
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
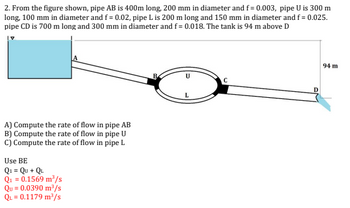
Transcribed Image Text:2. From the figure shown, pipe AB is 400m long, 200 mm in diameter and f= 0.003, pipe U is 300 m
long, 100 mm in diameter and f = 0.02, pipe L is 200 m long and 150 mm in diameter and f= 0.025.
pipe CD is 700 m long and 300 mm in diameter and f= 0.018. The tank is 94 m above D
A) Compute the rate of flow in pipe AB
B) Compute the rate of flow in pipe U
C) Compute the rate of flow in pipe L
Use BE
Q1 = Qu + QL
Q₁ = 0.1569 m³/s
Qu= 0.0390 m³/s
QL = 0.1179 m³/s
U
L
C
94 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The head-discharge relationship for a certain pump can be represented by the equation H = 28 -9Q². The pump is fixed 2.5 m above the water surface in a river and it forces the water to a tank at a level 10 m above the pump. The suction and delivery pipes are 15 m and 740 m long, respectively and each pipe is 0.5 m in diameter. The pipe coefficient of friction (f) is 0.017. Estimate the discharge (in m³/s) at the best operating point for the pumping system. Q = 0.6 m³/s Q = 0.9 m³/s Q = 0.4 m³/s Q = 1.1 m³/sarrow_forwardQUESTION SIX (6a) A siphon is made of a pipe whose inside diameter is 25.4 mm and is used to maintain a constant level in a 6.0975m deep tank (Fig. 6.1). If the siphon discharge is 9.144m below the top of tank, what will be the flow rate if the fluid level is 1.524m below the top of tank? Z₁ = 6.0975 m 1.524 m U tube Fig. 6.1 (6b) Briefly explain any five components of water cycle N Z₁ = 9.144 marrow_forwardGiven the following data for three pipes in parallel: Pipe 1: D1 = 450 mm, L1 = 800 m ; Pipe 2: D2 = 400 mm, L2 = 700 m; Pipe 3: D3 = 500 mm, L3 = 600 m. The total flow is 0.86 m3/s. Assume f = 0.02 for all pipes Determine the flow in pipe 1 in m3/s Determine the flow in pipe 2 in m3/s Determine the flow in pipe 3 in m3/sarrow_forward
- A pipeline x joins pipelines 1, 2 and 3 at junction A. The pipelines 1, 2 and 3 merges at junction B to form a single pipeline y. The pressure heads at A and B are 78m and 42m, respectively. Use Hazen-Williams constant C = 120 for all pipes. 1 X A В У 3 Pipe 1 Length 3,000 m 1,300 m 2,600 m Diameter 300 mm 200 mm 2 3 250 mm Which of the following most nearly gives the rate of flow in pipeline 1? 0.0859 cu.m/s O 0.1284 cu.m/s 0.0694 cu.m/s 0.1038 cu.m/sarrow_forward1. Compute the head loss in a pipe with diameter 300 mm for a length of 15,000 meters and carrying a flow of 0.097, if f=0.02. (Hint: Use h=(0.0826fL(Q^2))/(D^5)arrow_forward2. The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 3 vertical in 4 along the pipe which is 12 cm in diameter. The pipe is 7.2 m long; its lower end being just below the water surface in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is desirable that pressure at inlet to the pump Pump 4/3 shall fall to more than 75 kPa below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, determine the maximum discharge that the pump may deliver. Take atmospheric Suction pipe pressure as 101.32 kPa. F.W.S. Reservoir/sump 2. 7.2 marrow_forward
- Determine the flow rate in all pipes.arrow_forwardThe SN= 17arrow_forwardThe total flow in the pipe system in the figure is 0.86 m³/s. Assume f = 0.032 for all pipes. A. What is the flow in pipeline 1? (m³/s) B. What is the flow in pipeline 2? (m³/s) C. What is the flow in pipeline 3? (m³/s)arrow_forward
- Answer as fast as possible, use 3 decimalarrow_forwarda pipeline 50 cm diameter and 4500 m long connects two reservoirs (1 &2) whose constant difference of water level is 12 m, A branch pipe 1250 m long and taken from a point distant 1500 m from the upper reservoir(1) leads to another reservoir (3) whose water level is 15 m below reservoir (1) find the diameter of pipe (D3) so that the flow into both the reservoir is same if friction factor =0.0075 Select one: a. D3= 22.5 - 27.5 cm b. D3= 33.5 - 40.5 cm c. D3= 27.5 - 32.5 cm d. D3= 17,5- 22.5 cmarrow_forwardThree parts ...arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning