
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
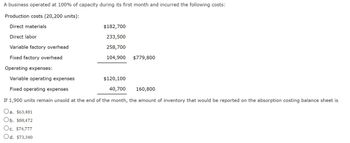
Transcribed Image Text:A business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs:
Production costs (20,200 units):
Direct materials
Direct labor
Variable factory overhead
Fixed factory overhead
Operating expenses:
Variable operating expenses
$120,100
Fixed operating expenses
40,700
160,800
If 1,900 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the absorption costing balance sheet is
a. $63,481
Ob. $88,472
Oc. $74,777
Od. $73,340
$182,700
233,500
258,700
104,900
$779,800
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following data is for a company that produces a single product. selling price 24 193 Units in beginning inventory Units produced Units sold 3,090 2,910 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials 24 24 24 24 53 Direct labor 59 variable manufacturing overhead variable selling and administrative expense Fixed costs: 15 13 Fixed manufacturing overhead Fixed selling and administrative $ 89,610 $ 8,730 Required: a. What is the unit product cost for the month under varlable costing? b. What Is the unit product cost for the month under absorption costing? C. Prepare a contribution format Income statement for the month using varlable costing. d. Prepare an Income statement for the month using absorption costing. e. Reconcile the varlable costing and absorption costing net operating incomes for the month. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required A Required B Required C Required D Required E Prepare a contribution format income statement for the month using…arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (19,700 units): Direct materials $181,900 Direct labor 237,500 Variable factory overhead 254,900 Fixed factory overhead 93,200 $767,500 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $121,300 Fixed operating expenses 43,000 164,300 If 1,800 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the absorption costing balance sheet is Oa. $61,611 Ob. $85,139 Oc. $72,694 Od. $70,128arrow_forwardWalsh Company manufactured 30,000 units during July. There were no units in inventory on July 1. Costs and expenses for July were as follows: Total Num Total Cost Number of Units Unit Cost Manufacturing costs: Variable $660,000 30,000 $22.00 Fixed 300,000 30,000 10.00 Total 960,000 Selling and administrative expenses: Variable $200,000 Fixed 160,000 Total. $360,000 If the company sells 25,000 units at $75 (units manufactured exceed units sold), prepare an income statement for July using: b. Variable costingarrow_forward
- At the end of the first year of operations, 5,600 units remained in the finished goods inventory. The unit manufacturing costs during the year were as follows: Direct materials $29.10 Direct labor 13.20 Fixed factory overhead 4.80 Variable factory overhead 4.20 Determine the cost of the finished goods inventory reported on the balance sheet under (a) the absorption costing concept and (b) the variable costing concept. Absorption costing $ Variable costing $arrow_forwardGurtner Corporation has provided the following data concerning last month’s operations. Cost of goods manufactured $170,000 Underapplied overhead $ 4,000 Beginning Ending Finished goods inventory $33,000 $40,000 Any underapplied or overapplied manufacturing overhead is closed out to cost of goods sold. How much is the adjusted cost of goods sold on the Schedule of Cost of Goods Sold? Multiple Choice A. $170,000 B. $167,000 C. $203,000 D. $163,000arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (19,800 units): Direct materials $177,000 Direct labor 227,000 Variable factory overhead 261,600 Fixed factory overhead 100,400 $766,000 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $132,300 Fixed operating expenses 42,700 175,000 If 1,800 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is a. $60,498 b. $72,536 Oc. $69,636 O d. $85,545arrow_forward
- A business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (17,100 units): Direct materials $183,100 Direct labor 227,700 Variable factory overhead 246,200 Fixed factory overhead 104,700 $761,700 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $122,200 Fixed operating expenses 49,300 171,500 If 1,600 units remain unsold at the end of the month and sales total $1,079,000 for the month, what would be the amount of income from operations reported on the absorption costing income statement? a.$216,975 b.$71,270 c.$207,274 d.$61,474arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (19,200 units): Direct materials Direct labor Variable factory overhead Fixed factory overhead Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $174,500 232,600 249,000 104,200 $760,300 $134,700 43,300 Fixed operating expenses 178,000 If 1,700 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is O a. $67,318 O b. $70,019 O c. $58,089 O d. $83,079arrow_forwardA business operated at 100% of capacity during its first month and incurred the following costs: Production costs (17,100 units): Direct materials $184,100 Direct labor 222,200 Variable factory overhead 241,500 Fixed factory overhead 104,400 $752,200 Operating expenses: Variable operating expenses $126,900 Fixed operating expenses 46,600 173,500 If 1,700 units remain unsold at the end of the month, the amount of inventory that would be reported on the variable costing balance sheet is:arrow_forward
- The following information pertains to Vladamir, Inc., for last year: Beginning inventory, units Units produced 1,400 100,000 Units sold 101,000 Variable costs per unit: Direct materials $8.00 Direct labor $9.00 Variable overhead $1.00 Variable selling expenses $2.00 Fixed costs per year: Fixed overhead $300,000 Fixed selling and administrative expenses $230,000 There are no work-in-process inventories. Normal activity is 100,000 units. Expected and actual overhead costs are the same. Costs have not changed from one year to the next. Required: 1. How many units are in ending inventory? 2. Without preparing an income statement, indicate what the difference will be between variable-costing income and absorption-costing income. 3. Assume the selling price per unit is $32. Prepare an income statement using (a) variable costing and (b) absorption costing.arrow_forwardOn October 31, the end of the first month of operations, Maryville Equipment Company pre- pared the following income statement, based on the variable costing concept: Maryville Equipment Company Variable Costing Income Statement For the Month Ended October 31 Sales (220,000 units).... $ 7,920,000 Variable cost of goods sold: Variable cost of goods manufactured . Inventory, October 31 (45,000 units) .. Total variable cost of goods sold... Manufacturing margin....... Variable selling and administrative expenses $ 6,360,000 (1,080,000) (5,280,000) $ 2,640,000 (330,000) $ 2,310,000 Contribution margin... Fixed costs: Fixed manufacturing costs ... Fixed selling and administrative expenses.. $ 530,000 100,000 Total fixed costs.... (630,000) $ 1,680,000 Operating income... Prepare an income statement under absorption costing.arrow_forwardCost per FIFO EUP In October, Pedraza Corp.'s production was 96,480 equivalent units for direct material, 87,840 equivalent units for direct labor, and 75,600 equivalent units for overhead. During October, direct material, conversion, and overhead costs incurred were as follows: Direct material $285,638 Conversion Overhead 303,437 153,360 Beginning WIP Inventory costs for October were $47,218 for direct material, $35,107 for direct labor, and $37,152 for overhead. The company had 12,960 EUP for direct material in October's beginning WIP Inventory, 14,400 EUP for direct labor, and 12,672 EUP for overhead. What was the October FIFO cost per EUP for direct material, direct labor, and overhead? Note: Round your answers to two decimal places. DM cost per EU S DL cost per EUS OH cost per EU Sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education