
Concept explainers
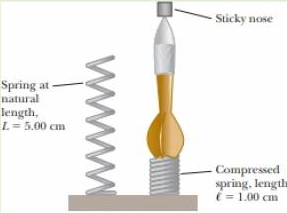
You are lying in your bedroom, resting after doing your physics homework. As you stare at your ceiling, you come up with the idea for a new game. You grab a dart with a sticky nose and a mass of 19.0 g. You also grab a spring that has been lying on your desk from some previous project. You paint a target pattern on your ceiling. Your new game is to place the spring vertically on the floor, place the sticky-nose dart facing upward on the spring, and push the spring downward until the coils all press together, as on the right in Figure P7.26. You will then release the spring, firing the dart up toward the target on your ceiling, where its sticky nose will make it hang from the ceiling. The spring has an uncompressed end-to-end length of 5.00 cm, as shown on the left in Figure P7.26, and can be compressed to an end-to-end length of 1.00 cm when the coils are all pressed together. Before trying the game, you hold the upper end of the spring in one hand and hang a bundle of ten identical darts from the lower end of the spring. The spring extends by 1.00 cm due to the weight of the darts. You are so excited about the new game that, before doing a test of the game, you run out to gather your friends to show them. When your friends are in your room watching and you show them the first firing of your new game, why are you embarrassed?
Figure P7.26
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- How can i solve this if n1 (refractive index of gas) and n2 (refractive index of plastic) is not known. And the brewsters angle isn't knownarrow_forward2. Consider the situation described in problem 1 where light emerges horizontally from ground level. Take k = 0.0020 m' and no = 1.0001 and find at which horizontal distance, x, the ray reaches a height of y = 1.5 m.arrow_forward2-3. Consider the situation of the reflection of a pulse at the interface of two string described in the previous problem. In addition to the net disturbances being equal at the junction, the slope of the net disturbances must also be equal at the junction at all times. Given that p1 = 4.0 g/m, H2 = 9.0 g/m and Aj = 0.50 cm find 2. A, (Answer: -0.10 cm) and 3. Ay. (Answer: 0.40 cm)please I need to show all work step by step problems 2 and 3arrow_forward
- look at answer show all work step by steparrow_forwardLook at the answer and please show all work step by steparrow_forward3. As a woman, who's eyes are h = 1.5 m above the ground, looks down the road sees a tree with height H = 9.0 m. Below the tree is what appears to be a reflection of the tree. The observation of this apparent reflection gives the illusion of water on the roadway. This effect is commonly called a mirage. Use the results of questions 1 and 2 and the principle of ray reversibility to analyze the diagram below. Assume that light leaving the top of the tree bends toward the horizontal until it just grazes ground level. After that, the ray bends upward eventually reaching the woman's eyes. The woman interprets this incoming light as if it came from an image of the tree. Determine the size, H', of the image. (Answer 8.8 m) please show all work step by steparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


