
(a)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(a)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom | |
| (a) | Tetrahedral |
|
Explanation of Solution
Tetrahedral
A molecule having tetrahedral geometry has the empirical formula
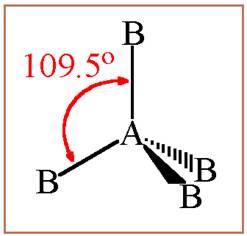
Figure 1
The bond angle between two atoms in a tetrahedral molecule is
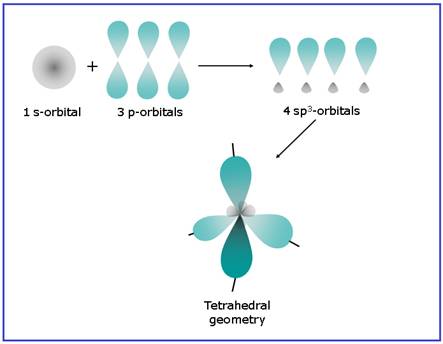
Figure 2
Thus a molecule having tetrahedral geometry has central atom with
(b)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(b)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom | |
| (b) | Trigonal planar |
|
Explanation of Solution
Trigonal planar
A molecule having trigonal planar geometry has the empirical formula
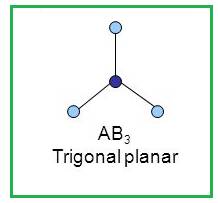
Figure 3
The bond angle between two atoms in a trigonal planar molecule is
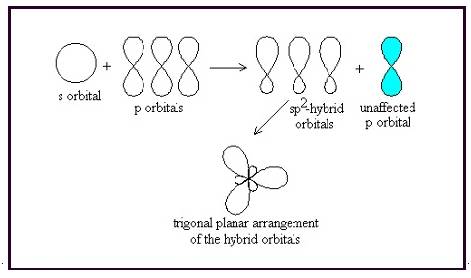
Figure 4
Thus a molecule having trigonal planar geometry has central atom with
(c)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(c)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (c) | Trigonal bipyramidal |
|
Explanation of Solution
Trigonal bipyramidal
A molecule having trigonal bipyramidal geometry has the empirical formula
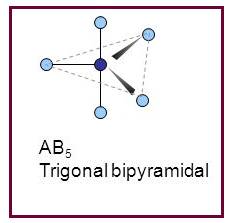
Figure 5
Trigonal bipyramidal molecule has two set of bonds – two axial bonds and three equatorial bonds. The two axial bonds are
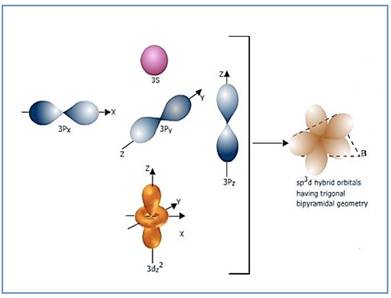
Figure 6
If the d-orbital of the
(d)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(d)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (d) | Linear |
|
Explanation of Solution
Linear
A molecule having linear geometry has the empirical formula
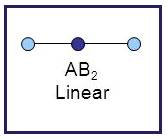
Figure 7
The bond angle between two atoms in linear molecule is
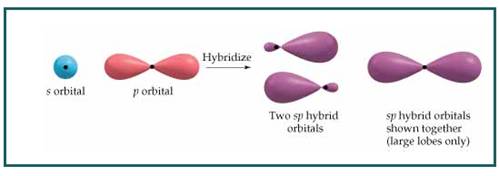
Figure 8
Thus a molecule having linear geometry has central atom with
(e)
Interpretation:
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the following molecular geometries has to be predicted.
- (a) Tetrahedral (b) trigonal planar (c) trigonal bipyramidal (d) linear (e) octahedral
Concept Introduction:
Hybridization is a hypothetical concept. It refers to overlapping of atomic orbitals and the resultant orbitals formed are known as hybrid orbitals. An orbital that doesn’t involve in hybridization is termed as unhybridized orbital. After hybridization, the orbitals cannot be distinguished individually. The orientation of the orbitals while overlapping impacts the nature of the bond forms. By knowing the hybridization of central atom in the molecule its geometry can be predicted and vice-versa.
(e)
Answer to Problem 7.52QP
| S.No | Molecular Geometry | Hybridization of the central atom |
| (e) | Octahedral |
|
Explanation of Solution
Octahedral
A molecule having octahedral geometry has the empirical formula
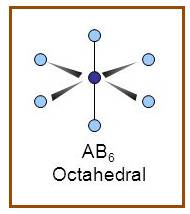
Figure 9
The bond angle between two atoms in octahedral molecule is
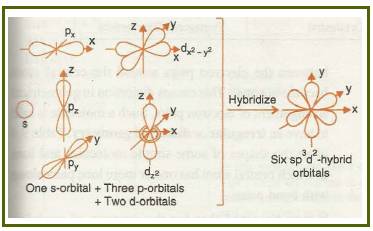
Figure 10
If the d-orbital of the
The hybridization of the central atom of the molecules with the given molecular geometries has been predicted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Chemistry: Atoms First
- In an experiment, the viscosity of water was measured at different temperatures and the table was constructed from the data obtained. a) Calculate the activation energy of viscous flow (kJ/mol). b) Calculate the viscosity at 30°C. T/°C 0 20 40 60 80 η/cpoise 1,972 1,005 0,656 0,469 0,356arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardLet's see if you caught the essentials of the animation. What is the valence value of carbon? a) 4 b) 2 c) 8 d) 6arrow_forward
- A laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardA laser emits a line at 632.8 nm. If the cavity is 12 cm long, how many modes oscillate in the cavity? How long does it take for the radiation to travel the entire cavity? What is the frequency difference between 2 consecutive modes?(refractive index of the medium n = 1).arrow_forwardThe number of microstates corresponding to each macrostate is given by N. The dominant macrostate or configuration of a system is the macrostate with the greatest weight W. Are both statements correct?arrow_forward
- For the single step reaction: A + B → 2C + 25 kJ If the activation energy for this reaction is 35.8 kJ, sketch an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for this reaction. Be sure to label the following on your diagram: each of the axes, reactant compounds and product compounds, enthalpy of reaction, activation energy of the forward reaction with the correct value, activation energy of the backwards reaction with the correct value and the transition state. In the same sketch you drew, after the addition of a homogeneous catalyst, show how it would change the graph. Label any new line "catalyst" and label any new activation energy.arrow_forwardHow many grams of C are combined with 3.75 ✕ 1023 atoms of H in the compound C5H12?arrow_forwarde. f. CH3O. יון Br NaOCH3 OCH 3 Br H₂Oarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





