
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: Second Semester Topics
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781119110651
Author: David R. Klein
Publisher: WILEY
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8.1, Problem 8.5P
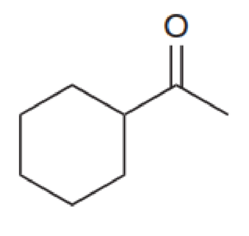
For each of the compounds below, identify all alpha protons (some compounds may not have any alpha protons).
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
6. What are the approximate pKa values for the groups marked with arrows?
о
•
1
1
OH
NH₂
2
2
3
ОН
-
SH
3
4
4
OH
5
:0
5
Using the atomic notation, label each of the accompanying atomic diagrams.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Some labels may not be used, and any label may be used more than once.
10. Nitric acid and nitrous acid are both acids that you would not want to spill on your feet.
But one is much more acidic than the other and would do real damage. Draw the
molecular structures of each of these and explain - based on what you learned in this
module - why nitric acid (pKa =-1.35) is much more acidic than nitrous acid (pKa = 3.15).
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: Second Semester Topics
Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.1 - For each of the compounds below, identify all...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.9PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.10PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.11PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 8.12P
Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 8.13PCh. 8.3 - Predict the products of each of the following...Ch. 8.3 - Predict the products of each of the following...Ch. 8.3 - Predict the products of each of the following...Ch. 8.3 - Predict the products of each of the following...Ch. 8.4 - Prob. 8.20PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.21PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.22PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 8.23PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.25PCh. 8.5 - Prob. 8.26PCh. 8.5 - On a separate piece of paper, draw a mechanism for...Ch. 8.6 - Prob. 8.29PCh. 8.6 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.6 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.6 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.6 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.6 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.6 - Identify the reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.7 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.7 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.7 - Predict the major product for each of the...Ch. 8.7 - Prob. 8.42PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.43PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.44PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.45PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.47PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.48PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.49PCh. 8.7 - Prob. 8.50PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.52PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.53PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.54PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.55PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.57PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.58PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.59PCh. 8.8 - Prob. 8.60PCh. 8.8 - Propose a mechanism for each of the following...Ch. 8.8 - Propose a mechanism for each of the following...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 8.64PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.66PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.67PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.68PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.69PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.70PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.71PCh. 8.9 - Prob. 8.72PCh. 8.9 - Identify what reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.9 - Identify what reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.9 - Identify what reagents you would use to achieve...Ch. 8.10 - Prob. 8.78PCh. 8.10 - Prob. 8.79PCh. 8.10 - Prob. 8.80PCh. 8.10 - Propose a synthesis for each of the following...Ch. 8.10 - Propose a synthesis for each of the following...Ch. 8.10 - Propose a synthesis for each of the following...Ch. 8.10 - Propose a synthesis for each of the following...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
APPLY 1.2 Express the following quantities in scientific notation
using fundamental SI units of mass and lengt...
Chemistry (7th Edition)
Determine [OH], [H+], and the pH of each of the following solutions. a. 1.0 M KCl b. 1.0 M KC2H3O2
Chemistry
9.1 Calculate the total mass of the reactants and the products for each of the following equations:
Basic Chemistry (5th Edition)
Q5. Convert to K.
a) 181.1 K
b) 358 K
c) 29.4 K
d) 302.6 K
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Complete each of the following equations by adding the missing species: (a) A1327l+H24e?+n01 (b) P94239u+?C96242m+n101 (c) N714+H24e?+H11 (d) U92235?+C55135s+4n01arrow_forwardWhich of the following nuclei lie within the band of stability shown in Figure 21.2? (a) chlorine-37 (b) calcium-4O (c) 204Bi (d) 56Fe (e) 206pb (f) 211pb (g) 222Rn (h) carbon-14arrow_forwardCompounds containing bonds with light isotopes are: O a. isotopes don't matter here, because both bonds are equally strong O b. easier to break than those including heavier isotopes more difficult to break than those including heavier isotopesarrow_forward
- This arrangement of water molecules in the pore of aquaporins -0-0-c O=o=c -0-0=c H-N Asn H-N Asn 0101c -O=o=c O-OTO=C allows hydrated ions to flow through the pore prevents movement of protons through the pore O facilitates proton hopping from water molecule to water molecule in the pore O both A and Carrow_forwardThe name for Hg22+ is Group of answer choices hydrogen ion hydrogen(II) ion mercury(I) ion mercury(II) ion mercury ionarrow_forwardThis arrangement of water molecules in the pore of aquaporins Omo=c -O=o=c 00101c H-N Asn H-N Asn -O=³0=c -O=o=c -Omo=c allows hydrated ions to flow through the pore prevents movement of protons through the pore O facilitates proton hopping from water molecule to water molecule in the pore O both A and Carrow_forward
- hi, can you solve this which one is false?The energy required to keep protons and neutrons together in the nucleus is called the core binding energy.If different atoms have the same number of neutrons and different protons, these atoms are called isotopes.The mass number is equal to the sum of the number of protons and neutrons.In an uncharged atom, the number of protons is equal to the number of electrons.The total number of protons in an atom is called its atomic number.arrow_forwardSubstance KspKsp Sn(OH)2Sn(OH)2 Ksp=4S3=5.45×10−27Ksp=4S3=5.45×10−27 CuCNCuCN Ksp=S2=3.47×10−20Ksp=S2=3.47×10−20 MgF2MgF2 Ksp=4S3=5.16×10−11Ksp=4S3=5.16×10−11 NiCO3NiCO3 Ksp=S2=1.42×10−7 The equilibrium constants for the dissolution (KspKsp) of various substances in aqueous solution at 25°C are listed in the table above. Which of the following provides a correct comparison of the molar solubilities (SS) of some of these substances based on their Ksp ? a.) The molar solubilities for CuCNCuCN and NiCO3NiCO3 are calculated using S=Ksp−−−√S=Ksp and NiCO3NiCO3 has a lower molar solubility than CuCNCuCN. b.) The molar solubilities for CuCNCuCN and NiCO3NiCO3 are calculated using S=Ksp−−−√S=Ksp and CuCNCuCN has a lower molar solubility than NiCO3NiCO3. c.) The molar solubilities for Sn(OH)2Sn(OH)2 and MgF2MgF2 are calculated using S=Ksp4−−−√S=Ksp4 and MgF2MgF2 has a lower molar solubility than NiCO3NiCO3. d.) The molar solubilities for Sn(OH)2Sn(OH)2 and MgF2MgF2…arrow_forwardComplete the following chart. Drag each label to the appropriate target. • View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 35 Sr Number of Electrons in Ion Number of Symbol Ion Charge Protons in Ion 38 -1 Ni 29 Cu 27 28 27 Br 36 Со -2 +1 37 +1 Se 36 34 +2 36 Zn +2 Rb 30arrow_forward
- could you help me with these question and explain to me step by step thanksarrow_forwardwhen the proton number of the nucleus exceeds 60 the nucleus show the tendency to be unstable? True or falsearrow_forwardPb2+ SO42- = PbSO4 2+ and 2- cancel each other out. Pb2+ Cl- = PbCl2 Where does the 2 from Cl2 come from?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co

 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax

Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285869759
Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar Torres
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Introductory Chemistry: A Foundation
Chemistry
ISBN:9781337399425
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305960060
Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. Hansen
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Matter and Change
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078746376
Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl Wistrom
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co


Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)
Chemistry
ISBN:9781938168390
Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark Blaser
Publisher:OpenStax
Enzymes - Effect of cofactors on enzyme; Author: Tutorials Point (India) Ltd;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AkAbIwxyUs4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Enzyme Catalysis Part-I; Author: NPTEL-NOC IITM;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aZE740JWZuQ;License: Standard Youtube License