
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:1. Recognize the following types of biomolecules when given images such as the ones below
and on the next page:
• glucose (which is a monosaccharide)
•
polysaccharide
• amino acid
●
I
• protein (recall a protein with less than 50 amino acids can also be called a peptide
whereas a protein with 50 or more amino acids can also called a polypeptide)
• steroids
• triglycerides
● phospholipids
● DNA
. RNA
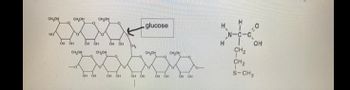
Transcribed Image Text:CH₂OH онон
НО
но но
но но
OH OH
скон CH,OH
OH OH
OH OH OH OH
но
glucose
онон
OH OH
НО НО
снон
OH OH
Н
H
N-C-C
'H
Н
0²
НО
CH₂
CH₂
S-CH3
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 6. Using the charges you calculated above, plot the characteristics of alanine over a range of pH values. Connect the points by estimating what the charge should be at pH values where you lack data. It is possible to calculate the charge at any pH, but if you understand the relationships presented here you will be able to make estimates quickly and easily. +2 +1.5 +1 - +0.5- -0.5 - -1- -1.5 - 7. 6. 11 13 14 pH of solution 7. Aspartic acid has a side chain bearing a carboxylic acid group; its pK, is 4. The a-amino and a-carboxylic groups have pKa values similar to those of alanine. Determine the net charge on aspartic acid at the following pH values: pH 1 pH 2 pH 4 pH 9 pH 13 Net charge of molecules 2.arrow_forwardMass spectrometry and X‑ray diffraction are common biochemical techniques for characterizing proteins. Classify each statement based on whether it applies to mass spectrometry, X‑ray diffraction, or both techniques.arrow_forwardThe following illustrations show examples of the secondary, supersecondary (motifs), tertiary, or quaternary structures, as we discussed. Select the most appropriate illustration marked "A-E. a-Keratin: A O A. A O B. B OC.C O D. D O E. Earrow_forward
- 6. Consider the following proteins to answer the questions below: Protein Size (kDa) ε at 280 nm 10 7000 14000 3000 50000 A B C D 50 10 50 pl 4 4 8 8 Red Colored? Yes No No No a. Sketch the UV-Vis spectrum of each pure protein (A, B, C, and D) from 240- 480 nm if they were all present at 20 µM. Note: I want four clearly labeled spectra on one plot.arrow_forward12. The sugars glucose, fructose, and inositol all have the same formula i.e. C6H12O6 yet they have 3 very similar but different structures. This is an example of: a) geometric isomers b) structural isomers c) stereo isomers d) none are correctarrow_forward6. Consider the following proteins to answer the questions below: Protein Size (kDa) pl ε at 280 nm 10 4 7000 50 4 14000 10 8 3000 50 8 50000 A B C C Red Colored? Yes No No No b. Describe a two-step purification procedure that could be used to purify/isolate protein A from the other proteins. In your response, describe the type of chromatography used, the pH of buffer needed, and a labeled chromatogram (include absorbances at both 280 and 400 nm). Make sure you note which "fraction/sample" is needed from the first step to proceed/use for the second step. Use another page if necessary.arrow_forward
- a. Why is it important to eat food containing antioxidants? Write at leasttwo reactions to prove the answer. b. Write in four ways the following nucleotide sequence: ATGCA. c. Explain i. Hoogsteen pairing & ii. Hyperchromic effectiii. Epimers Iv. Mutarotaton v. Aldose vi. Anomers vii. Mutarotationarrow_forward6. A control phospholipid membrane is isolated in which the phospholipid tails all have an 18-C chain length and are comprised of a 50:50 mixture of saturated and unsaturated tails. In addition, about 25% of the lipids are fluorescently labeled on the head groups. a) Draw a single plot of Fluidity vs. Temperature that contains the expected curves for: Control phospholipid (line- -) Control supplemented with 18-C saturated phospholipids (dashed line - Control supplemented with 16-C chain length (dotted line • • • • • • ) b) Draw a single plot of the Fluorescence Intensity vs. Time that contains the expected curves of a Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching (FRAP) using the same samples as in (a) above. The FRAP experiment is conducted at the same temperature for each sample (which is the Tm of the of the control phospholipid).arrow_forwardUV-vis spectroscopy can be used to determine protein and nucleic acid concentrations, provided the user knows the molar extinction coefficient of the protein or nucleic acid. Rank the wavelength absorption for the amino acids below from shortest wavelength to longest in the UV region.arrow_forward
- 30. The shown structure is a cyclic D-monosaccharide. Which of the following statements is true? HOCH₂ H OH H OH OH CH₂OH A. The chemical can react with methanol to form a hemiacetal in solution without forming an open chain structure B. The chemical needs to form an open chain structure to be able to react with methanol to produce a glycosidic linkage in solution C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor Barrow_forwardPlease discuss denaturation: Define it in your own words. What type of biological macromolecule is subject to denaturation? In what types of environments might denaturation occur?arrow_forwardVII. Analysis of a peptide antibiotic purified from a strain of Bacillus brevii resulted in the following significant information: Complete hydrolysis of the peptide yielded equimolar amounts of Leu, Orn, Phe, Pro, and Val Molecular weight of the peptide was estimated to be aroung 1,200 Da The peptide failed to undergo hydrolysis when treated with carboxypeptidase Partial hydrolysis and then chromatographic separation of products yielded the following di- and tripeptides: Leu-Phe, Phe-Pro, Orn-Leu, Val-Orn, Val-Orn-Leu, Phe-Pro-Val, Pro-Val-Orn Treament with dinitrofluorobenzene (DNFB) followed by complete hydrolysis yielded only free amino acids and the DNFB-derivatized ornithine at its side chain Using this set of information available to you, deduce the amino acid sequence of this peptide antibiotic. Write your final peptide sequence only using 3-letter abbreviations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education