
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
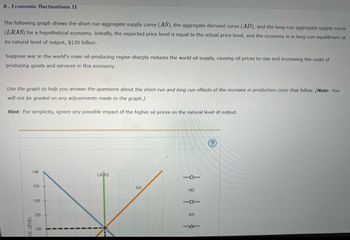
Transcribed Image Text:8. Economic fluctuations II
The following graph shows the short-run aggregate supply curve (AS), the aggregate demand curve (AD), and the long-run aggregate supply curve
(LRAS) for a hypothetical economy. Initially, the expected price level is equal to the actual price level, and the economy is in long-run equilibrium at
its natural level of output, $120 billion.
Suppose war in the world's main oil-producing region sharply reduces the world oil supply, causing oil prices to rise and increasing the costs of
producing goods and services in this economy.
Use the graph to help you answer the questions about the short-run and long-run effects of the increase in production costs that follow. (Note: You
will not be graded on any adjustments made to the graph.)
Hint: For simplicity, ignore any possible impact of the higher oil prices on the natural level of output.
?
140
LRAS
AS
CE LEVEL
135
130
125
120
AD
1
AS
-4
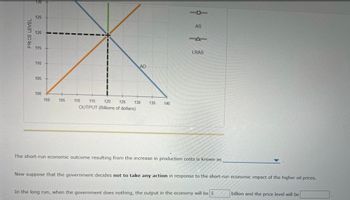
Transcribed Image Text:125
120
Q115
110
105
100
PRICE LEVEL
AS
14
LRAS
AD
100 105
110
115 120 125 130 135 140
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
The short-ru economic outcome resulting from the increase in production costs is known as
Now suppose that the government decides not to take any action in response to the short-run economic impact of the higher oil prices.
In the long run, when the government does nothing, the output in the economy will be $
billion and the price level will be
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3. Economic fluctuationsarrow_forward2arrow_forward6. Determinants of short-run aggregate supply The following graph shows an increase in short-run aggregate supply (AS) in a hypothetical economy where the currency is the dollar. Specifically, the short-run aggregate supply curve shifts to the right from AS1 to AS2, causing the quantity of output supplied at a price level of 100 to rise from $200 billion to $250 billion. 175 AS₁ 150 AS₂ 125 100 4 75 50 25 50 100 150 200 PRICE LEVEL 200 0 0 250 QUANTITY OF OUTPUT 300 350 400 ? The following table lists several determinants of short-run aggregate supply. Inflation expectations Tax rates Technology Fill in the table by indicating the changes in the determinants necessary to increase short-run aggregate supply. Change Needed to Increase ASarrow_forward
- 8. Critical analysis Q10 When output and employment slowed in early 2008, the Bush administration and the Democratic Congress passed legislation sending households a check for $600 for each adult (and $300 per child). These checks were financed by borrowing. Evaluate the following statement. True or False: A Keynesian would not favor this action because despite the fact that the U.S. economy seemed to operate below its potential capacity, the government should avoid financing its spending by borrowing at any cost. True Falsearrow_forwardQUESTION 17 Suppose the aggregate demand and short-run aggregate supply schedules for an economy whose potential output equals $2,700 are given by the table: Aggregate Quantity of Goods and Services Price Level Demanded Supplied 0.50 $3,500 $1,000 0.75 3,000 2,000 1.00 2,500 2,500 1.25 2,000 2,700 1.50 1,500 2,800 What is the size of the recessionary gap?arrow_forwardSuppose that firms become very pessimistic about future business conditions and cut heavily on investment in capital equipment. [Label A, B, C for the initial, new short-run and new long-run equilibrium respectively] a)Use an aggregate-demand/aggregate-supply model to show the short-run effect of this pessimism on the economy. Label the new levels of prices and real output. Explain in words why the aggregate quantity of output supplied changes. (Use the sticky wage theory in your explanation)arrow_forward
- 11. Recession True or False: The aggregate-demand curve slopes downward because it is the horizontal sum of the demand curves for individual goods. True Falsearrow_forward34) Unemployment would increase and prices would decrease if aggregate demand shifted left aggregate demand shifted right aggregate supply shifted left aggregate supply shifted rightarrow_forward(1) Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium. If there is a sharp increase in the expected price level, what do we expect to happen? Select one: (A) In the short run, the SRAS curve will shift left, real GDP and price will fall. (B) In the short run, SRAS will shift right, real GDP will rise and prices will fall. (C) In the short run, AD will shift left, real GDP and prices will fall. (D) In the short run, LRAS and SRAS will shift left, causing real GDP to fall.arrow_forward
- The following graph represents the short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS) based on an expected price level of 120. The economy's full- employment output level is $9 trillion. Major unions across the country have recently negotiated three-year wage contracts with employers. The wage contracts are based on an expected price level of 120, but the actual price level turns out to be 160. Show the short-run effect of the unexpectedly high price level by dragging the curve or moving the point to the appropriate position. PRICE LEVEL (CPI) 240 200 160 40 0 0 3 SRAS[120] 6 9 12 REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 15 18 SRAS[120] 0 (?) Interpret the change you drew on the previous graph by filling in the blanks in the following paragraph:arrow_forward8. Economic fluctuations I The following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion. Suppose the government increases spending on building and repairing highways, bridges, and ports. Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the increase in government spending. 240 AS 200 AD 160 AS 120 80 AD 40 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) In the short run, the increase in government spending on infrastructure causes the price level to the price level people expected and the quantity of output to the natural level of output. The increase in government spending will cause the unemployment rate to the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion, before the increase in…arrow_forward7. The long-run aggregate supply curve and short-run adjustments Suppose an economy's short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), current equilibrium aggregate price level (P₁), and real GDP (Q1) are shown on the graph that follows. The economy currently has Natural Real GDP (QN) of $6 trillion. Use this information to place the orange long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS, square symbols) in the correct position on the graph. 20 PRICE LEVEL 0 2 4 6 Q₁ REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 8 SRAS 10 LRASarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education