
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
At constant pressure p1, the substance goes from solid state to gas as temperature increases
At constant temperature T1, the substance goes from gas state to liquid as pressure increases
The substance exists in the liquid phase by lowering the pressure and the temperature beyond T
At temperature T, the substance coexists in solid, liquid and gas phases
At constant pressure p2, the substance goes from solid state to liquid to gas as temperature increases.
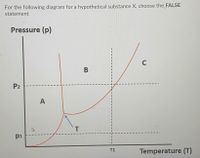
Transcribed Image Text:For the following diagram for a hypothetical substance X, choose the_FALSE
statement
Pressure (p)
C
P2
A
T
pi
Temperature (T)
T1
B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Difluoroethene has two isomers with very different properties despite having the same chemical formula. Based on the chemical structure shown for the first isomer, what intermolecular forces are present in this molecule?arrow_forwardStudy the following phase diagram of Substance X. pressure (atm) 36- 18- solid 0 100 liquid 200 gas temperature (K) Use this diagram to answer the following questions. Sunnose a small sample of pure X is held at -104 C and 19.6 atmarrow_forwardThis question as been getting rejected, but this is not a grade assigment. This just a pratice problem.arrow_forward
- A pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is a graph of the results: 140. 120. temperature (°C) 100. 80. I Don't Know 60. 0. What is the melting point of X? Use this graph to answer the following questions: 10. What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 5 kJ/mol of heat has been added? Submit 80 heat added (kJ/mol) 20. 888 0°C (check all that apply) solid liquid gas 30. X 5 40. DII FB © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibil F9 F10 ? S oloarrow_forwardRefer to the following phase diagram (not to scale!) for ammonia: 111.5 1.00 atm 0.059 195.3 195.4 239.8 405.5 T Kelvin A sample of ammonia at a pressure of 1.00 atm and a temperature of 197 K is heated at constant pressure to a temperature of 213 K. Which of the following are true? Choose all that apply O No phase change will occur. O The sample is initially a liquid. O The final state of the substance is a liquid. U The gas initially present will solidify. U The sample is initially a solidarrow_forwardThe following information is given for ethanol at 1 atm: Boiling point = 78.40°C Melting point =-114.5°C Specific heat gas = 0.3418 cal/g°C Specific heat liquid = 0.5880 cal/g°C Heat of vaporization = 200.0 cal/g Heat of fusion = 26.04 cal/g A 44.00 g sample of liquid ethanol is initially at -58.80°C. How many kcal of energy must be added to the sample to raise its temperature to 94.90°C? Energy added = kcalarrow_forward
- A pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is a graph of the results: temperature (°C) 160. 140. 120. 100. 80. 60. 0. 10. What is the boiling point of X ? Use this graph to answer the following questions: heat added (kJ/mol) 20. What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 12 kJ/mol of heat has been added? 30. Пос (check all that apply) solid O liquid gas 40.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.13 atm and -9. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.39 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 200 400 temperature (K) pressure (atm)arrow_forward
- Refer to the following phase diagram (not to scale!) for hydrogen: 12.8 1.00 atm 0.071 13.9 14.0 20.3 33.2 T Kelvin A sample of hydrogen at a pressure of 7.10x10 atm and a temperature of 11.4 K is compressed at constant temperature to a pressure of 18.2 atm. Which of the following are true? Choose all that apply O The liquid initially present will vaporize. O The final state of the substance is a solid. O The sample is initially a solid. O No phase change will occur. O The sample is initially a gas. Submit Answerarrow_forwardConsider the following phase diagram. Phase diagram for compound A 1000 2 760 3 50 10 -25 25 100 150 Temperature, °C (not to scale) Which red dot represents the melting point of this compound at 760 torr? [ Select ] What is the approximate melting temperature for this substance at 760 torr? [ Select ] Which red dot represents the boiling point of this compound at 760 torr? [ Select ] What is the approximate boiling temperature for this substance at 760 torr? [ Select ] Which red dot represents the triple point for this substance? [ Select ] |What is the approximate temperature of the triple point? [ Select ] Pressure, torr (not to scale)arrow_forwardUse the graph to provide the information below The location where the substance is only solid. The location where the substance condenses or vaporizes. The location where the substance is only liquid. The location where fusion or solidification occurs. The location where the substance is only vapor.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY