
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
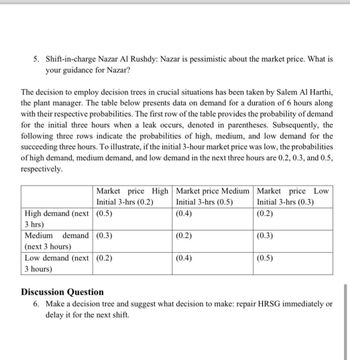
Transcribed Image Text:5. Shift-in-charge Nazar Al Rushdy: Nazar is pessimistic about the market price. What is
your guidance for Nazar?
The decision to employ decision trees in crucial situations has been taken by Salem Al Harthi,
the plant manager. The table below presents data on demand for a duration of 6 hours along
with their respective probabilities. The first row of the table provides the probability of demand
for the initial three hours when a leak occurs, denoted in parentheses. Subsequently, the
following three rows indicate the probabilities of high, medium, and low demand for the
succeeding three hours. To illustrate, if the initial 3-hour market price was low, the probabilities
of high demand, medium demand, and low demand in the next three hours are 0.2, 0.3, and 0.5,
respectively.
Market price High
Market price Medium
Initial 3-hrs (0.2)
Initial 3-hrs (0.5)
Market price Low
Initial 3-hrs (0.3)
High demand (next (0.5)
(0.4)
(0.2)
3 hrs)
Medium
demand (0.3)
(0.2)
(0.3)
(next 3 hours)
Low demand (next (0.2)
(0.4)
(0.5)
3 hours)
Discussion Question
6. Make a decision tree and suggest what decision to make: repair HRSG immediately or
delay it for the next shift.
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose 1,250 raffle tickets are being sold for $5 each. One ticket will be chosen to receive a cash prize of $2,500, and three tickets will be chosen to recelve cash prizes of $500. Let x be the amount of money won/lost by purchasing one raffle ticket. Find the expected value for . (Round your answer to the nearest penny. Do not include as sign in your answer. Your answer may be positive or negative.)arrow_forwarda and b pleasearrow_forwardConsider the following interaction between a student and a company. The student is either serious or lazy with probabilities 1/3 and 2/3 respectively. The student knows if they are serious or not, but the company does not. Initially, the student decides whether to revise for exams or not. Revising has a cost of 1 for a serious student and 3 for a lazy one. The company observes the student's exam result (that is, whether they have made the effort to revise), and based on this, offers a salary of 3 (for a serious student) or 1 (for a lazy student). The student learns of the proposed salary and can then either accept (and earn the salary) or refuse (and earn O). They also lose the revision effort if they worked. The company's gain is equal to the student's productivity (4 if they are serious, 2 if not) minus the salary if the student accepts the offer, and O otherwise. 1. Represent the game in extensive form. 2. Show that the game has a unique perfect Bayesian Equilibrium, and provide the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education