
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
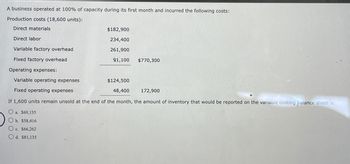
Transcribed Image Text:A business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs:
Production costs (18,600 units):
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable factory overhead
Fixed factory overhead
Operating expenses:
Variable operating expenses
Fixed operating expenses
$182,900
234,400
261,900
91,100 $770,300
$124,500
48,400
172,900
If 1,600 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is
O a. $69,135
Ob. $58,416
Oc. $66,262
Od. $81,135
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Variable Costing, Value of Ending Inventory, Operating Income Pattison Products, Inc., began operations in October and manufactured 42,000 units during the month with the following unit costs: Direct materials $4.30 Direct labor 2.30 Variable overhead 1.15 Fixed overhead* 6.30 Variable marketing cost 0.85 * Fixed overhead per unit = $264,600 / 42,000 units produced = $6.30 Total fixed factory overhead is $264,600 per month. During October, 40,800 units were sold at a price of $25.25, and fixed marketing and administrative expenses were $118,300. Required: Question Content Area 1. Calculate the cost of each unit using variable costing. Round the final answer to the nearest cent. $fill in the blank per unit 2. How many units remain in ending inventory?fill in the blank What is the cost of ending inventory using variable costing?$fill in the blank Question Content Area 3. Prepare a variable-costing income statement for Pattison Products, Inc., for the month…arrow_forwardWalsh Company manufactured 30,000 units during July. There were no units in inventory on July 1. Costs and expenses for July were as follows: Total Num Total Cost Number of Units Unit Cost Manufacturing costs: Variable $660,000 30,000 $22.00 Fixed 300,000 30,000 10.00 Total 960,000 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable $200,000 Fixed 160,000 Total. $360,000 If the company sells 25,000 units at $75 (units manufactured exceed units sold), prepare an income statement for July using: b. Variable costingarrow_forwardAt the end of the first year of operations, 5,600 units remained in the finished goods inventory. The unit manufacturing costs during the year were as follows: Direct materials $29.10 Direct labor 13.20 Fixed factory overhead 4.80 Variable factory overhead 4.20 Determine the cost of the finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet under (a) the absorption costing concept and (b) the variable costing concept. Absorption costing $ Variable costing $arrow_forward
- Aaron Corporation, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold Units in ending inventory Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead. Variable selling and administrative expense Multiple Choice Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative expense What is the unit product cost for the month under variable costing? $110 per unit $137 per unit $143 0 $120 per unit 6,850 6,550 300 $93 per unit $23 $53 $17 $17 $184,950 $ 27,300arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (19,800 units): Direct materials $177,000 Direct labor 227,000 Variable factory overhead 261,600 Fixed factory overhead 100,400 $766,000 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $132,300 Fixed operating expenses 42,700 175,000 If 1,800 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is a. $60,498 b. $72,536 Oc. $69,636 O d. $85,545arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (17,100 units): Direct materials $183,100 Direct labor 227,700 Variable factory overhead 246,200 Fixed factory overhead 104,700 $761,700 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $122,200 Fixed operating expenses 49,300 171,500 If 1,600 units remain unsold at the end of the month and sales total $1,079,000 for the month, what would be the amount of income from operations reported on the absorption costing income statement? a.$216,975 b.$71,270 c.$207,274 d.$61,474arrow_forward
- A business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (19,200 units): Direct materials Direct labor Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $174,500 232,600 249,000 104,200 $760,300 $134,700 43,300 Fixed operating expenses 178,000 If 1,700 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is O a. $67,318 O b. $70,019 O c. $58,089 O d. $83,079arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (17,100 units): Direct materials $184,100 Direct labor 222,200 Variable factory overhead 241,500 Fixed factory overhead 104,400 $752,200 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $126,900 Fixed operating expenses 46,600 173,500 If 1,700 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is:arrow_forwardOn October 31, the end of the first month of operations, Maryville Equipment Company pre- pared the following income statement, based on the variable costing concept: Maryville Equipment Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended October 31 Sales (220,000 units).... $ 7,920,000 Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured . Inventory, October 31 (45,000 units) .. Total variable cost of goods sold... Manufacturing margin....... Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 6,360,000 (1,080,000) (5,280,000) $ 2,640,000 (330,000) $ 2,310,000 Contribution margin... Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs ... Fixed selling and administrative expenses.. $ 530,000 100,000 Total fixed costs.... (630,000) $ 1,680,000 Operating income... Prepare an income statement under absorption costing.arrow_forward
- Variable Costing, Value of Ending Inventory, Operating Income Pattison Products, Inc., began operations in October and manufactured 47,000 units during the month with the following unit costs: Direct materials $4.80 Direct labor 2.80 Variable overhead 1.40 Fixed overhead* 6.80 Variable marketing cost 1.10 * Fixed overhead per unit = $319,600 / 47,000 units produced = $6.80 Total fixed factory overhead is $319,600 per month. During October, 46,000 units were sold at a price of $24.5, and fixed marketing and administrative expenses were $117,600. Required: 1. Calculate the cost of each unit using variable costing. Round your final answer to the nearest cent. $fill in the blank ce3411029f88017_1 per unit 2. How many units remain in ending inventory?fill in the blank ce3411029f88017_2 units What is the cost of ending inventory using variable costing?$fill in the blank ce3411029f88017_3 3. Prepare a variable-costing income statement for Pattison Products,…arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (20,700 units): Direct materials $179,300 Direct labor 234,800 Variable factory overhead 268,300 Fixed factory overhead 103,400 $785,800 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $124,300 Fixed operating expenses 48,100 172,400 If 1,900 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the absorption costing balance sheet is Oa. $72,124 Ob. $74,045 Oc. $87,951 Od. $62,636arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (10,000 units): Direct materials Direct labor $170,000 360,000 Variable factory overhead 190,000 Fixed factory overhead 50,000 $770,000 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses Fixed operating expenses $60,000 18,000 78,000 If 500 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is a. $36,000 b. $41,500 c. $38,500 d. $42,800arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education