
Concept explainers
An autosomal recessive form of deafness is caused by a mutation in the ESPN gene (E = dominant allele and e = recessive allele). An autosomal recessive disease called Usher syndrome is caused by a mutation in the USH2A gene (H = dominant allele and h = recessive allele). The ESPN and USH2A genes are far apart on chromosome 1.
Iris's genotype= eeHH
Zacharias' genotype= EEhh
Zacharias and Iris have a daughter named Gianna (EeHh) who produces an eh gamete.
Here are some pictures of metaphase I cells before recombination has been resolved. Which one of the pictures correctly depicts Gianna's metaphase I cell that could divide to produce her eh gamete? (Hint: it is useful to consider the gametes that Iris and Zacharias each contributed to Gianna)
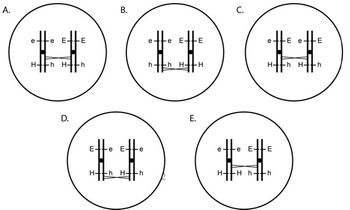
Prior to ascertaining the accurate depiction of Gianna's metaphase I cell, it is essential to revisit the parental genotypes.
The genotype of Iris is eeHH.
The genotype of Zacharias. The user's text lacks clarity and coherence.
Based on the above genotypes, it is possible to infer the specific alleles that were contributed by each parent to Gianna.
Iris made a contribution of "e" and "H" alleles.
Zacharias made a contribution of "E" and "h" alleles.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

What picture does it correspond to?
What picture does it correspond to?
- Amelogenesis imperfecta (AI) is a disorder of faulty tooth enamel formation. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant and X-linked dominant pattern. The expression of AI disorder is determined by mutations in the autosomal alleles. One copy of the mutated allele (A) will cause the disorder. The severity of the disorder is determined by mutations in a gene carried on the X chromosome. Normal (or non-severe) abnormality (XN) is dominant over the abnormality (or severe) (Xn) allele. In the absence of the autosomal dominant allele, the abnormality gene on the X chromosome is not expressed. Question:A woman with normal teeth had four children with a man with non-severe form of AI: A boy was born without amelogenesis imperfecta A girl was born without amelogenesis imperfecta A boy was born with severe amelogenesis imperfecta A boy was born with non severe amelogenesis imperfecta Identify the parental genotypes. Complete the Punnett square for the parental cross, and identify the…arrow_forwardRetinoblastoma can be seen as a familial cancer, inherited in an autosomal recessive manner (RB-/RB-), individuals heterozygous for the RB+ and RB- alleles can develop tumor as a result of… A mitotic crossover that leads to homozygosity for RB+ in some cells and RB- in other cells A meiotic mutation in the RB+ allele that leads to homozygosity for RB+ A somatic mutation in the RB- allele that leads to homozygosity for RB+ The fact that RB- is dominant to RB+arrow_forwardWhat is the Philadelphia chromosome? How is this chromosome related to cancer? Identify how this chromosome appears physically different in a karyotype than it appears in a normal karyotype. Include references to information sources used.arrow_forward
- A defective gene on chromosome 15 causes Tay-Sachs disease. It is a central nervous system neurodegenerative disease that most often affects infants, though older children and adults can have late-onset forms of the disease. The defective gene prevents the body from making a protein called hexosaminidase A. Without, hexosaminidase A, chemicals called gangliosides build up in the nerve cells of the brain, destroying brain cells. Pedigree information regarding the incidence of Tay-Sachs within a family is depicted above. The row below that indicates the genotypes of individuals II-1, II-2, and III-1 is Select one: a. II-1 II-2 III-1 Aa Aa aa b. II-1 II-2 III-1 XAY XAXa XAXa c. II-1 II-2 III-1 XAY XAXA XaXa d. II-1 II-2 III-1 AA aa Aaarrow_forwardFor the following diseases with their potential pedigree, mode of inheritance and the responsible gene: (Pedigrees A, B, and C) -> Do Pedigree A Pedigree B, Autosomal dominant, Huntingtin gene Pedigree B, Autosomal dominant, CFTR gene Pedigree B, Autosomal dominant, HexA gene Pedigree B, Autosomal dominant, FGFR3 gene Pedigree A, Autosomal recessive, CFTR gene Pedigree A, Autosomal recessive, Beta-globin gene Pedigree A, Autosomal dominant, FGFR3 gene Pedigree B, X-linked dominant. Factor VIII gene Pedigree A, Autosomal dominant, Beta-globin gene Pedigree A. Autosomal recessive, Huntingtin gene Pedigree C, X-linked recessive, Factor VIII gene Pedigree A, Autosomal recessive, HexA genearrow_forwardCan you please not type the answer can you write it on a paperarrow_forward
- Cystic fibrosis (CF) is an autosomal recessive condition triggered by the overproduction of sticky mucus that clogs the lungs and pancreas. It is a life-threatening disease, but medical advances helped the afflicted to live through adulthood. Betty's mother died from cystic fibrosis, but her father was normal and never had any relative with CF. Her fiancé, Jones, turned out to be a carrier of the CF allele. What are the genotypes of Betty and Jones? 1. Betty: ________________________ 2. Jones: _____________________ They planned to have four children. What is the probability that: 3. all children will be normal 4. at least two will be normalarrow_forwardThe questions below all refer to the following pedigree. The locus for allele D/d determines how cilia function within the body. Mutations at this allele cause abnormal ciliary function, resulting in a clinical disorder characterized by frequent respiratory infections (including in the ears, sinuses, and lungs), as well as infertility. In the pedigree, black circles/squares represent individuals affected by the disorder. White circles/squares represent unaffected individuals. Remember, if a trait is rare in a population (such as this one), we assume individuals marrying into the family are NOT carriers unless the information provided indicates otherwise. A1 A2 II B1 B2 B3 B4. B5 B6_ II C1. C2 C3. C4. C5 IV D1. D2, D4 . D5 Individuals C2 and C3 are considering having additional children. However, having already had a child with this disorder, they visit a genetic counselor to determine what the probability is that their future child would have the disorder. If C2 and C3 have another…arrow_forwardGenetic Inheritance Patterms Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) can be autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, or x-linked. Apparently the dominant forms are often less severe. Eric's form of RP is Usher's Syndrome, which is an autosomal recessive inheritance (i.e., you must get a copy of the defective gene from your Mom and one from your Dad). Autosomal means it is not carried on one of the chromosomes that determines sex. Usher's Type II is recessive, so for Eric this means that both his Mom and Dad are carriers of this condition. His brother, Dirk, does not have any symptoms of RP. Draw a pedigree of Eric's family showing possible genotypes and chances of having RP. Your pedigree must include his parents, Eric, his brother Dirk, and a potential daughter of Eric's. Draws a pedigree that shows the correct genotypes and chances of having retinitis pigmentosa for Eric and his family. D.Focus (United States) a S W 37 F 八 口arrow_forward
- X-linked Recessive Inheritance A gene is described as X-linked when it occurs on the X chromosome and not the Y. Our convention is to indicate X-linkage by attaching the appropriate gene symbol as a superscript on the letter X. Commonly, the wild-type (+) allele is indicated with only a "+" to avoid having to type a superscript on a superscript. For example, a female that is heterozygous and carrying a recessive mutant allele is indicated as X+Xm. Note the convenience of the shorthand + for m+ in this situation. A mutant male has the genotype XmY. When working with X-linked inheritance, always include the X and Y chromosomes in the descriptions of genotypes, and include the sex (male or female) in the descriptions of the phenotypes (e.g., mutant male, wild-type female, etc.). Here are the genotypes and associated phenotypes for X-linked recessive inheritance: X+X+ Wild-type female X+Xm Wild-type female xmxm Mutant female X+Y xmy Wild-type male Mutant malearrow_forwardHow many males have hemopilia? (refer to image).arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





