
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:5
(a) Water at 10°C (p = 999.7 kg/m³ and μ =1.307 x 10-³ Pa-s ) is flowing steadily in a 0.20-cm-
diameter, 15-m-long pipe at an average velocity of 1.2 m/s. Determine (i) the pressure drop,
(ii) the head loss, and (iii) the pumping power requirement to overcome this pressure drop.
(b) If the average water velocity is increased to 2.4 m/s in the same pipe then compare the
pumping power requirement.
Given that
64
Re D
—=5×10-5; APL = F/P1²
LpV²
f
D 2
f = ;
Note: Use Moody's Chart/diagram if required (next page)
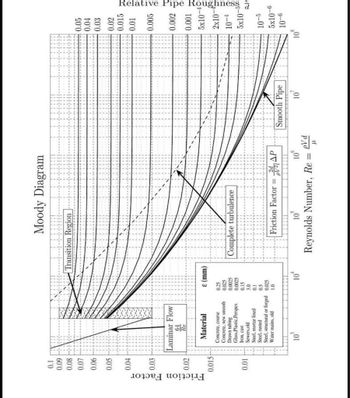
Transcribed Image Text:Friction Factor
0.1
0.09
0.08
0.07
0.06
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.015
0.01
Laminar Flow
64
Re
Material
Concrete, coarse
Concrete, new smooth
0.25
0.025
0.0025
0.0025
0.15
3.0
0.1
0.5
Steel, structural or forged 0.025
Water mains, old
1.0
Drawn tubing
Glass Plastic Perspex
Iron, cast
Sewers,old
Steel, mortar lined
Steel, rusted
10
ε (mm)
10
Moody Diagram
Transition Region
Complete turbulence
2d
Friction Factor P
PV²1²
10³
10°
pVd
Reynolds Number, Re= "
=
Smooth Pipe
10'
0.05
0.04
0.03
0.02
0.015
0.01
0.005
0.002
0.001
5x10-4
2x10-
10-4
5x10
Relative Pipe Roughness à
10-5
5x10-6
10-6
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 500 mm diameter pipe carries water at a rate of 500 L/s. A pump in the pipe is used to move the water from point A (El 30 m) to point B (El 40 m). The pressure is 70 kPa in A and 350 kPa in B. Assume a head loss of 3 m from point A to point B. a.What is the velocity of flow? ts) b. What is the head supplied by the pump? c. What horse power must be supplied to the flow by the pump if it is 85% efficient?arrow_forward12.10 Find the flow rate in the siphon in figure 12.39. What is the pressure at point A, which is 150 mm above the outlet? Estimate the minimum pressure in the system. 1.8 m #11 Curva de retorno cerrada Petróleo, S=0.8 = 0.01 N-s/m² 100-mm-diam tubería lisa 3.6 m 150 mm 50-mm diam boquilla Pérdida = 0.1 Figura 12.39 Problema 12.10. Iarrow_forwardSITUATION 2: Three reservoirs A, B, and C are connected respectively with pipes 1, 2, and 3 joining at a common junction P. Reservoir A is at elevation 80 m, reservoir B at elevation 70 m and reservoir C is at elevation 60 m. The properties of each pipe are as follows: Elev 80 ha hez Elev 70 B 4000 m- 250 mm f-0.018 he 3500 m f- 0.018 Elev 60 Pipe 1: L= 5000 m, D = 300 mm Pipe 2: L= 4000 m, D = 250 mm Pipe 3: L= 3500 m 5000 m - 300 mm f= 0.018arrow_forward
- The three water-filled tanks shown in the figure below are connected by pipes as indicated. If minor losses are neglected, determine the flow rate in each pipe (+ is out and-is into the reservoir) Assume ha - 20 m, he-50m.hc-0m., = 400 m, ₂= 250 m, and 3 = 500 m. QA- QB Qc- Elevation - h D-0.08 m 7,-0.020 Elevation- V B D-0.10m -0.015 D-0.08 m -0.020 Elevation - he Carrow_forwardA reservoir discharges a liquid to the atmosphere through a horizontal of pipes. Thepipeline consists pipe A (D= 10 cm & L = 25 m) and pipe B (D= 12 cm & L = 35 m) areconnected in series. The water level in the tank is 10 m from centreline pipe entranceand f = 0.02 for both pipe. Calculate the discharge by considering all losses.arrow_forwardCalculate the discharge from a tubewell of 20-cm diameter penetrating fully into a confined aquifer of 20-m thick and having a permeability of 40 m/day. The drawdown in the well is 3 m and zero drawdown at 300 m from the well. Q = 2.72 T (H-h) log 10 R/r Select one: O a. 1315.9 O b. 1303.7 O C. O d. 1257.3 1200.4arrow_forward
- Q2: A is 4500 m length-gas flow line, and B is 2000 m length-liquid flow line (0.1 m diameter) both are connected with left side of 2500 m in length C-pipeline (0.15 m). If the pressure at A-pipeline inlet = 2400 kPa, pressure at C-pipeline out let = 2000 kPa, liquid flow rate = 0.009 m³/s, Gas Oil Ratio = 40 m³/m², PL 680 kg/m³, p=0.922 kg/m³, gas flowing temperature-300 K, base temperature-288 K, base pressure 101.3 kPa, Z-0.9, gas gravity 9.4x10-3 Pa.s, calculate the 0.6, gas viscosity-0.015x10³ Pa.s, and liquid viscosity diameter of gas pipeline and inlet pressure of liquid pipeline? Assume all pipes are flat and horizontal. =arrow_forwardA reservoir is fitted with a pump discharging into the open air at point B. The pressure at section A is considered to be under a vacuum of 10 inHg ad the discharge rate is given at 3 ft/sec. Determine the total head for this system with the datum elevation at the base of the reservoir. 10-in-diameter 8-in-diameter suction pipe discharge pipe 40 ft Pump 15 ft 25 ft O 81.15 ft O 92.45 ft O 71.33 ft O 120.71 ftarrow_forwardA pump draws water from reservoir A and lifts it to reservoir B as shown. The loss of head from A to 1 is 3 times the velocity head in the 150mm pipe and the loss of head from 2 to B is 20 times the velocity head in the 100mm pipe. When the discharge is 20 liters/sec. Compute the pressure head at point 1 and 2. B EL240m ELO 150 mm EL-20m • ura 001arrow_forward
- A cylindrical tank (Figure 2) of diameter 50cm connected to a horizontal pipe (diameter is 8 cm) flow resulting in tank filling. The pipe inlet velocity is 5m/s while the outlet velocity is 3.5 m/s. Determine; a)The rate of change of height of water inside the tank b)The time required to fill the tank if the tank was initially empty. Note: Flow is incompresible. (Answer 3.84cm/s & 65.1s) Figure 2 Alli 50cm D=8cm 2.5marrow_forwardThe tank has a square base and is filled with water to the depth of y = 0.4 m. If the 20-mm-diameter drain pipe is opened, determine the initial volumetric flow of the water and the volumetric flow when y = 0.2 m. 2 m Barrow_forwardSituation 7: From reservoir A whose water surface elevation is 225 m. Water is pumped through a 350 mm pipe across a valley at a second reservoir B at a elevation of 240 m. During pump, the pressure is 570 kPa at a point C and at elevation of 195 m. Assume that the headloss in the pipe from reservoir A to point C is 30 times its velocity head and from point C to reservoir B is 50 times its velocity head 23. Compute the discharge in the pipeline in L/s 24. Compute the head added by the pump 25. Compute the horsepower exerted by the pump IVA E1225 m El 240 m El 195 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning