
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
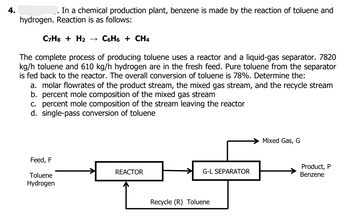
Transcribed Image Text:4.
In a chemical production plant, benzene is made by the reaction of toluene and
hydrogen. Reaction is as follows:
C7H8 + H₂
C6H6 + CH4
The complete process of producing toluene uses a reactor and a liquid-gas separator. 7820
kg/h toluene and 610 kg/h hydrogen are in the fresh feed. Pure toluene from the separator
is fed back to the reactor. The overall conversion of toluene is 78%. Determine the:
a. molar flowrates of the product stream, the mixed gas stream, and the recycle stream
b. percent mole composition of the mixed gas stream
c. percent mole composition of the stream leaving the reactor
d. single-pass conversion of toluene
Mixed Gas, G
Feed, F
REACTOR
G-L SEPARATOR
Toluene
Hydrogen
Recycle (R) Toluene
Product, P
Benzene
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- how to draw and label a process flowchartarrow_forwardRef Example 9.5-3: The dehydrogenation of ethanol to form acetaldehyde is carried out in a continuous adiabatic reactor. Ethanol vapor is fed to the reactor at 400 °C, and a conversion of 30% is obtained. Calculate the product Temperature. CpSisto 48 có xio 7 +2.38 X10 T 05 x 10-872 C₂H5OH(v)→ CH3CHO(v) + H₂(g) Solution REACTOR 100 mol C₂H5OH(v) 400°C C₂H50H (V), CH³ CHO (V), H₂ a 70 mol C₂H5OH(v) 30 mol CH3CHO(v) 30 mol H₂(g) Tad (°C)arrow_forwardBenzene vapor is burned in air. Find the molar enthalpy of the reactants and the products if all heat is extracted from the reaction and the initial and final temperatures are equal. (Assume the H2O product is a liquid)arrow_forward
- Alumina from bauxite separation stage calculations A crucial step in the production of aluminum from bauxite ore is the separation of alumina from the remaining mineral impurities in the ore. In the Bayer process this is accomplished by treating bauxite with aqueous NaOH to produce NaAIO2 (alumina). NaOH(aq) + Al(OH)3(s) → NaAIO2(aq) + 2H2O(1) Since NaAIO2 is water soluble while the residual mineral constituents of bauxite are not, a separation can be achieved by allowing the minerals to settle out and decanting the aqueous solution of NAAIO2 and unreacted NaOH. In order to further recover any NAAIO2 entrained in the settled mineral solids, this "mud" is repeatedly washed with water and allowed to settle, and the wash water is decanted. The figure below shows one stage of this washing-settling process. Wash water Slurry - Open to air Mixer/Wash tank Setling tank Decanted solution System boundary Washed mud In this stage, a feed slurry consisting of 10 wt% solids, 11 wt% NaOH, 16 wt%…arrow_forwardMonochlorobenzene (M) is produced commercially by the direct catalytic chlorination of benzene (B) at 50.0 °C and 140.0 kPa absolute. In the process, dichlorobenzene (D) is generated as a co-product: CH6 + Cl2- CgH;CI + HCI CGH5CI + Cl2 – C&H4CI2 + HCI Liquid and gas streams leave the reactor. The liquid contains 39.2 wt% M, 32.6 % D, and the remainder unreacted B. The gas, which is sent to a treatment facility, contains 92.0 %(v/v) HCl and 8 % unreacted chlorine. Assume ideal-gas behavior. Volume of Gas Check stoichiometry and gas behavior. What volume of gas leaves the reactor (m³) per kg B fed? i ! m3arrow_forwardOne of the ways that benzene is produced on a large scale is the hydrodealkylation of toluene. C,H,CH; + H, C,H, + CH4 A stream of toluene is mixed with a recycle stream and enters a reactor along with a stream of pure hydrogen. The reaction products at 550 °C enter a condenser, where they are cooled to 41.0 °C. A vapor stream containing Y5CH, = 0.600 mol CH,/mol leaves the process, and a liquid stream containing x66 = 0.810 mol benzene/mol and x6 = 0.190 mol toluene/mol enters a distillation column. The distillate of the column leaves the process at n7 = 668.0 mol/h and contains y7h = 0.9000 mol benzene/mol and y7 = 0.1000 mol toluene/mol. The bottoms of the column contains X8b = 0.250 mol benzene/mol and xgt = 0.750 mol toluene/mol and is recycled back to the fresh feed. Hydrogen is fed into the process at ni = 1183 mol H,/h. This process is carried out at 760 mmHg. A n, mol/h mol H/mol YSH2 YSCH, mol CH_/mol Ysh mol b/mol Ys mol t/mol n̟ mol/h n, mol/h Condenser Улн, тol H/mol Усн,…arrow_forward
- #3 The first step in the reaction sequence for the production of nitric acid via the oxidation of ammonia is: 4NH3 + 502 2 4NO + 6H2O 75% conversion is achieved with an equimolar mixture of ammonia and oxygen fed at the rate of 100 mol/h. Determine the outlet compositions. (Hint: determine the limiting reactant).arrow_forwardReview | Constants | PeriIodic Table The standard heat of formation, Ar H°, is defined as the enthalpy change for the formation of one mole of substance from its constituent elements in their standard states. Thus, elements in their standard states have AfH® =0. Heat of formation values can be used to calculate the enthalpy change of any reaction. Part A For which of the following reactions is A,H° equal to Ar H° of the product(s)? Consider, for example, the reaction You do not need to look up any values to answer this question. 2NO(g) + O2(9) = 2NO2(9) Check all that apply. with heat of formation values given by the following table: • View Available Hint(s) Substance (kJ mol-1) NO(9) O C(s) + 02 (9)→CO2(9) 90.2 O2 (9) O Li(s) + F2(1)→LIF(s) NO2(9) 33.2 O Li(s) + F2(9)→LİF(s) O 2Li(s) +F2(9)→2LİF(s) Then the heat of formation for the overall reaction is A,H°= EnpAf H° (products)- nA¢H° (reactants) O CO(g) + ÷O2(9)→CO2(9) 2(33.2) [2(90.2) + 0] -114 kJ mol-1 O BaCO3(s)→BA0(s) + CO2(9)…arrow_forwardUse the chemical reaction below to answer the following questions HCI(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (I) AH298 = -58 kJ/mol (a) How much heat is produced when 200 mL of 0.3 M HCL (density = 1.00 g/mL) and 250 mL of 0.25 M NaOH (density = 1.00 g/mL) are mixed? (b) If both of the solutions at the same temperature and the heat capacity of the products are 5.39 J/g °C , how much will the temperature increase? (c) What assumptions are made when calculating your answersarrow_forward
- A feed stream containing 15% wt solids and 85% wt water is introduced in a certain process where the solids are being crushed. The crushed solids and preservatives are mixed in a 4:5 mass ratio and the mixture is heated to evaporate water. The residue has 1/3 water by mass. write step by step process: how many unknowns how many independent equations can be made? calculate the mass fraction of the solids in the product stream after producing 100 g of the product residue. Report your answer to 4 decimal places.arrow_forwardFresh methanol (CH3OH) reactant is combined with recycled reactant and vaporized before being sent to a fixed-bed reactor. The reactor effluent is then cooled before being sent to the first of two distillation columns. DME (CH3)2O product is taken overhead from the first column. The second column separates the water from the unused methanol. The methanol is recycled back to the front end of the process, and the water is sent to wastewater treatment to remove trace amounts of organic compounds. Draw a block flow diagram for this process. The main reaction is 2CH3OH → (CH3)2O + H2Oarrow_forwardBenzaldehyde is produced from toluene by the following catalytic reaction : C6H5CH3 + O2 → C6H5CHO + H2O Dry air and toluene vapor are fed to the reactor at 350 F and 1 atm. Air is supplied 100% in excess. Of the toluene that is fed to the reactor, 13% reacts to form benzaldehyde and 0.5% reacts with oxygen to form CO2 and H2O. The gases produced leave the reactor at 379 F and 1 atm. Water is circulated through the jacket surrounding the reactor, and it enters at 20 ° C and exits at 55 ° C. Calculate: a. Moles of benzaldehyde formed (mol)?Note: Do not use decimals for your answer. b. Moles of toluene that did not react (mol)? c. Moles of water generated (mol)? d. Moles of carbon dioxide generated (mole)? e. Moles of oxygen that do not react (mol)? f. Reactor heat transfer rate (kJ / h) g. Cooling water flow rate (cm3 / h) Data: Δhvap benzaldehyde (179 ° C) = 38.40 kJ / mol Cp benzaldehyde (Liq) = 59.42x10-2 kJ / mol Cp benzaldehyde (vap) = 40.05x10-2 kJ / molarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The