
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:Te-1 - Compatibility Mode
Word
9 Search
ces
Mailings
Review
View
Help
E - E- E E AL I
AaBbCcC AaBbCcl AaBbCcC AaBbCcC AaBbCcC AaBb( AaB
三三三 、 、田v
I Normal
1 Body Text 1 List Para. I No Spac. 1 Table Pa.. 1 Heading 1 1 Hea
Paragraph
Styles
. I .1 I 2 I 3 .....
4. 5 6 I
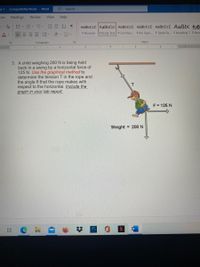
3. A child weighing 200 N is being held
back in a swing by a horizontal force of
125 N. Use the graphical method to
determine the tension T in the rope and
the angle e that the rope makes with
respect to the horizontal. Include the
graph in your lab report.
F = 125 N
Weight = 200 N
%2:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A rope is run through a frictionless pulley and then attached to a 16 kg block as shown. The other end of the rope is then pulled at a 45 deg angle to keep the block suspended in the air. What force, F, is required to keep the block suspended motionless? M N 1450 Farrow_forward1. A car of mass 1000.0 kg is stationary on a slope forming an angle = 20° with the horizontal line. The car is located at a distance of 50 m from the foot of the slope. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the road is μ = 0.20. a. Draw a free-body-diagram of the problem including all the information that is provided. b. Will the car slide down the slope? Motivate your answer to obtain any points. Once the car starts sliding down the slope, the coefficient of dynamic friction becomes μ = 0.15. c. Calculate the acceleration of the car. d. Calculate the velocity of the car at the foot of the slope. e. Calculate the kinetic energy of the car at the beginning and at the end of the motion. f. Calculate the total work done on the car. g. Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the car at the beginning and at the end of the motion. h. Calculate the work done on the car by the gravitational force. i. Calculate the work done on the car by the frictional force.arrow_forwardThere are two images, one has the question information and the other is the question.arrow_forward
- In the figure provided, a 265 kg crate, to the right of the pulley, is released from rest and begins to fall to the ground. If the mass on the left is m = 140. kg, what is the magnitude of the tension of the rope attached to the 265 kg crate? Assume the rope and pulley are massless. select correct answer. a) 898 Nb) 2.60×103 Nc) 1.80×103 Nd) 1.37×103 Narrow_forwardDon't use chat gpt Itarrow_forward5. A block of weight w = 100 N is suspended from a rope tied to two other ropes at point O. One rope is horizontally attached to a wall and the other is fastened to the ceiling. The angle between ceiling and the rope is 60°. Assume the weights of the ropes and the knot are negligible. Calculate the tension in each rope (T₁, T2, and T3). I T2 0 T3 W 60° Earrow_forward
- A loudspeaker of mass 16.0 kg is suspended a distance of h= 2.00 m below the ceiling by two cables that make equal angles with the ceiling. Each cable has a length of I = 3.30 m. (Figure 1) Part A What is the tension T in each of the cables? Use 9.80 m/s for the magnitude of the acceleration due to gravity. T = Submit Request Answer Figurearrow_forwardYou need to push a couch 4 m to the other side of the room. After the initial push to get it going you push on the 90kg couch with a steady horizontal force of 600 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the couch and the floor is 0.6. 1. What is the magnitude and direction of the frictional force on the couch? 2. What is the magnitude and direction of the net force on the couch? 3. What is the magnitude and direction of the acceleration of the couch?arrow_forwardI Review Part A Find the tension in the string connecting mj and m2. Assume the table is frictionless and the masses move freely. (Figure 1) Express your answer using two significant figures. Υ ΑΣΦ T = Submit Request Answer Figure 1 of 1 Part B m, = 1.0 kg m2 = 2.0 kg Find the tension in the string connecting m2 and m3. Express your answer using two significant figures. m, = 3.0 kg 0 ΑΣφ T2 = Pearsonarrow_forward1. A man pulls a crate with a rope. The crate slides along the floor in the horizontal direction (x direction). The man exerts a force of 50 N on the rope, and the rope is at an angle . Describe how the force components change as the angle increases from 0° to 90° and use your graph to explain your answer. Give a detailed explanation of the forces at 0 = 0°,45°, and 90°. Show a sample calculation at one angle for both components.arrow_forwardA block of mass 3.7 kg is stationary on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction, µg= 0.25. Calculate the magnitude of the maximum possible static friction force, in N, which can be generated, if an external force is applied to the block. Use 2 s.f. in your answer. L. FN +X F f. W = mgarrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of a normal force on a 22.7 kg block in the following circumstances. a. the block is resting on a level surface. b. the block is resting on a surface tilted up at 40.8 degrees with respect to the horizontal. c. the block is resting on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward at 2.53 m.s^2 d. the block is on the level surface and a force of 115 N is exerted on it at an angle of 40.8 degrees below the horizontal.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON