
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
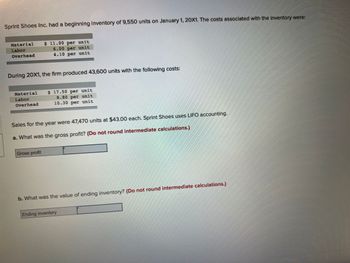
Transcribed Image Text:Sprint Shoes Inc. had a beginning inventory of 9,550 units on January 1, 20X1. The costs associated with the inventory were:
Material
Labor
Overhead
During 20X1, the firm produced 43,600 units with the following costs:
Material
Labor
Overhead
$ 11.00 per unit
6.00 per unit
4.10 per unit
Gross profit
$ 17.50 per unit
8.80 per unit
10.30 per unit
Sales for the year were 47,470 units at $43.00 each. Sprint Shoes uses LIFO accounting.
a. What was the gross profit? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
b. What was the value of ending inventory? (Do not round intermediate calculations.)
Ending inventory
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Prior to the first month of operations ending October 31, Marshall Inc. estimated the following operating results: 1 Sales (28,800 × $75) $2,160,000.00 2 Manufacturing costs (28,800 units): 3 Direct materials 1,209,600.00 4 Direct labor 316,800.00 5 Variable factory overhead 115,200.00 6 Fixed factory overhead 221,760.00 7 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 28,400.00 8 Variable selling and administrative expenses 34,900.00 The company is evaluating a proposal to manufacture 36,000 units instead of 28,800 units, thus creating an ending inventory of 7,200 units. Manufacturing the additional units will not change sales, unit variable factory overhead costs, total fixed factory overhead cost, or total selling and administrative expenses. Required: a. Prepare an estimated income statement, comparing operating results if 28,800 and 36,000 units are manufactured in (1) the absorption costing…arrow_forwardThe following data pertain to the operations of Deci, Inc. in the most recent month for the production of its only product, which sells for $297: Beginning inventory: 4, 000 Units Produced: 46,000 Units Sold: 47,000 Variable Costs per unit: Direct materials: $84 Direct Labor: $93 Manufacturing Overhead: $18 Selling and Administrative: $30 Fixed Costs: Manufacturing overhead: $1,912, 680 Selling and administrative: $1,954, 260 What is the variable costing unit product cost?arrow_forwardAt the end of the first year of operations, 5,600 units remained in the finished goods inventory. The unit manufacturing costs during the year were as follows: Direct materials $29.10 Direct labor 13.20 Fixed factory overhead 4.80 Variable factory overhead 4.20 Determine the cost of the finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet under (a) the absorption costing concept and (b) the variable costing concept. Absorption costing $ Variable costing $arrow_forward
- Trainor Incorporated, which has only one product, has provided the following data concerning its most recent month of operations: Selling price $ 112 Units in beginning inventory 0 Units produced 4,900 Units sold 4,500 Units in ending inventory 400 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials Direct labor Variable manufacturing overhead Variable selling and administrative $ 19 $ 45 $ 6 $ 9 Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 1,17,600 Fixed selling and administrative $ 22,500 What is the net operating income for the month under absorption costing? A. ($19,600) B. $9,600 C. $8,400 D. $18,000arrow_forwardMahoko PLC's planned production for the year just ended was 18,400 units. This production level was achieved, and 21,200 units were sold. Other data follow: Direct material used $ 552,000 Direct labor incurred 259,440 Fixed manufacturing overhead 390,080 Variable manufacturing overhead 198,720 Fixed selling and administrative expenses 329,360 Variable selling and administrative expenses 100,280 Finished-goods inventory, January 1 3,500 units The cost per unit remained the same in the current year as in the previous year. There were no work-in-process inventories at the beginning or end of the year. Required: 1. What would be Mahoko PLC’s finished-goods inventory cost on December 31 under the variable-costing method? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations. 2-a. Which costing method, absorption or variable costing, would show a higher operating income for the year? 2-b. By what amount?arrow_forward2arrow_forward
- Denton Company manufactures and sells a single product. Cost data for the product are given: Variable costs per unit: Direct materials $ 5 Direct labor 10 Variable manufacturing overhead 3 Variable selling and administrative 1 Total variable cost per unit $ 19 Fixed costs per month: Fixed manufacturing overhead $ 108,000 Fixed selling and administrative 169,000 Total fixed cost per month $ 277,000 The product sells for $48 per unit. Production and sales data for July and August, the first two months of operations, follow: Units Produced Units Sold July 27,000 23,000 August 27,000 31,000 The company's Accounting Department has prepared the following absorption costing income statements for July and August: July August Sales $ 1,104,000 $1,488,000 Cost of goods sold 506,000 682,000 Gross margin 598,000 806, 000 Selling and administrative expenses 192,000 200,000 Net operating income $ 406,000 $ 606,000 Required: 1. Determine the unit product cost under: a. Absorption costing. b. Variable…arrow_forwardCost per FIFO EUP In October, Pedraza Corp.'s production was 96,480 equivalent units for direct material, 87,840 equivalent units for direct labor, and 75,600 equivalent units for overhead. During October, direct material, conversion, and overhead costs incurred were as follows: Direct material $285,638 Conversion Overhead 303,437 153,360 Beginning WIP Inventory costs for October were $47,218 for direct material, $35,107 for direct labor, and $37,152 for overhead. The company had 12,960 EUP for direct material in October's beginning WIP Inventory, 14,400 EUP for direct labor, and 12,672 EUP for overhead. What was the October FIFO cost per EUP for direct material, direct labor, and overhead? Note: Round your answers to two decimal places. DM cost per EU S DL cost per EUS OH cost per EU Sarrow_forwardJoplin Company Absorption Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended April 30 Sales (2,500 units) Cost of goods sold: Cost of goods manufactured (2,900 units) Inventory, April 30 (400 units) Total cost of goods sold Gross profit Selling and administrative expenses Operating income $75,400 (10,400) $92,500 (65,000) $27,500 (16,050) $11,450 If the fixed manufacturing costs were $18,096 and the fixed selling and administrative expenses were $7,860, prepare an income statement according to the i variable costing concept. Round all final answers to whole dollars.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education