
Concept explainers
For Exercises 1 through 20, perform each of the following steps.
a. State the hypotheses and identify the claim.
b. Find the critical value(s).
c. Compute the test value.
d. Make the decision.
e. Summarize the results.
Use the traditional method of hypothesis testing unless otherwise specified.
1. Lifetime of $1 Bills The average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is 18 months. A researcher believes that the average lifetime is not 18 months. He researched the lifetime of 50 $1 bills and found the average lifetime was 18.8 months. The population standard deviation is 2.8 months. At α = 0.02, can it be concluded that the average lifetime of a circulated $1 bill differs from 18 months?
a.
To state: The null and alternative hypotheses and identify the claim.
Answer to Problem 8.2.1RE
Null hypothesis:
Alternative hypothesis:
The claim is “the average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is not 18 months”.
Explanation of Solution
Given info:
A sample of 50 $1 bills selected and found the average lifetime was 18.8 months. The population standard deviation is 2.8 months.
Justification:
Here, the claim is that the average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is not 18 months. This can be written as
The test hypotheses are given below:
Null hypothesis: The average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is 18 months
Alternative hypothesis (claim): The average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is not 18 months.
b.
To find: The critical values.
Answer to Problem 8.2.1RE
The critical value is ±2.326.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.02.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
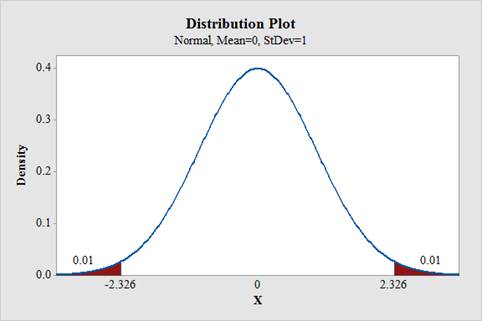
From the output, the critical value is ±2.326.
c.
To find: The test value.
Answer to Problem 8.2.1RE
The test value is 2.02.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the test value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > 1-Sample Z.
- In Summarized data, enter the sample size as 50 and mean as 18.8.
- In Standard deviation, enter 2.8.
- In Perform hypothesis test, enter the test mean as 18.
- Check Options; enter Confidence level as 98%.
- Choose not equal in alternative.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:

From the output, the test value is 2.02.
d.
To make: The decision.
Answer to Problem 8.2.1RE
The decision is “fail to reject the null hypothesis”.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Software Procedure:
Step-by-step procedure to indicate the appropriate area and critical value using the MINITAB software:
- Choose Graph > Probability Distribution Plot choose View Probability > OK.
- From Distribution, choose ‘Normal’ distribution.
- Click the Shaded Area tab.
- Choose Probability Value and Both Tail for the region of the curve to shade.
- Enter the Probability value as 0.02.
- Enter 2.02 under show reference lines at X values.
- Click OK.
Output using the MINITAB software is given below:
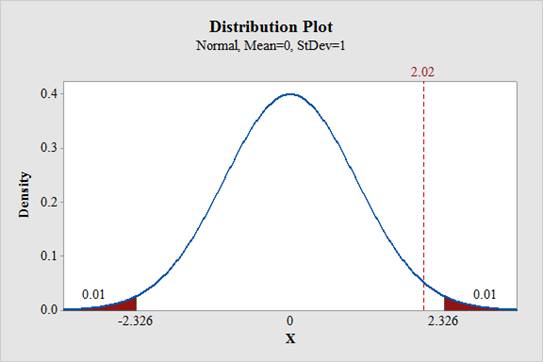
From the output, it can be observed that the test statistic value do not falls in the critical region. Therefore, the null hypothesis is not rejected.
e.
To summarize: The result.
Answer to Problem 8.2.1RE
The conclusion is that, there is no enough evidence to support the claim that the average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is not 18 months.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
From part d, the null hypothesis is not rejected. Therefore, there is no enough evidence to support the claim that the average lifetime of circulated $1 bills is not 18 months.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Elementary Statistics: A Step By Step Approach
- There are four white, fourteen blue and five green marbles in a bag. A marble is selected from the bag without looking. Find the odds of the following: The odds against selecting a green marble. The odds in favour of not selecting a green marble The odds in favor of the marble selected being either a white or a blue marble. What is true about the above odds? Explainarrow_forwardPlease show as much work as possible to clearly show the steps you used to find each solution. If you plan to use a calculator, please be sure to clearly indicate your strategy. 1. The probability of a soccer game in a particular league going into overtime is 0.125. Find the following: a. The odds in favour of a game going into overtime. b. The odds in favour of a game not going into overtime. c. If the teams in the league play 100 games in a season, about how many games would you expect to go into overtime?arrow_forwardexplain the importance of the Hypothesis test in a business setting, and give an example of a situation where it is helpful in business decision making.arrow_forward
- A college wants to estimate what students typically spend on textbooks. A report fromthe college bookstore observes that textbooks range in price from $22 to $186. Toobtain a 95% confidence level for a confidence interval estimate to plus or minus $10,how many students should the college survey? (We may estimate the populationstandard deviation as (range) ÷ 4.)arrow_forwardIn a study of how students give directions, forty volunteers were given the task ofexplaining to another person how to reach a destination. Researchers measured thefollowing five aspects of the subjects’ direction-giving behavior:• whether a map was available or if directions were given from memory without a map,• the gender of the direction-giver,• the distances given as part of the directions,• the number of times directions such as “north” or “left” were used,• the frequency of errors in directions. Identify each of the variables in this study, and whether each is quantitative orqualitative. For each quantitative variable, state whether it is discrete or continuous. Was this an observational study or an experimental study? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardexplain the difference between the confident interval and the confident level. provide an example to show how to correctly interpret a confidence interval.arrow_forward
- Sketch to scale the orbit of Earth about the sun. Graph Icarus’ orbit on the same set of axesWhile the sun is the center of Earth’s orbit, it is a focus of Icarus’ orbit. There aretwo points of intersection on the graph. Based on the graph, what is the approximate distance between the two points of intersection (in AU)?arrow_forwardThe diameters of ball bearings are distributed normally. The mean diameter is 67 millimeters and the standard deviation is 3 millimeters. Find the probability that the diameter of a selected bearing is greater than 63 millimeters. Round to four decimal places.arrow_forwardSuppose you like to keep a jar of change on your desk. Currently, the jar contains the following: 22 Pennies 27 Dimes 9 Nickels 30 Quarters What is the probability that you reach into the jar and randomly grab a penny and then, without replacement, a dime? Express as a fraction or a decimal number rounded to four decimal places.arrow_forward
- A box contains 14 large marbles and 10 small marbles. Each marble is either green or white. 9 of the large marbles are green, and 4 of the small marbles are white. If a marble is randomly selected from the box, what is the probability that it is small or white? Express as a fraction or a decimal number rounded to four decimal places.arrow_forwardCan I get help with this step please? At a shooting range, instructors can determine if a shooter is consistently missing the target because of the gun sight or because of the shooter's ability. If a gun's sight is off, the variance of the distances between the shots and the center of the shot pattern will be small (even if the shots are not in the center of the target). A student claims that it is the sight that is off, not his aim, and wants the instructor to confirm his claim. If a skilled shooter fires a gun at a target multiple times, the distances between the shots and the center of the shot pattern, measured in centimeters (cm), will have a variance of less than 0.33. After the student shoots 28 shots at the target, the instructor calculates that the distances between his shots and the center of the shot pattern, measured in cm, have a variance of 0.25. Does this evidence support the student's claim that the gun's sight is off? Use a 0.025 level of significance. Assume that the…arrow_forwardThe National Academy of Science reported that 38% of research in mathematics is published by US authors. The mathematics chairperson of a prestigious university wishes to test the claim that this percentage is no longer 38%. He has no indication of whether the percentage has increased or decreased since that time. He surveys a simple random sample of 279 recent articles published by reputable mathematics research journals and finds that 123 of these articles have US authors. Does this evidence support the mathematics chairperson's claim that the percentage is no longer 38 % ? Use a 0.02 level of significance. Compute the value of the test statistic. Round to two decimal places.arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
