
a.
To determine:
The
Introduction:
Test cross is the genetic cross between an individual that has dominant phenotype in specific trait to homozygous recessive for these specific traits. Test cross is used to identify the genotype of individual carrying dominant phenotype, and also used to check the linkage between the genes. In drosophila melanogaster, ebony eyes (e), and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive gene that is present on chromosome they are separated by 20 map units. The gene that code for fork bristle (f) is X-linked recessive and assort independently of (e), and (ro).
a.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The cross between (e+ ro+e ro) (f+f) is represented as below:
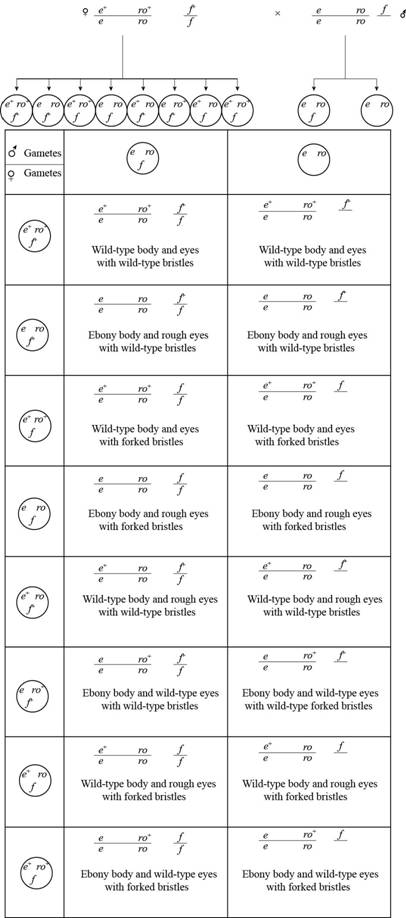
Fig.1: The cross between (e+ ro+e ro) (f+f).
Two autosomal genes in drosophila melanogaster, for body type and eyes are located 20 map unit apart from each other on chromosome 3.
1m.u.=1% recombinant frequency (R.F.)Thus, 20 m.u.=20 % R.F.
Therefore, total percentage of recombinant would be 20 and non recombinant would be 80.
In females eight gametes are possible which will have four parental and four recombinants. Total percentage of recombinants is 20% so for each recombinant 5%. Similarly total percentage of non recombinant is 80% so each non recombinant will have 20%.
Given information is that, when drosophila is heterozygous for autosomal genes that are present in cis configuration with X-linked gene for heterozygous bristle. This female is crossed with homozygous recessive male for two autosomal genes and hemizygous for the X-linked gene.
The female are able to produce eight types of different gametes and these gametes are:
e+ ro+_ f+_e+ ro+_ fe ro_ f+_e ro_ f_]Non recombinant
e+ ro+_ f+_e ro+_ f+e+ ro_ f_e ro+_ f_]Recombinant
The result of the cross is:
The following table represents the expected proportion from the cross:
| Genotype | Body color | Eyes | Bristles | Proportion |
| e+ ro+ f+ | Normal | Normal | Normal | 20% |
| e+ ro+ f | Normal | Normal | Forked | 20% |
| e ro f+ | Ebony | Rough | Normal | 20% |
| e ro f | Ebony | Rough | Forked | 20% |
| e+ ro f+ | Normal | Rough | Ebony | 5% |
| e ro+ f+ | Ebony | Normal | Normal | 5% |
| e+ ro f | Normal | Rough | Forked | 5% |
| e ro+ f | Ebony | Normal | Forked | 5% |
Table 1: The expected proportion from the cross.
b.
To determine:
The phenotype of progeny and their expected proportion when a female of each genotype is test crossed with the male (e+ roe ro+) (f+f).
Introduction:
Test cross is the genetic cross between an individual that has dominant phenotype in specific trait to homozygous recessive for these specific traits. Test cross is used to identify the genotype of individual carrying dominant phenotype, and also used to check the linkage between the genes. In drosophila melanogaster, ebony eyes (e), and rough eyes (ro) are encoded by autosomal recessive gene that is present on chromosome they are separated by 20 map units. The gene that code for fork bristle (f) is X-linked recessive and assort independently of (e), and (ro).
b.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The cross between (e+ roe ro+) (f+f) is represented as below:
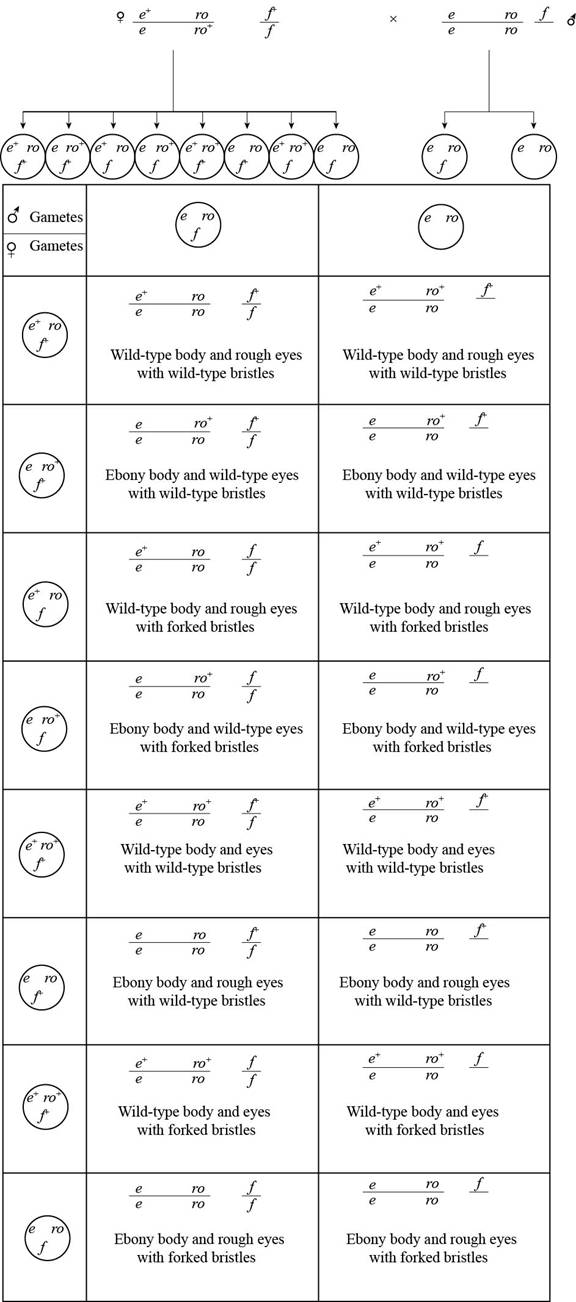
Fig. 2: The cross between (e+ roe ro+) (f+f)
Given information is that, when drosophila is heterozygous for autosomal genes that are present in Tran’s configuration with X-linked gene for heterozygous bristle. This female is crossed with homozygous recessive male for two autosomal genes and hemizygous for the X-linked gene.
The female are able to produce eight types of different gametes and these gametes are:
e+ ro_ f+_e ro+_ f+_e+ ro_ f+_e ro+_ f_]Non recombinant
e+ ro+_ f+_e+ ro+_ f_e ro_ f+_e ro_ f_]Recombinant
The result of the cross is:
The following table represents the expected proportion from the cross:
| Genotype | Body color | Eyes | Bristles | Proportion |
| e+ ro f+ | Normal | Rough | Normal | 20% |
| e ro+ f+ | Ebony | Normal | Normal | 20% |
| e+ ro f | Normal | Rough | Forked | 20% |
| e ro+ f | Ebony | Normal | Forked | 20% |
| e+ ro+ f+ | Normal | Normal | Normal | 5% |
| e+ ro+ f | Normal | Normal | Forked | 5% |
| e ro f+ | Ebony | Rough | Normal | 5% |
| e ro f | Ebony | Rough | Forked | 5% |
Table 2: The expected proportion from the cross.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Genetics: A Conceptual Approach
- Identify the indicated structure?arrow_forwardrewrite: Problem 1 (Mental Health): The survivor victim is dealing with acute stress and symptoms of a post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) due to their traumatic experience during the January 2025 wildfire. Goal 1: To alleviate the client's overall level, frequency, and intensity of anxiety and PTSD symptoms so that daily functioning remains unimpaired. Objective 1: The client will learn and regularly use at least two anxieties management techniques to reduce anxiety symptoms to less than three episodes per week. Intervention 1: The therapist will provide psychoeducation about anxiety and PTSD, including their symptoms and triggers. The therapist will also teach and assist the client in adopting relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing exercises and progressive muscle relaxation, to better manage anxiety and lessen PTSD symptoms.arrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning You have 0.100 M solutions of acetic acid (pKa = 4.76) and sodium acetate. If you wanted to prepare 1.00 L of 0.100 M acetate buffer of pH 4.00, how many milliliters of acetic acid and sodium acetate would you add? acetic acid: mL sodium acetate: mLarrow_forward
- How does the cost of food affect the nutritional choices people make?arrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Zero-Order Absorption Questions SHOW ALL WORK, including equation used, variables used and each step to your solution, report your regression lines and axes names (with units if appropriate) :Calculate a-q a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardWhat are some external influences that keep people from making healthy eating decisions?arrow_forward
- What type of structure(s) would you expect to see in peripheral membrane proteins? (mark all that apply) A. Amphipathic alpha helix (one side is hydrophilic and one side is hydrophobic) B. A hydrophobic beta barrel C. A hydrophobic alpha helix D. A chemical group attached to the protein that can anchor it to the membranearrow_forwardTemporal flexibility (the ability to change over time) of actin structures within a cell is maintained by… A. The growth/shrinkage cycle B. Periodic catastrophe C. GTP hydrolysis D. Treadmilling E. None of the abovearrow_forwardDuring in vitro polymerization of actin and microtubule filaments from their subunits, what causes the initial delay in filament growth? A.Nucleation B.Reaching homeostasis C.Nucleotide exchange D.ATP or GTP hydrolysis E.Treadmillingarrow_forward
- You expect to find which of the following in the Microtubule Organizing Center (MTOC)...(mark all that apply) A. Gamma tubulin B. XMAP215 C. Centrioles D. Kinesin-13arrow_forwardThe actin-nucleating protein formin has flexible “arms” containing binding sites that help recruit subunits in order to enhance microfilament polymerization. What protein binds these sites? A.Thymosin B.Profilin C.Cofilin D.Actin E.Tropomodulinarrow_forwardWhile investigating an unidentified motor protein, you discover that it has two heads that bind to actin. Based on this information, you could confidently determine that it is NOT... (mark all that apply) A. A myosin I motor B. A dynein motor C. A myosin VI motor D. A kinesin motorarrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





