
Concept explainers
A uniform rod AB of length 5.0 m and mass M=3.S kg is hinged at A and held in equilibrium by a light cord, as shown in Fig. 9-57.A load W=22N hangs from the rod at a distance d so that the tension in the cord is 85 N. (a) Draw a free-body diagram for the rod. (b) Determine the vertical and horizontal forces on the rod exerted by the hinge, (c) Determine d from the appropriate torque equation.
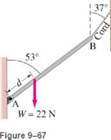
Part (a)
A free-body diagram for the rod.
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
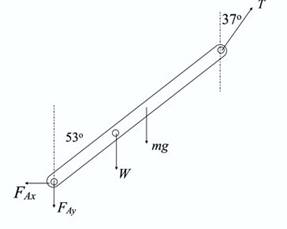
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Weight of the load, W=22 N
Tension in cord, T=85 N
Mass of the rod, M=3.8 kg
Formula used:
Equilibrium condition: the net force and torque would be zero.
∑F=0∑τ=0
Calculation:
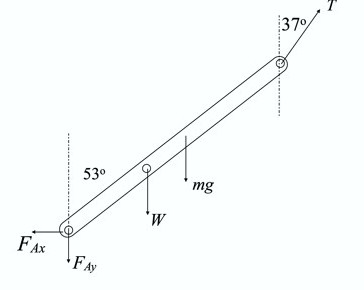
Conclusion:
Thus, the forces acting on the rod are:
Weight of the rod, weight of hanging object, Tension, vertical and horizontal components of force on the rod exerted by the hinge.
Part (b)
The vertical and horizontal forces on the rod exerted by the hinge.
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
Vertical component of the force exerted by the hinge =8.64 N and the horizontal component of the force exerted by the hinge =51.2 N .
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Weight of the load, W=22 N
Tension in cord, T=85 N
Mass of the rod, M=3.8 kg
Formula used:
Equilibrium condition: the net force and torque would be zero.
∑F=0∑τ=0
Calculation:
∑Fy=0Fay+W+mg−Tcos37°=0Fay+22+3.8(9.8)−85cos37°=0Fay=8.64 N∑Fx=0Fax−Tsin37°=0Fax=85sin37°Fax=51.2 N
Conclusion:
Thus the vertical component of the force exerted by the hinge is 8.64N and the horizontal component of the force exerted by the hinge is 51.2N.
Part (c)
d from the appropriate torque equation.
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
d =2.44 m
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Weight of the load, W=22 N
Tension in cord, T=85 N
Mass of the rod, M=3.8 kg
Formula used:
Equilibrium condition: the net force and torque would be zero.
∑F=0∑τ=0
Calculation:
About A: ∑τ=0
W(dsin53)+mg(2.5sin53)+Tcos37(5sin53)+Tsin37(5cos53)=022(dsin53)=85(5)(cos37sin53−sin37cos53)−3.8(9.8)(2.5sin53)22(dsin53)=42.793d=2.44m
Conclusion:
Thus, the distance is d =2.44 m .
Chapter 9 Solutions
Physics: Principles with Applications
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Microbiology: An Introduction
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
- A small postage stamp is placed in front of a concave mirror (radius = 1.1 m), such that the image distance equals the object distance. (a) What is the object distance? (b) What is the magnification of the mirror (with the proper sign)?arrow_forwardCalculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers. Record these values in Data Table 5. Ruler = 11.56 g, small washer = 1.85 g, large washer = 24.30 g. Calculate the % Difference in the Torques and record the values in Data Table 5. Is ΣAnticlockwise torque and Anticlockwise torque the same thing, are they solved in the same way?arrow_forwardA window washer stands on a uniform plank of mass M = 142 kg and length l = 2.80 m supported by 2 ropes attached at the ends of the plank. The window washer has a mass m = 68.0 kg. What is the tension in each of the ropes, T1 and T2, if the window washer's displacement from the center of mass of the plank is x = 0.930 m as shown in Figure 1: Window Washer Problem?arrow_forward
- A man holds a double-sided spherical mirror so that he is looking directly into its convex surface, 33 cm from his face. The magnification of the image of his face is +0.17. What will be the image distance when he reverses the mirror (looking into its concave surface), maintaining the same distance between the mirror and his face? Be sure to include the algebraic sign (+ or -) with your answer.arrow_forwardHow do you draw a diagram of the ruler and mass system in equilibrium identifying the anti-clockwise torque and clockwise torque? How do I calculate the anti-clockwise torque and the clockwise torque of the system with the ruler and the washers, does it come from the data in table 4? Please help, thank you!arrow_forwardExample Double pane windows have two panes of glass (n = 1.5), with a layer of air sandwiched between them. If light from outside enters the first pane at an angle of 25° from the surface normal, what angle does it enter the house at? ☑ 3 5arrow_forward
- Did your experiment results in Data Table 3 verify, to within a reasonable experimental error, the condition of equilibrium of Equation 6: Στanti-clockwise = Στclockwise? Support your response with experimental data. What does this Σ mean? My results do not show they are equal to each other, what does this mean then, and what does the data show? Thanks!arrow_forwardmicro wave.arrow_forwardmicro wave.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





