
Concept explainers
a)
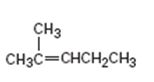
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 2-methyl-2-pentene is to be given.
Concept introduction:
To give:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 2-methyl-2-pentene.
b)
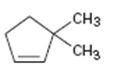
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 3,3-dimethylcyclopentene is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Alkenes react with H2 in the presence of metal catalysts such as palladium or platinum to yield the corresponding alkanes as the products. The addition occurs with syn stereochemistry. Normally only a single product is produced as the catalyst will interact only from the least hindered and most accessible face of the alkene.
To give:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 3,3-dimethylcyclopentene.
c)
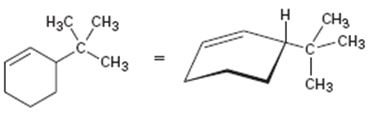
Interpretation:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 3-tert-butylcyclohexene is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Alkenes react with H2 in the presence of metal catalysts such as palladium or platinum to yield the corresponding alkanes as the products. The addition occurs with syn stereochemistry. Normally only a single product is produced as the catalyst will interact only from the least hindered and most accessible face of the alkene.
To give:
The product obtained by the catalytic hydrogenation of 3-tert-butylcyclohexene.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Hi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. Ensure all figures, reaction mechanisms (with arrows and lone pairs please!!), and structures are clearly drawn to illustrate the synthesis of the product as per the standards of a third year organic chemistry course. ****the solution must include all steps, mechanisms, and intermediate structures as required. Please hand-draw the mechanisms and structures to support your explanation. Don’t give me AI-generated diagrams or text-based explanations, no wordy explanations on how to draw the structures I need help with the exact mechanism hand drawn by you!!! I am reposting this—ensure all parts of the question are straightforward and clear or please let another expert handle it thanks!!arrow_forwardHi!! Please provide a solution that is handwritten. Ensure all figures, reaction mechanisms (with arrows and lone pairs please!!), and structures are clearly drawn to illustrate the synthesis of the product as per the standards of a third year organic chemistry course. ****the solution must include all steps, mechanisms, and intermediate structures as required. Please hand-draw the mechanisms and structures to support your explanation. Don’t give me AI-generated diagrams or text-based explanations, no wordy explanations on how to draw the structures I need help with the exact mechanism hand drawn by you!!! I am reposting this—ensure all parts of the question are straightforward and clear or please let another expert handle it thanks!!arrow_forward. (11pts total) Consider the arrows pointing at three different carbon-carbon bonds in the molecule depicted below. Bond B 2°C. +2°C. < cleavage Bond A • CH3 + 26. t cleavage 2°C• +3°C• Bond C Cleavage CH3 ZC '2°C. 26. E Strongest 3°C. 2C. Gund Largest BDE weakest bond In that molecule a. (2pts) Which bond between A-C is weakest? Which is strongest? Place answers in appropriate boxes. Weakest C bond Produces A Weakest Bond Most Strongest Bond Stable radical Strongest Gund produces least stable radicals b. (4pts) Consider the relative stability of all cleavage products that form when bonds A, B, AND C are homolytically cleaved/broken. Hint: cleavage products of bonds A, B, and C are all carbon radicals. i. Which ONE cleavage product is the most stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. 人 8°C. formed in bound C cleavage ii. Which ONE cleavage product is the least stable? A condensed or bond line representation is fine. methyl radical •CH3 formed in bund A Cleavagearrow_forward
- Which carbocation is more stable?arrow_forwardAre the products of the given reaction correct? Why or why not?arrow_forwardThe question below asks why the products shown are NOT the correct products. I asked this already, and the person explained why those are the correct products, as opposed to what we would think should be the correct products. That's the opposite of what the question was asking. Why are they not the correct products? A reaction mechanism for how we arrive at the correct products is requested ("using key intermediates"). In other words, why is HCl added to the terminal alkene rather than the internal alkene?arrow_forward
- My question is whether HI adds to both double bonds, and if it doesn't, why not?arrow_forwardStrain Energy for Alkanes Interaction / Compound kJ/mol kcal/mol H: H eclipsing 4.0 1.0 H: CH3 eclipsing 5.8 1.4 CH3 CH3 eclipsing 11.0 2.6 gauche butane 3.8 0.9 cyclopropane 115 27.5 cyclobutane 110 26.3 cyclopentane 26.0 6.2 cycloheptane 26.2 6.3 cyclooctane 40.5 9.7 (Calculate your answer to the nearest 0.1 energy unit, and be sure to specify units, kJ/mol or kcal/mol. The answer is case sensitive.) H. H Previous Nextarrow_forwardA certain half-reaction has a standard reduction potential Ered +1.26 V. An engineer proposes using this half-reaction at the anode of a galvanic cell that must provide at least 1.10 V of electrical power. The cell will operate under standard conditions. Note for advanced students: assume the engineer requires this half-reaction to happen at the anode of the cell. Is there a minimum standard reduction potential that the half-reaction used at the cathode of this cell can have? If so, check the "yes" box and calculate the minimum. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. If there is no lower limit, check the "no" box.. Is there a maximum standard reduction potential that the half-reaction used at the cathode of this cell can have? If so, check the "yes" box and calculate the maximum. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. If there is no upper limit, check the "no" box. yes, there is a minimum. 1 red Πν no minimum Oyes, there is a maximum. 0 E red Dv By using the information in the ALEKS…arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

