
Interpretation:
How the rate of the reaction between an
Concept Introduction:
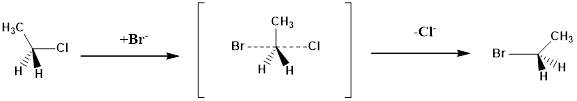
Structure of the substrate plays a major role in
Solvent: it is substance which dissolves the chemical substrate. They are classified as polar protic and
Polar parotic solvent: It contains at least one
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Essential Organic Chemistry (3rd Edition)
- In an SN2 reaction between 2-chlorobutane and iodide ion, what happens to the rate of the reaction if: (a) the concentration of 2-chlorobutane is doubled? (b) the concentration of iodide is doubled?arrow_forwardBulky, nonnucleophilic bases favor elimination over substitution. Define this ?arrow_forwardRank the following compounds from most reactive to least reactive in an electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction:arrow_forward
- Pleas explain how this process occurs. Identify SN1, SN2, E2, E1, nucleophiles and electrophiles.arrow_forwardRank the attached compounds in order of increasing reactivity in asubstitution reaction with −CN as nucleophile.arrow_forwardThe reaction of an amine with an alkyl halide gives an ammonium salt. The rate of this SN2 reaction is sensitive to the polarity of the solvent. Draw an energy diagram for this reaction in a nonpolar solvent and another in a polar solvent. Consider the nature of the transition state, and explain why this reaction should be sensitive to the polarity of the solvent. Predict whether it will be faster or slower in a more polar solvent.arrow_forward
- Rank the reactivity of the compounds below toward nucleophilic acyl substitution by writing the compounds' letters in the proper blanks in the box below. `NH CI Br CH3 CH3 A В C E rank compounds for acyl substitution reactivity most least reactive reactivearrow_forwardConsider the following SN1 reaction: (CH3)3CBR + H2O → (CH3)3COH + HBr What is the effect of doubling both the t-butyl bromide and water concentrations on the rate of the reaction? O doubles the rate O quadruples the rate O triples the rate O halves the rate O no change O quarters the rate O 1/16th the ratearrow_forwardWhat type of reaction is this? Br + Br + H2О O SN1 O SN2 O E1 O E2 O Nucleophilic aromatic substitutionarrow_forward
- Consider carbonyl compounds A– E attached below. Which compound is most reactive in nucleophilic addition?arrow_forwardRank the nucleophiles in following group in order of increasing nucleophilicity. H2O, −OH, CH3CO2-arrow_forwardHow is nucleophilicity (nucleophile strength) related to basicity?arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning


