
Corporate Finance
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259918940
Author: Ross, Stephen A.
Publisher: Mcgraw-hill Education,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 13CQ
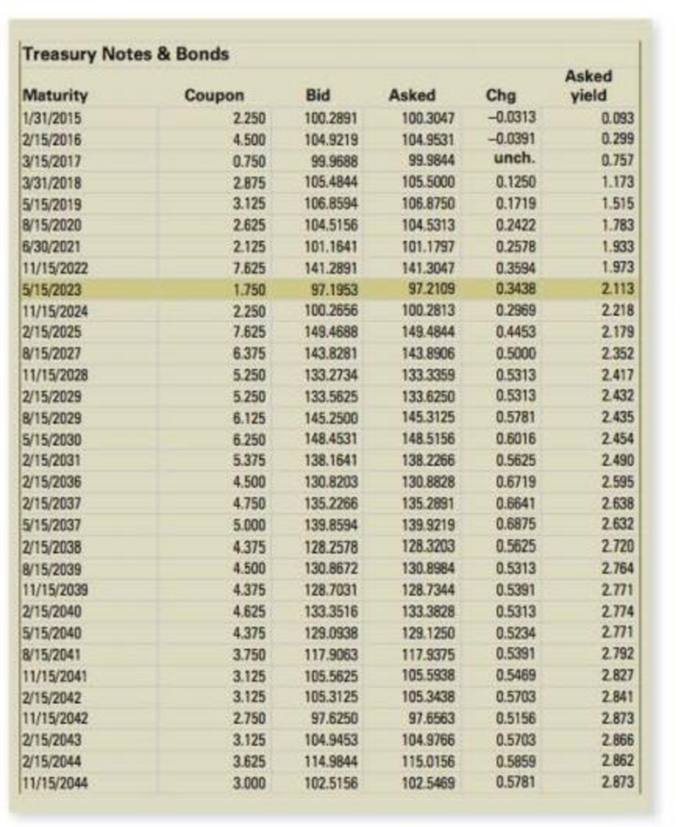
Treasury Market Take a look back at Figure 8.4. Notice the wide range of coupon rates. Why are they so different?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
answer pls
The yield curve varies over time based the relative riskiness of buying a single long-term bond versus purchasing multiple short-term bonds. This explanation of the yield curve is most consistent with
A.the Fisher Effect theoryB.the market segmentation theoryC.the unbiased expectations theoryD.the liquidity preference theory
We discussed the expectations theory of the term structure of interest rates. What does it says about the factors that influence the shape (upward, downward or flat) of the yield curve. Why does the yield curve sometimes inverts (become downward sloping) even though most of the time it is upward sloping?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Corporate Finance
Ch. 8 - Prob. 1CQCh. 8 - Prob. 2CQCh. 8 - Prob. 3CQCh. 8 - Yield to Maturity Treasury bid and ask quotes are...Ch. 8 - Coupon Rate How does a bond issuer decide on the...Ch. 8 - Real and Nominal Returns Are there any...Ch. 8 - Prob. 7CQCh. 8 - Prob. 8CQCh. 8 - Term Structure What is the difference between the...Ch. 8 - Crossover Bonds Looking back at the crossover...
Ch. 8 - Municipal Bonds Why is it that municipal bonds are...Ch. 8 - Prob. 12CQCh. 8 - Treasury Market Take a look back at Figure 8.4....Ch. 8 - Prob. 14CQCh. 8 - Bonds as Equity The 100-year bonds we discussed in...Ch. 8 - Bond Prices versus Yields a. What is the...Ch. 8 - Interest Rate Risk All else being the same, which...Ch. 8 - Prob. 1QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 2QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 3QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 4QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 5QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 6QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 7QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 8QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 9QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 10QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 11QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 12QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 13QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 14QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 15QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 16QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 17QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 18QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 19QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 20QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 21QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 22QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 23QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 24QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 25QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 26QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 27QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 28QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 29QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 30QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 31QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 32QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 33QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 34QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 35QAPCh. 8 - Prob. 1MCCh. 8 - Prob. 3MCCh. 8 - Prob. 5MCCh. 8 - Prob. 6MCCh. 8 - Prob. 7MC
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Exploring Finance: The Security Market Line and Inflation Changes Security Market Line: Inflation Changes Conceptual Overview: Explore how inflation changes the security market line. The Security Market Line defines the required rate of return for a security to be worth buying or holding. The line, depicted in blue in the graph, is the sum of the risk-free return (rf in the slider) and a risk premium determined by the market-risk premium (RPM) multiplied by the security's beta coefficient for risk. Drag the slider below the graph to change the amount of the risk-free return. These changes reflect changes in inflation. Drag left or right on the graph to move the cursor to evaluate securities with different beta coefficients. In this graph, the market-risk premium is fixed at 5%. r = r_{RF} + RP_M * beta = 6\% + 5\% * 1 = 6\% + 5.00\% = 11.00\%r=rRF+RPM∗beta=6%+5%∗1=6%+5.00%=11.00% 1. If the risk-free return were 4.0% and a security's beta coefficient were 2.0, what would be…arrow_forwardQuestion 1: a. The risk structure of interest rates and the term structure of interest rates are identical. True or False? Explain. b. The yield curve is a forecasting tool for inflation, the business cycle, and monetary policy. True or False? Explain.arrow_forwardUsing the money market diagram, explain the effect Of this policy measure on the real interest rate.arrow_forward
- If the yield curve in the bond market shows a flat curve, what do you think about the prediction of the liquidity premium in explaining this phenomenon? Then do you prefer the prediction of expectation theory in explaining this phenomenon?arrow_forwardFor the cost of equity (stock) is it better to use the current US Treasury bill rate or a longer-termgovernment bond rate as the risk-free rate of return?arrow_forwardQuestion No. 3: What is financial market equilibrium? And then explain its relation to required rate of return.arrow_forward
- What is the connection between the interest rate and the price of a fixed coupon bond? Why is this relationship still going strong?arrow_forwardAccording to the ,long-term interest rates are a function of expected short-term interest rates Maturity theory Expectations theory Market segmentation theory Preferred habitat theoryarrow_forwardhelp me with this practice problemarrow_forward
- An efficient capital market is best defined as a market in which security prices reflect which one of the following? Multiple Choice A Current inflation B A risk premium C All available information D The historical arithmetic rate of return E The historical geometric rate of returnarrow_forwardWhat happens when investors rate of return is greater than YTM and coupon rates?arrow_forwardIf the credit quality of the issuer falls sharply, what is your main concern? a.The share price. b.The volatility of the underlying c.The default risk. d.A rise in risk free interest rates Give typing answer with explanation and conclusionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395083
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. Daves
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Portfolio return, variance, standard deviation; Author: MyFinanceTeacher;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RWT0kx36vZE;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY