
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
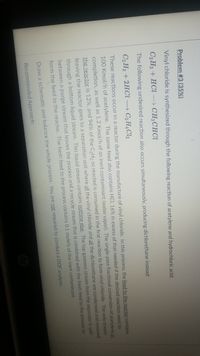
Transcribed Image Text:Problem #3 (35%)
Vinyl chloride is synthesized through the following reaction of acetylene and hydrochloric acid:
C2 H2+ HCl → CH2CHC
The following undesired reaction also occurs simultaneously, producing dichlorethane instead:
C2 H2 + 2HCI C2 H4CL2
-
These reactions occur in a reactor during the manufacture of vinyl chloride. In this process, the feed to the reactor contains
100 Kmol/h of acetylene. The same feed also contains HCI, 16% in excess of that needed if the desired reaction went to
completion, as well as 1.2 Kmol/h of an inert contaminant (water vapor). The single-pass fractional conversion of acetylene in
the reactor is 12%, and 94% of the C2H2 so reacted is consumed in the first reaction to form vinyl chloride. The only stream
leaving the reactor goes to a separation unit where all the vinyl chloride and all the dichlorethane are condensed and removed
through a bottom liquid stream. This liquid stream contains nothing else. The top gaseous stream from the separator is split
between a purge stream that leaves the process and a recycle stream that is combined with the fresh feed to the process to
form the feed to the reactor. The fresh feed to the process contains 0.1 mole% of the inert contaminant.
Draw a schematic and balance the whole process. You are not required to conduct a DOF analysis.
Recommended Approach:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help with the material balances!!!!! Please!!arrow_forwardAlumina from bauxite separation stage calculations A crucial step in the production of aluminum from bauxite ore is the separation of alumina from the remaining mineral impurities in the ore. In the Bayer process this is accomplished by treating bauxite with aqueous NaOH to produce NaAIO2 (alumina). NaOH(aq) + Al(OH)3(s) → NaAIO2(aq) + 2H2O(1) Since NaAIO2 is water soluble while the residual mineral constituents of bauxite are not, a separation can be achieved by allowing the minerals to settle out and decanting the aqueous solution of NAAIO2 and unreacted NaOH. In order to further recover any NAAIO2 entrained in the settled mineral solids, this "mud" is repeatedly washed with water and allowed to settle, and the wash water is decanted. The figure below shows one stage of this washing-settling process. Wash water Slurry - Open to air Mixer/Wash tank Setling tank Decanted solution System boundary Washed mud In this stage, a feed slurry consisting of 10 wt% solids, 11 wt% NaOH, 16 wt%…arrow_forwardBasic Principles of Chemical Engineering Question Please solve step by steparrow_forward
- One of the ways that benzene is produced on a large scale is the hydrodealkylation of toluene. C,H,CH; + H, C,H, + CH4 A stream of toluene is mixed with a recycle stream and enters a reactor along with a stream of pure hydrogen. The reaction products at 550 °C enter a condenser, where they are cooled to 41.0 °C. A vapor stream containing Y5CH, = 0.600 mol CH,/mol leaves the process, and a liquid stream containing x66 = 0.810 mol benzene/mol and x6 = 0.190 mol toluene/mol enters a distillation column. The distillate of the column leaves the process at n7 = 668.0 mol/h and contains y7h = 0.9000 mol benzene/mol and y7 = 0.1000 mol toluene/mol. The bottoms of the column contains X8b = 0.250 mol benzene/mol and xgt = 0.750 mol toluene/mol and is recycled back to the fresh feed. Hydrogen is fed into the process at ni = 1183 mol H,/h. This process is carried out at 760 mmHg. A n, mol/h mol H/mol YSH2 YSCH, mol CH_/mol Ysh mol b/mol Ys mol t/mol n̟ mol/h n, mol/h Condenser Улн, тol H/mol Усн,…arrow_forward#3 The first step in the reaction sequence for the production of nitric acid via the oxidation of ammonia is: 4NH3 + 502 2 4NO + 6H2O 75% conversion is achieved with an equimolar mixture of ammonia and oxygen fed at the rate of 100 mol/h. Determine the outlet compositions. (Hint: determine the limiting reactant).arrow_forwardPlease answer the question with the steps... Thank youarrow_forward
- 1. In a process for the manufacture of chlorine by direct oxidation of HCI with air over a catalyst to form Cl₂ and H₂O (only), the exit product is composed of HCI (4.4%), Cl₂ (19.8%), H₂O (19.8%), O₂ (4.0%), and N₂ (52.0%). The chemical reaction involved is as follow: 4HC1+02 → 2Cl2 + 2H₂0 Find a) limiting reactant and excess reactant, b) percent excess reactant, c) degree of completion of the reaction, d) extent of reactionarrow_forward3. Kindly answer this and show your solution.arrow_forwardA barytes composed of 100 percent BaSO4 is fused with carbon in the form of cokecontaining 6 percent ash (which is infusible). The composition of the fusion mass is:BaSO4 11.1%BaS 72.8%C 13.9%Ash 2.2 100% Reaction: BaSO4 + 4 C → BaS + 4 COFind the :4.1 Excess reactant. (10)4.2. The percentage of the excess reactant. (3)4.3. The degree of completion of the reaction. ?arrow_forward
- 4. At 1084 °C solid copper melts to form a liquid. The phase change can be described as Cu(s) → Cu(t). The density of solid and liquid copper are 8.96 g/cm' and 7.75 g/cm' respectively. The enthalpies of combustion of the solid and liquid are -156.06 kJ/mol and -167.92 kJ/mol respectively. The product of combustion of both the solid and liquid is CuO(s). Calculate the standard enthalpy changes for the fusion process in kJ/mol. Calculate the change in internal energy when the sample is under a pressure of 500 kbar. Cu(s) → Cu(e) Solid copper liquid copper enthalples of combustion 8.96 g/cm3 7.75 g 1cm² said: -156.06 kJ/mol liquid-162.42 kJ/molarrow_forwardMaterial and energy balancearrow_forwardAmmonia can react with oxygen according to the following two reactions: 4 NH3 + 5 O2 → 4 NO + 6 H2O 2 NH3 + 3/2 O2 → N2 + 3 H2O 28.8 mole NH3 enter the reactor, along with 180 mole O2. The reaction proceeds to 0.61 fractional conversion of ammonia and the selectivity of NO over N2 is 4.7. Determine the mole of oxygen exiting the reactor. Report your answer with two decimal place.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The