
Essentials Of Investments
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781260013924
Author: Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
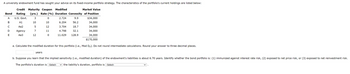
Transcribed Image Text:A university endowment fund has sought your advice on its fixed-income portfolio strategy. The characteristics of the portfolio's current holdings are listed below:
Credit Maturity Coupon Modified
Bond Rating (yrs.) Rate (%) Duration Convexity
U.S. Govt.
3
2.724
9.9
A1
10
6.204
56.2
Aa2
5
3.704
18.7
Agency
7
4.798
32.1
Aa3
12
11.029 128.9
A
B
C
D
E
Market Value
of Position
$34,000
34,000
34,000
34,000
34,000
$170,000
a. Calculate the modified duration for this portfolio (i.e., Mod Dp). Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to three decimal places.
years
0
10
12
11
0
b. Suppose you learn that the implied sensitivity (i.e., modified duration) of the endowment's liabilities is about 6.70 years. Identify whether the bond portfolio is: (1) immunized against interest rate risk, (2) exposed to net price risk, or (3) exposed to net reinvestment risk.
The portfolio's duration is -Select-
the liability's duration, portfolio is -Select-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Using the expectations hypothesis theory for the term structure of interest rates, determine the expected return for securities with maturities of two, three, and four years based on the following data. Note: Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places. 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 1 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 21 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 3 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 4 2-year security 3-year security 4-year security Expected Return % % % Interest Rate 7% 9% 10% 12%arrow_forwardb. Suppose you are considering two possible investment opportunities: a 12-year Treasury bond and a 7-year, AA-rated corporate band. The current real risk-free rate is 5%, and inflation is expected to be 2% for the next 2 years, 3% for the following 4 years, and 4% thereafter. The maturity risk premium is estimated by this formula: MRP = 0.03 (t-1) %. The liquidity premium (LP) for the corporate bond is estimated to be 0.2%. You may determine the default risk premium (DRP), given the company's bond rating, from the following table. Remember to subtract the bond's LP from the corporate spread given in the table to arrive at the bond's DRP. Rate 0.83% 1.03 1.35 1.73 Corporate Bond Yield Spread = DRP + LP U.S. Treasury AAA corporate 0.20% AA corporate 0.52 A corporate 0.90 What yield would you predict for each of these two investments? Round your answers to three decimal places, 12-year Treasury yield: 7-year Corporate yield: % %arrow_forward(c)) Discuss the following graphic, which shows the relationship between expected return and portfolio weights. The portfolio is comprised of a debt security D and an equity security E. What would the portfolio strategy be when Wp = 2 and ba WE = -1? 38 (33) -0.5 Expected Return 13% 8% Debt Fund 0 (ebenso) esenicut adol leu@ ledol (loorba (ognerloxel) Ismet tametnl Equity Fund 1.0 0 OC) becida nieu to 2.0 w (stocks) AB -1.0 68 XO.YOUTS RO w (bonds)=1-w (stocks) 15 V10 anollesup Figure 7.3 Portfolio expected return as a function of investment proportions la 21101TOarrow_forward
- 9. Interest Rate Risk. Suppose that you are a fixed income portfolio manager at Bourbon Street Capital. You have the following bonds issued by Royal, Inc. and Chartres, LLC in your portfolio and you want to understand the risk profile of your portfolio. Given that both bonds pay semiannual coupons, answer the following questions. (Remember to convert your answer to units of full years.) Coupon Yield to maturity Maturity (years) Royal, Inc. Chartres, LLC. Bond A Bond B 9% 8% 5 $100.00 $104.055 8% 8% 2 Par $100.00 Price $100.00 (a) What is the DV01 (at current prices) for bonds A and B? (b) What are the Macaulay Durations (at current prices) for the two bonds? (c) What are the modified durations for the two bonds? (d) What is the convexity of the two bonds?arrow_forwardAssume that the Pure Expectations Theory of the term structure is correct. Also assume that the interest rate today on a 9-year security is 6.40%, while the interest rate today on a 15-year security is 8.00%. Finally assume that the interest rate on a 3-year security to be bought at Year 9 and held over Years 10, 11, and 12 is 6.80%. Given this information, determine the average annual return that investors today must expect that they will receive from investing in a 3-year security in 12 Years (that is, buying the security at Year 12 and holding it over Years 13, 14, and 15). O 13.00% O 12.50% 13.50% O 12.00% O 14.00%arrow_forwardYou are given the following information for Securities J and K for the coming year: State of Nature Probability Return J 20.00% 14.00% 50.00% 19.00% 30.00% 16.00% 1 2 3 Return K 14.00% 16.00% 25.00% You create a portfolio, with 40 percent of your money invested in Security K, and the rest of your money invested in Security J. Given this information, determine the standard deviation of this portfolio for the coming year. O 0.0301 O 0.0239 O 0.0195 O 0.0263 O 0.0154arrow_forward
- Nikularrow_forwardplease this part of the question ASAP too What is the standard deviation of the rate of return on your client's portfolio? (Round your intermediate calculations and final answer to 1 decimal place.)arrow_forwardUsing the expectations hypothesis theory for the term structure of interest rates, determine the expected return for securities with maturities of two, three, and four years based on the following data. (Input your answers as a percent rounded to 2 decimal places.) 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 1 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 2 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 3 1-year T-bill at beginning of year 4 2-year security 3-year security 4-year security Expected Return % % % Interest Rate 61 98 7% 108arrow_forward
- Unlike the coupon interest rate, which is fixed, a bond's yield varies from day to day depending on market conditions. To be most useful, it should give us an estimate of the rate of return an investor would earn if that investor purchased the bond today and held it for its remaining life. There are three different yield calculations: Current yield, yield to maturity, and yield to call. A bond's current yield is calculated as the annual interest payment divided by the current price. Unlike the yield to maturity or the yield to call, it does not represent the actual return that investors should expect because it does not account for the capital gain or loss that will be realized if the bond is held until it matures or is called. This yield was popular before calculators and computers came along because it was easy to calculate; however, because it can be misleading, the yield to maturity and yield to call are more relevant. The yield to maturity (YTM) is the rate of return earned on a…arrow_forwardConsider a portfolio that offers an expected rate of return of 11% and a standard deviation of 26%. T-bills offer a risk-free 7% rate of return. What is the maximum level of risk aversion for which the risky portfolio is still preferred to T-bills? (Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardSuppose you are considering two possible investment opportunities: a 12-year Treasury bond and a 7-year, AA-rated corporate bond. The current real risk-free rate is 3%, and inflation is expected to be 2% for the next 2 years, 3% for the following 4 years, and 4% thereafter. The maturity risk premium is estimated by this formula: MRP = 0.02(t - 1)%. The liquidity premium (LP) for the corporate bond is estimated to be 0.3%. You may determine the default risk premium (DRP), given the company's bond rating, from the following table. Remember to subtract the bond's LP from the corporate spread given in the table to arrive at the bond's DRP. Corporate Bond Yield Rate Spread = DRP + LP U.S. Treasury 0.73 % — AAA corporate 0.93 0.20 % AA corporate 1.33 0.60 A corporate 1.75 1.02 What yield would you predict for each of these two investments? Round your answers to three decimal places. 12-year Treasury yield: 6.553%----->correct 7-year Corporate yield: ? %…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education