
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
8. Economic fluctuations I
The following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion. Suppose the government increases spending on building and repairing highways, bridges, and ports.
Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the increase in government spending.
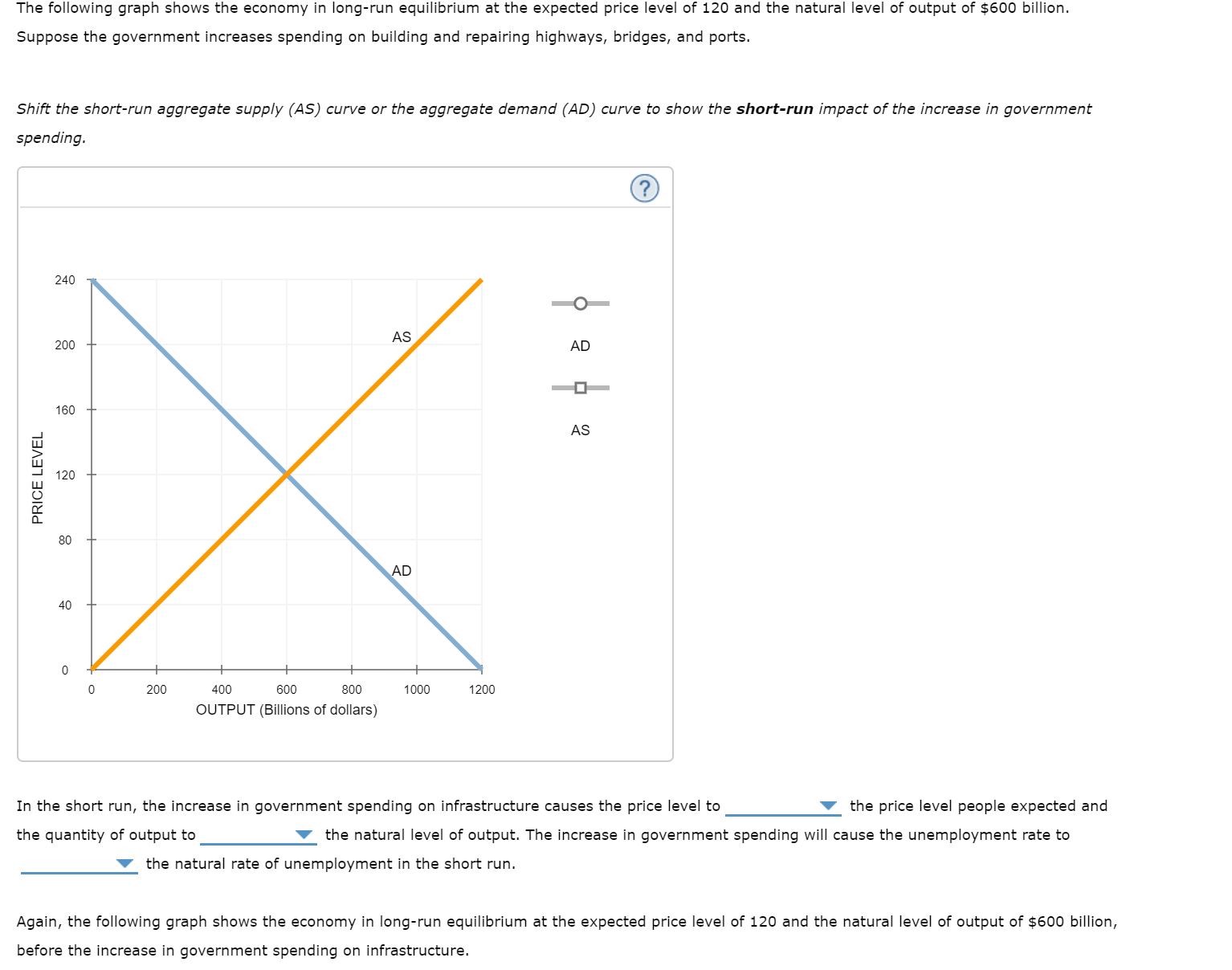
Transcribed Image Text:The following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion.
Suppose the government increases spending on building and repairing highways, bridges, and ports.
Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the increase in government
spending.
240
AS
200
AD
160
AS
120
80
AD
40
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
In the short run, the increase in government spending on infrastructure causes the price level to
the price level people expected and
the quantity of output to
the natural level of output. The increase in government spending will cause the unemployment rate to
the natural rate of unemployment in the short run.
Again, the following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion,
before the increase in government spending on infrastructure.
PRICE LEVEL
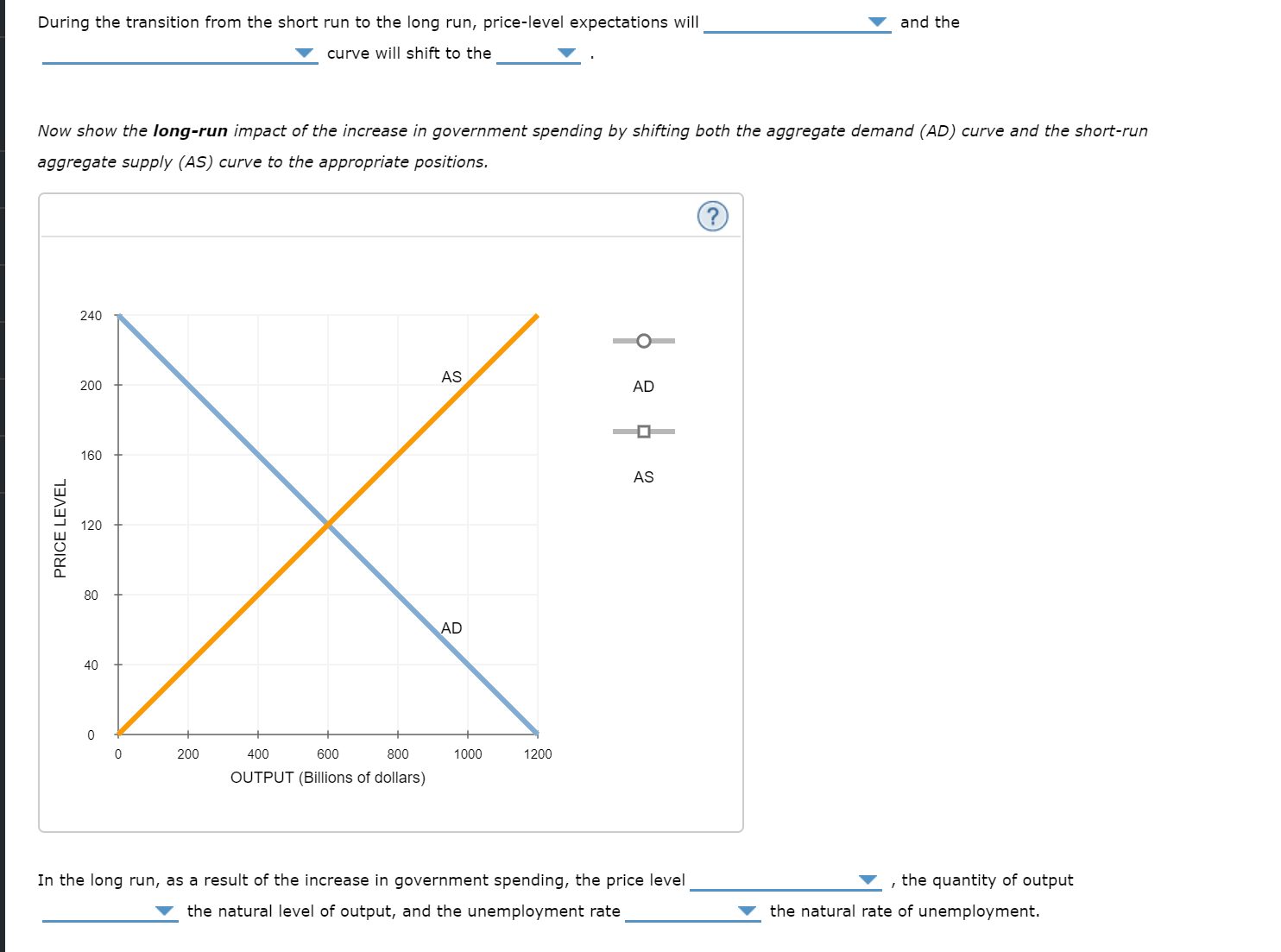
Transcribed Image Text:During the transition from the short run to the long run, price-level expectations will
and the
curve will shift to the
Now show the long-run impact of the increase in government spending by shifting both the aggregate demand (AD) curve and the short-run
aggregate supply (AS) curve to the appropriate positions.
240
AS
200
AD
160
AS
120
80
AD
40
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
OUTPUT (Billions of dollars)
In the long run, as a result of the increase in government spending, the price level
the quantity of output
the natural rate of unemployment.
the natural level of output, and the unemployment rate
PRICE LEVEL
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thank you!arrow_forwardWhen President Obama was President he had discussed raising income taxes for individuals earning over $250,000 in income. Question: Explain how these higher income taxes will affect the aggregate demand curve. Analyze how higher taxes can impact the spending of consumers and the overall economy.arrow_forward11. Recession True or False: The aggregate-demand curve slopes downward because it is the horizontal sum of the demand curves for individual goods. True Falsearrow_forward
- Worksheet 5: Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand Complete the questions below. Be sure to show your work. Upload this worksheet to Moodle. Consider the following Aggregate Supply and Aggregate Demand curves. 2. 3. D P 10 8 6 4 2 20 AS/AD 40 LRAS 60 80 140 SRAS AD Name: 100 120 GDP 4. Suppose the government increased spending (G). What would happen to Aggregate Demand? Draw the resulting curve, and mark a new equilibrium on the graph.arrow_forward8. Economic fluctuations I The following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion. Suppose the government increases spending on building and repairing highways, bridges, and ports. Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the increase in government spending. 240 AS 200 AD 160 AS 120 80 AD 40 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 OUTPUT (Billions of dollars) In the short run, the increase in government spending on infrastructure causes the price level to the price level people expected and the quantity of output to the natural level of output. The increase in government spending will cause the unemployment rate to the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion, before the increase in…arrow_forward7. The long-run aggregate supply curve and short-run adjustments Suppose an economy's short-run aggregate supply curve (SRAS), current equilibrium aggregate price level (P₁), and real GDP (Q1) are shown on the graph that follows. The economy currently has Natural Real GDP (QN) of $6 trillion. Use this information to place the orange long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS, square symbols) in the correct position on the graph. 20 PRICE LEVEL 0 2 4 6 Q₁ REAL GDP (Trillions of dollars) 8 SRAS 10 LRASarrow_forward
- 8. Economic fluctuations I The following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of $600 billion. Suppose a sudden and severe contraction in the housing market reduces the value of homes and causes consumers to spend less. Shift the short-run aggregate supply (AS) curve or the aggregate demand (AD) curve to show the short-run impact of the housing market slump. (2) 240 AS 200 AD 140 AS 120 80 AD 40 200 400 800 1000 1200 OUTPUT (BIlons of dollars) In the short run, the decrease in consumption spending associated with the housing market contraction causes the price level to * the price level people expected and the quantity of output to v the natural level of output. The housing market slump will cause the unemployment rate to the natural rate of unemployment in the short run. Again, the following graph shows the economy in long-run equilibrium at the expected price level of 120 and the natural level of output of…arrow_forwardi have provided two screenshots. thank youuuuuuuarrow_forward8arrow_forward
- 3. Explain whether each of the following events will increase, decrease, or have no effect on longrun aggregate supply in your country. a. There is an increase in immigration into your country. b. Your government introduces a minimum wage above the market-clearing wage rate. c. Intel invents a new and more powerful computer chip. d. A severe flood damages factories.arrow_forwardEconomics 8arrow_forwardIf the price level rises, what happens to aggregate supply? Aggregate supply _______. A. doesn't change, but the quantity of real GDP supplied increases B. decreases C. increases D. doesn't change, but the quantity of real GDP supplied decreasesarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education