
Using Appendix G, complete the following table that describes the characteristics of the Galilean moons of Jupiter, starting from Jupiter and moving outward in distance.
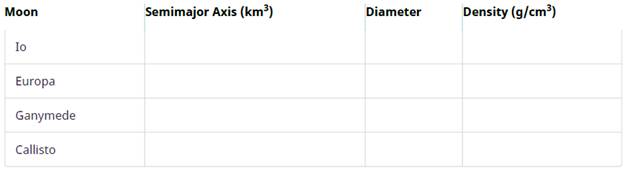
Table A
This system has often been described as a mini solar system. Why might this be so? If Jupiter were to represent the Sun and the Galilean moons represented planets, which moons could be considered more terrestrial in nature and which ones more like gas/ice giants? Why? (Hint: Use the values in your table to help explain your categorization.)
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Astronomy
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
An Introduction to Thermal Physics
Sears And Zemansky's University Physics With Modern Physics
University Physics Volume 2
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach with Modern Physics (4th Edition)
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Edition)
- Tutorial Based on the orbital properties of Uranus, how far across the sky in arc seconds does it travel in one Earth day? The average orbital radius is 2.88 x 109 km and the period is 84.0 years. (Assume Uranus and the Earth are at the closest point to one another in their orbits.) How many full Moons does this distance cover if the Moon has an angular diameter of 0.5 degrees? Part 1 of 4 We first need to determine how fast the planet is moving across the sky. If we know the period and the distance between the Sun and the planet we can calculate the velocity using: 2ar which will tell us how many kilometers the planet travels in a day if we convert the period into days. days = (P years' |days/year Pdays days Submit Skip (you cannot come back)arrow_forwardA classmate claims that if Jupiter’s Galilean moons were all the same distance from Jupiter, they would all experience the same amount of gravitational force. Using what you have learned and the evidence from the data table how would you respond to his claim? (a) His claim is incorrect; if the moons were at an equal distance from Jupiter; then the pull of gravity would be the strongest on Ganymede because it has the greatest mass (b) his claim is incorrect; if the moon were at an equal distance from Jupiter; then the pull of gravity would be the strongest on Europa; because it has the smallest mass (c) his claim is incorrect; if the moon were at an equal distance from Jupiter; then the pull of gravity from Jupiter would be experienced equally by all four moons. (d) his claim is incorrect; if the moon were at an equal distance from Jupiter; then the pull of gravity would be the strongest on Ganymede because it is the largest moonarrow_forwardSuppose there were a planet in our Solar System orbiting at a distance of 0.5 AU from theSun, and having ten times the mass and four times the radius of Earth. For reference, theEarth has a mass of 5.97 × 1024 kg and a radius of 6,378 km a) Calculate the density of this hypothetical planet.b) Based on your answer from part a), what do you think this planet would be made of?Explain your reasoning.c) Do this planet’s properties agree with the condensation theory for the formation of ourSolar System? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- We need to create a scale model of the solar system (by shrinking the sun down to the size of a basketball or ~30cm). First, we will need to scale down actual solar system dimensions (planet diameters and average orbital radiuses) by converting our units. There are two blank spaces in the table below. We will effectively fill in the missing data in the next set of questions. Use the example below to help you. Example: What is the scaled diameter of Mercury if the Sun is scaled to the size of a basketball (30 cm)? The actual diameter of Mercury is 4879 km The Sun's diameter is 1392000 km If the Sun is to be reduced to the size of a basketball, then the conversion we need for this equation will be: 30cm1392000km Here is how we run the conversion: 4879km×30cm1392000km=0.105cm or 0.11cm if we were to round our answer. This means that if the sun in our model is the size of a basketball, Mercury is the size of a grain of sand. We can also see by looking at the table, that we would…arrow_forwardI would like you to compare the size of some of the largest moons of the solar system to their host planets. Using diameters of 12,700 km, and 140,000 km, 116,000 km for Earth, Jupiter, and Saturn respectively, please provide the ratios of the following moons to their host planets (you can use Table 12.1 from the book to get the diameters of the moons): Luna (Earth's moon), Io, Callisto, Ganymede, Europa, and Titan. After collecting those ratios, please tell me one thing that you notice that stands out about those results.arrow_forwardYou are given the following data from observations of an exoplanet: Using Kepler’s Third Law (r3 = MT2 where M is the mass of the central star) find the orbital radius in astronomical units of this planet. M = 1.5 times the mass of the sun. Remember to convert days to years using 365.25 as the length of a year in days. What is the semimajor axis of this planet in AU? - Knowing the orbital radius in both kn and AU, use the value in km to find the circumference of the orbit, then convert that to meters. (Assume the orbit is a perfect circle). - Knowing the orbital circumference and the period in days, convert the days to seconds (multiply by 86,400) and find the orbital velocity in m/s - With that orbital velocity, the radius of the orbit in meters, find the centripetal acceleration of our exoplanet - Knowing the acceleration that our planet experiences, calculate the force that the host star exerts on the planet - Knowing the force on the planet, the orbital radius, and the mass of the…arrow_forward
- Present theory suggests that giant planets cannot form without condensation of water ice, which becomes vapor at the high temperatures close to a star. So how can we explain the presence of jovian-sized exoplanets closer to their star than Mercury is to our Sun?arrow_forwardDescribe the location of the equinoxes and solstices in the Uranian sky. What are the seasons like on Uranus?arrow_forwardDescribe the different processes that lead to substantial internal heat sources for Jupiter and Saturn. Since these two objects generate much of their energy internally, should they be called stars instead of planets? Justify your answer.arrow_forward
- What is the maximum angular diameter of Jupiter as seen from Earth? Repeat this calculation for Neptune. Relevant data can be found in Celestial Profiles 7 and 10. (Hint: Use the small-angle formula in Reasoning with Numbers 3-1.)arrow_forwardCalculate the radius of Jupiters Roche limit for a satellite with density equal to the planet. Which of Jupiters moons is closest to the Roche limit? What might that tell you about the relationship between that moon and Jupiters ring? (Note: Necessary data are given in Celestial Profile: Jupiter and Appendix Table A-11.)arrow_forwardWhich step(s) listed in the previous question can be eliminated in models that form Jovian planets in thousands of years, a time frame that solves the Jovian problem? Order the following steps in the formation of a Terrestrial planet chronologically: gravitational collapse, accretion, outgassing, condensation, and differentiation.arrow_forward
 AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax
AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9781938168284Author:Andrew Fraknoi; David Morrison; Sidney C. WolffPublisher:OpenStax Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Foundations of Astronomy (MindTap Course List)PhysicsISBN:9781337399920Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Horizons: Exploring the Universe (MindTap Course ...PhysicsISBN:9781305960961Author:Michael A. Seeds, Dana BackmanPublisher:Cengage Learning




