322
S=0
S=S
523
418
Si-O 368
B-O
B-F
536
Si-CI 464
613
B-CI
456
B-Br
377
O2
495
Acid
pK,
so Solids
Naci 72.1
HC=C-H
25
Liquids
HBr
сH,он 237.6
CH,
228.9 H,0
Ca,(PO 236
Gases
HCI
| N.O
Mg
CaCo,
198.7
32.7
MgH, 31.1
29.1
51.4
64.7
27.2
92.9
186.9
219.9
211.2
240.1
304.3
232.0
Cacl,
H,C=CH-H
44
N,0
NO
113.8
Li
Cа(он), 76.1
Na
K
Fe
172.8
69.9
216.3
NO,
H;C-CH2-H
50
PCI,
Cac,
glucose
352.7
70.0
209.2
5.6
186.9
B,H,
CH
NH2-H
FeCl, 142.3
35
Gases
H,
N,
186.3
в
B
5.90
130.7
C,H,
C,H.
C,H,
200.8
219.6
229.6
126.0
146.2
Si
I
18.8 NH,CI
Ca,(PO, 238.5 Mg(OH), 63.2
191.5
H-H
36
205.1
192.5
238.9
197.7
H,PO, "110
Na,so, 149.6
Na,co, 136.0
NaOH 52.3
Na, PO, 224.7
LICI
Mgo
MgCl,
Naci(aq) 115.5
Не
CH,CH,OH
15.9
kJ/mol
2.1
4.2
Ne
CI
OH
Ar
154.8
co,
F2
ci,
213.7
202.8
223
310
Kr
R-CO2-H
5
164.0
169.6
CH,
55.2
26.8
89.5
7.6
8.0
9.2
22.8
Xe
CH,CH,
HCI
-8
ipr
t-Bu
Strong Base
Weak Base
Weak Base
Strong Base
Weak Nucleophile Strong Nucleophile Strong Nucleophile Weak Nucleophile
H', DBN, DBU
OH", RO
I, Br", CI', RS"
HS', RSH, H,S
H20, ROH
DBN
DBU
Radical Stability
Bond Dissociation Energy, kJ/mole
CH, CH;CH; (CH3)2CH2 (CH3);CH allyl-H Benzyl-H phenyl-H vinyl-H
431
410
396
381
356
356
431
427
allyl, benzyl > 3° > 2° > 1° > CH3
Reactions: Can only use Radical, Alkene, Substitution and Elimination.

Transcribed Image Text:In THF, which is imiscible with water, the kinetics are first order in both reactants for the following
reaction. If the concentration of water is set at 0.500 M, use the following time-concentration
data to calculate the first order rate constant for bromoporpane
С3Н7-Br + H20
С3H7-ОН + НВr
minutes M, C3H7Br
2.20x10-3
2
1.87x10-3
ABC
ттT Arial
3 (12pt)
Path: p
Words:0
II
!!
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following molecules has the greatest bond energy? 02 H2 O N2arrow_forwardUse the average bond enthalpies in the table to estimate AH for the combustion of propanol based on the number of moles present in the balanced chemical equation. ннн || | Н-С-С-С-0-Н нннarrow_forwardWhat changes in relative energy you would expect as the SN2 conversion from CH3-Br to CH3-Cl takes place. (The CH3-Br bond energy is 293 kJ/mol and the CH3-CI bond energy is 356 kJ/mol.) i ! kJ/molarrow_forward
- ding 1.pdf (63.5 KB) AH (kJ) -400 Chemical Equation Process Formation M(s) +1/2X2(g)→MX(s) 55 Sublimation 246 First lonization Energy Bond dissociation 200 -150 X(g) + e (g) → X(g) Electron Affinity Lattice Energy చంత తarrow_forwardG hool- Google Sear X G TOTAL equivalent lik x G brol- Google Sear X G pbr3 - Google Searc x G sof4 - Google Seard xO Chem 101 0 hem101 os//app. 101edu.co Question 6 of 20 Draw the Lewis structure for the bromate ion (BrO) with minimized formal charges. How many TOTAL equivalent likely resonance structures exist for BrOs ? A) 1 B) 2 - C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Click to edit moleculearrow_forwardPredict which bond in the following groups is the most ionic in character. Calculate ∆EN for each to check your predictions. H–Cl, H–Br, H–F Na–O, Li–O, K–Oarrow_forward
- Predict whether each of these 3 substituents owill be axial or equatorial: t-butyl- CH,CH3 CH3arrow_forwardCalculate the standard energy of formation of CI0 from the following bond energies. f Cl2: 242.7 kJ/mol O2: 498.7 kJ/mol C10: 206 kJ/mol kJ/molarrow_forward[References] The compound oxygen difluoride is quite reactive, giving oxygen and HF when treated with water: OF2(g) + H20(g)→ 0g) + 2HF(g) =-318 kJ ot Using bond energies, calculate the bond dissociation energy of the O-F bond in OF7. Average Bond Energies (kJ/mol) Single Bonds Multiple Bonds pt N-H 391 149 C=C 614 432 565 H-H 839 495 745 1072 607 418 941 pt H--F N-N 160 208 C=C N-F 272 |-Br 175 H-CI H-Br 427 363 295 N-CI N-Br C=0* C=D0 200 pt H-1 243 S-H 347 N-O 201 S-F 327 N=N N N 253 S-CI S-Br 467 413 347 305 358 C-H 146 218 C--C C--N C-O C--F C-CI C-Br O-O 891 C=N C-N S-S 266 190 203 O-F 615 0-CI 340 393 360 452 485 O-I 一 234 Si-Si 339 276 Si-H Si-C Si-O e F-F 154 253 240 259 F-CI F-Br Cl-CI C-S 237 239 218 193 Cl--Br Br--Br *C== O(in CO,) - 799 O-F bond dissociation energy: kJ mol Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remaining nything %3Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY